A Complete Information To Spanish Components Of Speech: A Detailed Chart And Evaluation
A Complete Information to Spanish Components of Speech: A Detailed Chart and Evaluation
Associated Articles: A Complete Information to Spanish Components of Speech: A Detailed Chart and Evaluation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to A Complete Information to Spanish Components of Speech: A Detailed Chart and Evaluation. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
A Complete Information to Spanish Components of Speech: A Detailed Chart and Evaluation

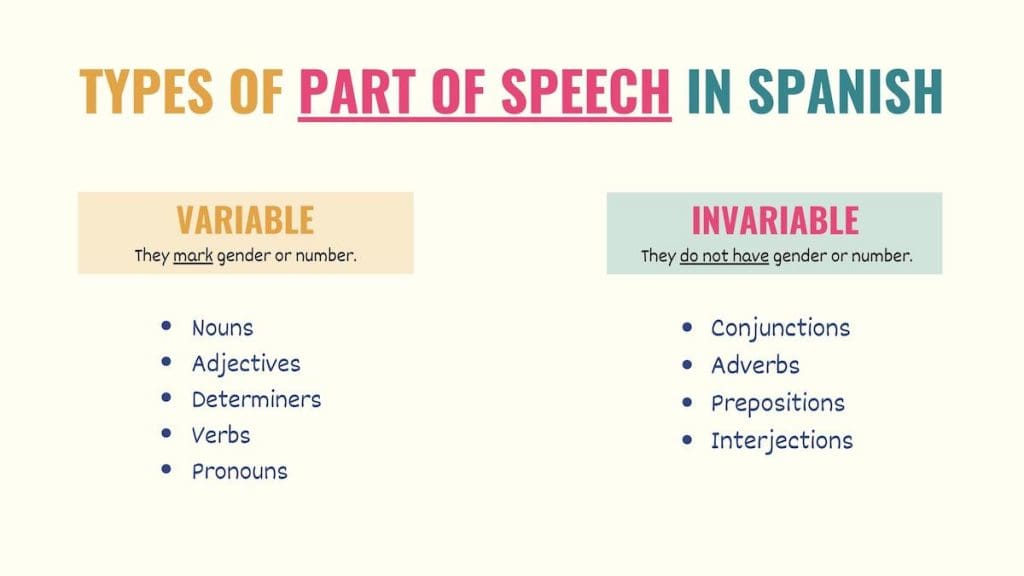
Spanish, like English, possesses a wealthy grammatical construction constructed upon a basis of elements of speech. Understanding these elements is essential for mastering the language, enabling correct sentence building and efficient communication. This text supplies an in depth exploration of the Spanish elements of speech, introduced in a transparent chart format, adopted by in-depth explanations and examples for every class.
I. The Spanish Components of Speech Chart:
| A part of Speech | English Equal | Instance | Operate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noun (Sustantivo) | Noun | gato (cat), casa (home), amor (love) | Names an individual, place, factor, or thought. | Will be singular or plural, masculine or female. |
| Pronoun (Pronombre) | Pronoun | yo (I), él (he), ella (she), nosotros (we), ellos (they) | Replaces a noun or noun phrase. | Varies in kind relying on gender, quantity, and case. |
| Verb (Verbo) | Verb | ser (to be), hablar (to talk), comer (to eat) | Expresses motion or a state of being. | Conjugated to agree with the topic in individual, quantity, tense, temper, and side. |
| Adjective (Adjetivo) | Adjective | grande (huge), rojo (pink), feliz (glad) | Modifies a noun or pronoun. | Agrees in gender and quantity with the noun it modifies. |
| Adverb (Adverbio) | Adverb | rápidamente (shortly), muy (very), aquí (right here) | Modifies a verb, adjective, or one other adverb. | Usually ends in "-mente." |
| Preposition (Preposición) | Preposition | a (to), en (in), de (of), para (for), con (with) | Reveals the connection between a noun or pronoun and one other phrase within the sentence. | Introduces prepositional phrases. |
| Conjunction (Conjunción) | Conjunction | y (and), o (or), pero (however), porque (as a result of) | Connects phrases, phrases, or clauses. | Coordinating conjunctions be a part of comparable grammatical parts; subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses. |
| Interjection (Interjección) | Interjection | ¡Ay! (Oh!), ¡Hola! (Hiya!), ¡Guau! (Wow!) | Expresses sturdy emotion. | Usually adopted by an exclamation level. |
| Determiner (Determinante) | Determiner | el (the), un (a/an), este (this), mi (my) | Modifies a noun, indicating definiteness, amount, or possession. | Contains articles, possessive adjectives, demonstrative adjectives, and quantifiers. |
II. Detailed Clarification of Every A part of Speech:
A. Nouns (Sustantivos): Spanish nouns have gender (masculine or female) and quantity (singular or plural). Masculine nouns typically finish in "-o" within the singular and "-os" within the plural, whereas female nouns typically finish in "-a" within the singular and "-as" within the plural. Nevertheless, there are a lot of exceptions. Understanding gender is essential as a result of adjectives and articles should agree with the noun’s gender. For instance: el gato (the cat – masculine), la gata (the cat – female).
B. Pronouns (Pronombres): Pronouns substitute nouns to keep away from repetition. Spanish pronouns are extremely inflected, altering kind primarily based on individual (first, second, third), quantity (singular, plural), gender (masculine, female), and case (topic, object). Topic pronouns (like yo, tú, él, ella) act because the sentence’s topic, whereas object pronouns (like me, te, lo, la) act because the direct or oblique object. Possessive pronouns (mío, tuyo, suyo) point out possession. Demonstrative pronouns (este, ese, aquel) level to particular issues.
C. Verbs (Verbos): Verbs are the guts of a sentence, indicating motion or state of being. Spanish verbs are extremely conjugated, that means they alter kind to point tense (previous, current, future), temper (indicative, subjunctive, crucial), side (perfective, imperfective), and individual and quantity. Common verbs comply with predictable conjugation patterns, whereas irregular verbs have distinctive varieties. Mastering verb conjugation is crucial for fluent Spanish.
D. Adjectives (Adjetivos): Adjectives describe nouns. They agree in gender and quantity with the nouns they modify. For instance, un libro grande (an enormous e-book – masculine singular), unas casas grandes (some huge homes – female plural). Many adjectives have completely different varieties for masculine and female, singular and plural.
E. Adverbs (Adverbios): Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or different adverbs. They typically reply questions like how, when, the place, or to what extent. Many adverbs are fashioned by including "-mente" to the female singular type of an adjective (e.g., rápido (quick) turns into rápidamente (shortly)).
F. Prepositions (Preposiciones): Prepositions present the connection between a noun or pronoun and one other phrase within the sentence. They introduce prepositional phrases, which frequently operate as adverbials or adjectivals. The that means of a preposition can range relying on context.
G. Conjunctions (Conjunciones): Conjunctions join phrases, phrases, or clauses. Coordinating conjunctions (like y, o, pero) be a part of parts of equal grammatical rank. Subordinating conjunctions (like porque, aunque, si) introduce dependent clauses that can’t stand alone as sentences.
H. Interjections (Interjecciones): Interjections specific sturdy feelings. They’re typically standalone phrases or phrases and are usually punctuated with exclamation marks.
I. Determiners (Determinantes): Determiners specify the noun they modify. This class contains articles (particular – el, la, los, las; indefinite – un, una, unos, unas), possessive adjectives (mi, tu, su, and so forth.), demonstrative adjectives (este, ese, aquel, and so forth.), and quantifiers (mucho, poco, algunos, and so forth.).
III. Superior Concerns:
This chart and rationalization present a basis for understanding Spanish elements of speech. Nevertheless, the nuances of Spanish grammar prolong past this fundamental framework. Think about these superior facets:
-
Verb Moods: Spanish verbs have three principal moods: indicative (for factual statements), subjunctive (for expressing doubt, needs, or hypothetical conditions), and crucial (for instructions). Mastering the subjunctive is especially essential for superior fluency.
-
Verb Tenses: A variety of tenses exists in Spanish, permitting for exact expression of time and side. Studying the completely different tenses and their delicate variations is crucial for correct communication.
-
Pronoun Placement: The location of pronouns in Spanish sentences will be complicated, various relying on the verb tense and sort.
-
Relative Clauses: Relative clauses add descriptive data to nouns, and their building includes particular pronoun utilization and verb conjugation.
-
Nominalization: This course of transforms verbs or adjectives into nouns, impacting sentence construction and that means.
-
Phrase Order: Whereas Spanish sentence construction is mostly subject-verb-object, variations are potential for emphasis or stylistic impact.
IV. Conclusion:
This complete information supplies a stable basis for understanding the Spanish elements of speech. By mastering these parts, learners can construct a robust grammatical base, enabling them to assemble well-formed sentences and talk successfully in Spanish. Continued apply and publicity to the language are important for creating fluency and a deeper understanding of the intricacies of Spanish grammar. Additional research of verb conjugation, pronoun utilization, and sentence construction will improve your potential to navigate the complexities of this lovely and expressive language. Keep in mind to seek the advice of grammar textbooks and make the most of on-line assets to additional refine your understanding of every a part of speech and its numerous functions inside the broader context of Spanish syntax.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into A Complete Information to Spanish Components of Speech: A Detailed Chart and Evaluation. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!