Charting The Course: Visualizing Database Information For Perception And Motion
Charting the Course: Visualizing Database Information for Perception and Motion
Associated Articles: Charting the Course: Visualizing Database Information for Perception and Motion
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Charting the Course: Visualizing Database Information for Perception and Motion. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Charting the Course: Visualizing Database Information for Perception and Motion
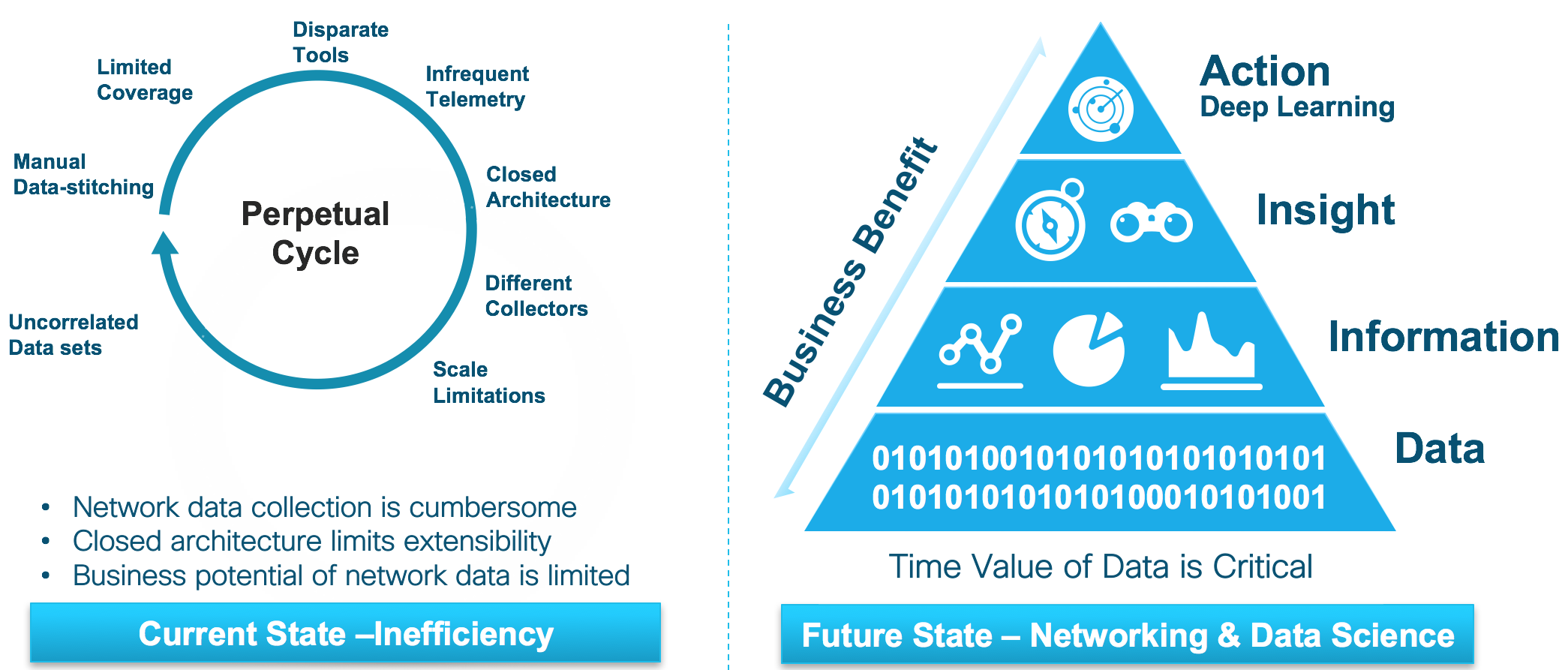
Information, in its uncooked kind, is usually a chaotic jumble of numbers and textual content. It holds immense potential, however with out correct group and interpretation, it stays inert. That is the place information visualization, particularly charting information from a database, comes into play. Charts remodel complicated datasets into simply digestible visible representations, revealing developments, patterns, and anomalies which may in any other case stay hidden. This text delves into the method of making insightful charts from database information, exploring the varied chart varieties, their purposes, and the applied sciences concerned.
The Energy of Visible Information Illustration:
The human mind is remarkably adept at processing visible info. A well-constructed chart can convey info much more successfully than pages of tables or uncooked information. That is essential for a number of causes:
- Improved Understanding: Charts make complicated information units accessible to a wider viewers, together with these with out specialised information evaluation expertise. A easy bar chart can immediately reveal which product has the best gross sales, whereas a line chart can illustrate development developments over time.
- Sooner Insights: Visible representations permit for fast identification of key developments, outliers, and correlations. This velocity is invaluable in time-sensitive decision-making processes.
- Enhanced Communication: Charts are efficient instruments for speaking data-driven insights to stakeholders. They supply a compelling visible narrative that may assist shows, studies, and dashboards.
- Figuring out Anomalies: Visualizations can spotlight sudden patterns or anomalies that could be missed in a purely numerical evaluation. These anomalies can sign potential issues or alternatives.
Selecting the Proper Chart Kind:
The effectiveness of a chart relies upon closely on the kind of information being offered and the insights sought. Totally different chart varieties are suited to totally different information constructions and analytical goals. Listed here are a number of the commonest chart varieties and their typical purposes:
-
Bar Charts: Ultimate for evaluating discrete classes. They’re glorious for displaying gross sales figures throughout totally different product strains, buyer demographics, or geographical areas. Variations embrace grouped bar charts (for evaluating a number of variables inside classes) and stacked bar charts (for displaying the composition of an entire).
-
Line Charts: Finest fitted to displaying developments over time. They’re often used to trace web site site visitors, inventory costs, or gross sales efficiency over a interval. A number of strains will be overlaid to match totally different variables.
-
Pie Charts: Successfully symbolize proportions or percentages of an entire. They’re helpful for displaying market share, finances allocation, or the composition of a product. Nonetheless, they grow to be much less efficient with many slices.
-
Scatter Plots: Illustrate the connection between two steady variables. They’re notably helpful for figuring out correlations and recognizing outliers. As an illustration, they will present the connection between promoting spend and gross sales income.
-
Space Charts: Much like line charts, however they fill the world below the road, emphasizing the magnitude of the info over time. They’re helpful for highlighting cumulative totals or general developments.
-
Histograms: Present the distribution of a single steady variable. They’re helpful for understanding the frequency of various values inside a dataset. As an illustration, they will show the distribution of buyer ages or order values.
-
Field Plots: Summarize the distribution of a dataset, displaying the median, quartiles, and outliers. They’re helpful for evaluating the distributions of various teams.
-
Heatmaps: Signify information utilizing colour gradients to point out the depth of a variable throughout two dimensions. They’re usually used to visualise correlation matrices, geographical information, or web site site visitors patterns.
The Database Connection:
The method of making charts from database information begins with establishing a connection to the database. This sometimes entails utilizing a database connector library particular to the database system (e.g., MySQL Connector/Python, psycopg2 for PostgreSQL, and many others.) and offering the required credentials (username, password, database identify, and many others.).
As soon as the connection is established, SQL queries are used to retrieve the info wanted for the chart. The complexity of those queries depends upon the chart’s necessities. Easy charts might require a single SELECT assertion, whereas extra complicated charts may contain joins, aggregations, and subqueries.
Information Extraction and Transformation:
After retrieving the info, it usually must be remodeled earlier than it may be used to create a chart. This may increasingly contain:
- Information Cleansing: Dealing with lacking values, outliers, and inconsistencies within the information.
-
Information Aggregation: Summarizing the info utilizing features like
SUM,AVG,COUNT,MIN, andMAX. - Information Transformation: Making use of mathematical transformations (e.g., logarithms, normalization) to enhance the visible illustration.
- Information Filtering: Choosing particular subsets of the info primarily based on sure standards.
Charting Libraries and Instruments:
Quite a few libraries and instruments can be found for creating charts from the extracted information. These instruments supply a spread of functionalities, from easy plotting to extremely interactive and customizable visualizations. In style choices embrace:
- Matplotlib (Python): A flexible and broadly used library for creating static, interactive, and animated visualizations in Python.
- Seaborn (Python): Constructed on prime of Matplotlib, Seaborn offers a higher-level interface for creating statistically informative and visually interesting charts.
- Plotly (Python, JavaScript): A robust library for creating interactive web-based charts.
- D3.js (JavaScript): A extremely versatile and highly effective JavaScript library for creating customized visualizations.
- Tableau and Energy BI: Industrial enterprise intelligence instruments that supply in depth capabilities for information visualization, evaluation, and dashboarding.
Constructing Interactive Dashboards:
For dynamic information exploration and monitoring, interactive dashboards are invaluable. These dashboards mix a number of charts and different visible components, permitting customers to filter, drill down, and discover the info in real-time. Instruments like Tableau, Energy BI, and frameworks like Shiny (R) and Sprint (Python) are generally used for constructing interactive dashboards.
Challenges and Concerns:
Whereas charting database information affords quite a few benefits, a number of challenges have to be thought of:
- Information Quantity: Dealing with extraordinarily massive datasets will be computationally intensive and require specialised methods for environment friendly information processing and visualization.
- Information Complexity: Complicated information constructions and relationships might require subtle querying and information transformation methods.
- Chart Readability: Overly complicated or poorly designed charts will be complicated and ineffective. Simplicity and readability are essential for efficient communication.
- Information Safety: Guaranteeing the safety and privateness of delicate information is paramount when accessing and visualizing database info.
Conclusion:
Charting information from a database is a strong method for extracting beneficial insights and speaking these insights successfully. By fastidiously choosing the suitable chart kind, utilizing appropriate instruments, and addressing potential challenges, organizations can unlock the total potential of their information and make data-driven choices with confidence. The power to visualise information transforms uncooked info into actionable intelligence, driving knowledgeable choices and in the end contributing to organizational success. The journey from database to insightful chart is an important step within the information evaluation course of, reworking numbers into narratives and fostering a data-driven tradition.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Charting the Course: Visualizing Database Information for Perception and Motion. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!