Decoding The Circle: A Deep Dive Into Pie Chart Percentages And Their Efficient Use
Decoding the Circle: A Deep Dive into Pie Chart Percentages and Their Efficient Use
Associated Articles: Decoding the Circle: A Deep Dive into Pie Chart Percentages and Their Efficient Use
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Circle: A Deep Dive into Pie Chart Percentages and Their Efficient Use. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Circle: A Deep Dive into Pie Chart Percentages and Their Efficient Use

Pie charts, with their visually interesting round segments, are a staple in knowledge visualization. Their effectiveness hinges on the correct illustration and clear interpretation of percentages, conveying proportions inside an entire. Whereas seemingly easy, understanding the nuances of pie chart percentages, their limitations, and greatest practices for creation and interpretation is essential for efficient communication of knowledge. This text gives a complete exploration of pie chart percentages, masking their development, interpretation, and the circumstances the place they excel and the place they fall quick.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Developing a Pie Chart from Percentages
The muse of a pie chart lies within the idea of proportions. The whole circle represents 100%, and every phase represents a portion of that entire, expressed as a share. To assemble a pie chart, the next steps are important:
-
Knowledge Assortment and Preparation: Start with a dataset containing categorical variables and their corresponding frequencies or values. For instance, you might need knowledge on the various kinds of fruits bought in a market and the amount of every.
-
Calculating Percentages: Decide the overall worth of all classes. Then, for every class, calculate its share contribution to the overall utilizing the next components:
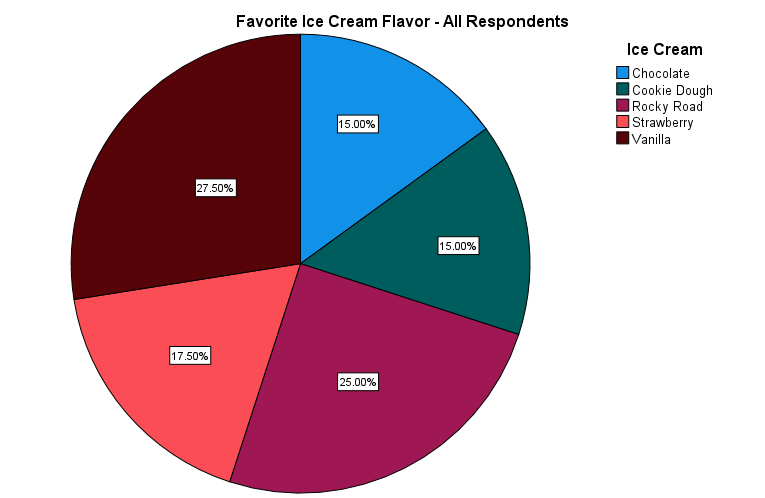
(Class Worth / Complete Worth) * 100%As an illustration, if you happen to bought 100 apples, 50 oranges, and 50 bananas, the odds could be:
- Apples: (100 / 200) * 100% = 50%
- Oranges: (50 / 200) * 100% = 25%
- Bananas: (50 / 200) * 100% = 25%
-
Figuring out Phase Angles: Every share corresponds to a particular angle inside the 360-degree circle. To calculate the angle for every phase, use the next components:
(Proportion / 100) * 360°Utilizing the fruit instance:
- Apples: (50 / 100) * 360° = 180°
- Oranges: (25 / 100) * 360° = 90°
- Bananas: (25 / 100) * 360° = 90°
-
Creating the Chart: Utilizing knowledge visualization software program or drawing instruments, create the pie chart by drawing segments with the calculated angles. Every phase needs to be clearly labeled with its corresponding class and share. Think about using completely different colours to differentiate the segments and enhance visible enchantment. Including a title summarizing the information is essential for readability.
Deciphering Pie Chart Percentages: Past the Visible
Whereas the visible illustration of a pie chart is intuitive, cautious interpretation is important to keep away from misinterpretations. Key elements to think about embody:
-
Relative Proportions: The first objective of a pie chart is to spotlight the relative sizes of various classes inside the entire. Deal with the comparative sizes of the segments slightly than absolutely the values.
-
Proportion Labels: All the time embody share labels inside or adjoining to every phase. This enables for exact understanding of every class’s contribution. Keep away from relying solely on visible estimations of phase sizes.
-
Knowledge Accuracy: Guarantee the information used to create the pie chart is correct and dependable. Errors within the supply knowledge will straight impression the accuracy of the odds and the general interpretation.
-
Contextual Understanding: The interpretation of a pie chart ought to at all times be positioned inside the broader context of the information. Think about any related components that may affect the noticed proportions.
-
Limitations of Visible Notion: Human notion of space might be subjective. Small variations in phase sizes could be tough to discern visually, particularly when coping with quite a few classes or intently related percentages.
When to Use (and To not Use) Pie Charts:
Pie charts are handiest when:
-
The variety of classes is comparatively small: Pie charts grow to be cluttered and tough to interpret when there are too many segments. Usually, limiting the variety of classes to 5 – 6 is advisable.
-
The main focus is on relative proportions: Pie charts excel at displaying the relative contributions of various classes to the entire.
-
The information is easy and simply understood: Pie charts are greatest suited for easy datasets that do not require complicated evaluation.
Pie charts are not appropriate when:
-
The information entails many classes: As talked about, too many segments make the chart tough to learn. Think about various visualizations like bar charts or column charts for datasets with quite a few classes.
-
Exact comparisons are required: Whereas pie charts present relative proportions, they don’t seem to be perfect for exact comparisons between classes, notably when percentages are very shut. Bar charts are higher suited to this objective.
-
The information modifications over time: Pie charts are static and do not successfully present developments or modifications over time. Line charts or space charts are extra acceptable for time-series knowledge.
-
The information entails percentages that sum to lower than 100%: Whereas doable, it is essential to obviously point out why the overall does not attain 100%, as this may result in misinterpretations.
Superior Strategies and Issues:
-
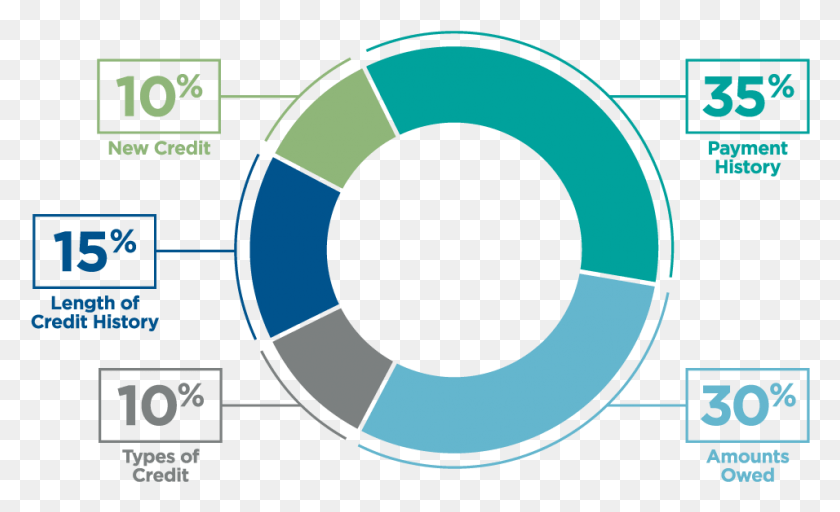
Exploded Pie Charts: Highlighting a particular phase by barely separating it from the remainder of the pie can draw consideration to a specific class. Use this sparingly to keep away from overwhelming the viewer.
-
3D Pie Charts: Whereas visually interesting, 3D pie charts can distort the notion of phase sizes, making correct comparisons tough. Usually, 2D pie charts are most well-liked for readability.
-
Knowledge Labels and Legends: Clear and concise labels are important for simple interpretation. Legends are helpful when house inside the chart is proscribed for labels.
-
Colour Choice: Use a constant shade scheme that enhances visible readability and avoids confusion. Think about shade blindness when selecting colours.
-
Software program and Instruments: Many software program packages, equivalent to Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, Tableau, and others, provide instruments for creating and customizing pie charts. Select the software program that most accurately fits your wants and talent degree.
Conclusion:
Pie charts, when used appropriately, might be highly effective instruments for visualizing knowledge and speaking proportions. Understanding the rules of calculating percentages, establishing the chart, and deciphering the outcomes is significant for efficient knowledge visualization. Nonetheless, it is essential to be conscious of the constraints of pie charts and select probably the most appropriate visualization method based mostly on the precise knowledge and the meant message. By adhering to greatest practices and contemplating the nuances mentioned on this article, you’ll be able to create and interpret pie charts that successfully convey info and keep away from frequent pitfalls. The bottom line is to prioritize readability, accuracy, and a considerate strategy to knowledge illustration.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Decoding the Circle: A Deep Dive into Pie Chart Percentages and Their Efficient Use. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!