Decoding The Bar Chart Schedule: A Complete Information
Decoding the Bar Chart Schedule: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the Bar Chart Schedule: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Bar Chart Schedule: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Bar Chart Schedule: A Complete Information
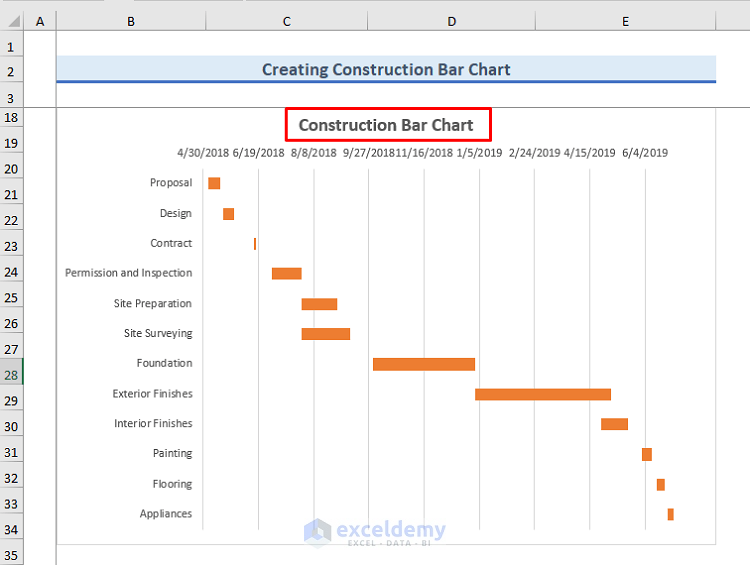
Bar chart schedules, also called Gantt charts (although technically Gantt charts are a particular kind of bar chart schedule), are visible undertaking administration instruments that present a transparent and concise illustration of a undertaking’s timeline. They use horizontal bars to symbolize duties or actions, exhibiting their begin and finish dates, length, and dependencies. Whereas seemingly easy, their effectiveness lies of their skill to speak advanced undertaking data rapidly and intuitively, making them indispensable for planning, monitoring, and controlling tasks of all sizes and complexities.
This text dives deep into the intricacies of bar chart schedules, exploring their parts, benefits, limitations, creation course of, and numerous functions throughout varied industries.
Understanding the Parts of a Bar Chart Schedule:
A typical bar chart schedule includes a number of key components that work collectively to color a complete image of the undertaking’s progress:
-
Duties/Actions: These are the person items of labor that represent the undertaking. Every process is represented by a horizontal bar. They need to be clearly outlined, measurable, achievable, related, and time-bound (SMART). Examples embody "design web site mockup," "develop backend performance," or "conduct consumer testing."
-
Timeline/Time Scale: That is the horizontal axis of the chart, representing the undertaking’s length. It’s sometimes divided into items of time, equivalent to days, weeks, months, or quarters, relying on the undertaking’s size and complexity.
-
Period: The size of every horizontal bar corresponds to the estimated length of the respective process. That is essential for visualizing process lengths and potential overlaps.
-
Begin and Finish Dates: The start and finish factors of every bar point out the deliberate begin and end dates of the duty.
-
Dependencies: That is the place the ability of the bar chart actually shines. Arrows or different visible indicators show the relationships between duties. A process is perhaps depending on the completion of one other (e.g., "write code" depends upon "design database"). This visible illustration of dependencies highlights crucial paths and potential bottlenecks.
-
Milestones: These are important factors within the undertaking timeline, typically representing the completion of main phases or deliverables. They’re sometimes represented by diamonds or different distinct markers on the timeline.
-
Sources: Some bar chart schedules embody data on the sources allotted to every process, equivalent to personnel, gear, or funds. This helps in useful resource allocation and capability planning.
-
Progress Monitoring: A vital side of bar chart schedules is the flexibility to trace progress. That is typically finished by shading a portion of the bar to symbolize the finished work. This visible illustration permits for simple identification of duties forward or not on time.
Benefits of Utilizing Bar Chart Schedules:
The recognition of bar chart schedules stems from their quite a few benefits:
-
Visible Readability: The visible nature of the chart makes it straightforward to grasp the undertaking’s timeline, process durations, and dependencies at a look. This fosters higher communication and collaboration amongst workforce members and stakeholders.
-
Straightforward to Perceive: Even people and not using a undertaking administration background can readily grasp the data introduced in a bar chart schedule. This simplifies communication throughout departments and with purchasers.
-
Improved Planning and Coordination: The visible illustration of duties and dependencies helps in figuring out potential conflicts and scheduling points early on. This permits for proactive planning and coordination to mitigate dangers.
-
Efficient Progress Monitoring: The flexibility to trace progress visually permits for well timed identification of delays and potential issues. This allows proactive intervention and corrective actions.
-
Enhanced Communication: The bar chart serves as a typical visible language for all stakeholders, facilitating efficient communication and understanding of the undertaking’s standing.
-
Easy to Create: Numerous software program functions and even spreadsheet packages make creating and managing bar chart schedules comparatively easy.
-
Price-Efficient: In comparison with refined undertaking administration software program, bar chart schedules could be created and maintained with minimal price, making them accessible to organizations with restricted sources.
Limitations of Bar Chart Schedules:
Regardless of their benefits, bar chart schedules have sure limitations:
-
Restricted Complexity Dealing with: Whereas efficient for smaller tasks, managing extremely advanced tasks with quite a few interdependencies and complex relationships can change into difficult utilizing solely a bar chart. The chart can change into cluttered and tough to interpret.
-
Static Illustration: A bar chart schedule is basically a snapshot in time. Modifications to the undertaking plan require guide updates, which could be time-consuming and susceptible to errors.
-
Oversimplification: The simplicity of the bar chart can result in oversimplification of the undertaking’s complexities. It won’t adequately seize the nuances of process dependencies or useful resource allocation.
-
Lack of Detailed Info: Bar charts primarily deal with time and process sequencing. They sometimes do not present detailed data on process assignments, useful resource prices, or danger assessments.
-
Incapability to Deal with Concurrent Duties Successfully: Whereas dependencies are proven, successfully representing a number of concurrent duties and their useful resource allocation can change into visually difficult.
-
Issue in Representing Iterative Processes: Tasks involving iterative growth cycles or agile methodologies won’t be successfully represented utilizing a standard bar chart.
Making a Bar Chart Schedule: A Step-by-Step Information:
Creating an efficient bar chart schedule includes a scientific strategy:
-
Outline Mission Scope and Targets: Clearly outline the undertaking’s targets, deliverables, and total timeline.
-
Break Down the Mission into Duties: Decompose the undertaking into smaller, manageable duties. Guarantee every process is clearly outlined and measurable.
-
Estimate Activity Durations: Estimate the time required to finish every process. Think about potential dangers and uncertainties.
-
Establish Activity Dependencies: Decide the relationships between duties. Which duties have to be accomplished earlier than others can start?
-
Create the Bar Chart: Use undertaking administration software program or a spreadsheet program to create the bar chart. Signify every process with a horizontal bar, indicating its begin and finish dates and length.
-
Add Milestones: Establish and mark important milestones on the timeline.
-
Evaluate and Refine: Evaluate the finished bar chart to establish potential conflicts or scheduling points. Make obligatory changes to optimize the schedule.
-
Recurrently Replace: Monitor progress and replace the bar chart recurrently to mirror precise progress and any modifications to the undertaking plan.
Purposes of Bar Chart Schedules Throughout Industries:
Bar chart schedules discover functions throughout a broad spectrum of industries:
-
Building: Managing advanced building tasks, monitoring milestones, and monitoring progress.
-
Software program Growth: Planning software program growth sprints, monitoring characteristic growth, and managing releases.
-
Manufacturing: Scheduling manufacturing processes, managing stock, and optimizing workflow.
-
Advertising and marketing: Planning advertising and marketing campaigns, monitoring deadlines, and monitoring progress.
-
Occasion Planning: Organizing occasions, scheduling duties, and managing sources.
-
Analysis and Growth: Planning analysis tasks, monitoring experiments, and managing timelines.
Conclusion:
Bar chart schedules stay a priceless software for undertaking administration, providing a transparent and concise visible illustration of undertaking timelines. Whereas limitations exist, significantly when coping with extremely advanced tasks, their simplicity, ease of understanding, and cost-effectiveness make them a sensible selection for a variety of functions. By understanding their parts, benefits, and limitations, undertaking managers can successfully leverage bar chart schedules to plan, monitor, and management tasks effectively, fostering higher communication and collaboration amongst stakeholders. Nonetheless, for extremely advanced tasks, integrating bar chart schedules with extra refined undertaking administration instruments and methodologies can present a extra complete and sturdy strategy to undertaking planning and execution.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Decoding the Bar Chart Schedule: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!
