Decoding The Eye Chart: A Complete Information To Understanding And Utilizing Imaginative and prescient Checks
Decoding the Eye Chart: A Complete Information to Understanding and Utilizing Imaginative and prescient Checks
Associated Articles: Decoding the Eye Chart: A Complete Information to Understanding and Utilizing Imaginative and prescient Checks
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Eye Chart: A Complete Information to Understanding and Utilizing Imaginative and prescient Checks. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Eye Chart: A Complete Information to Understanding and Utilizing Imaginative and prescient Checks
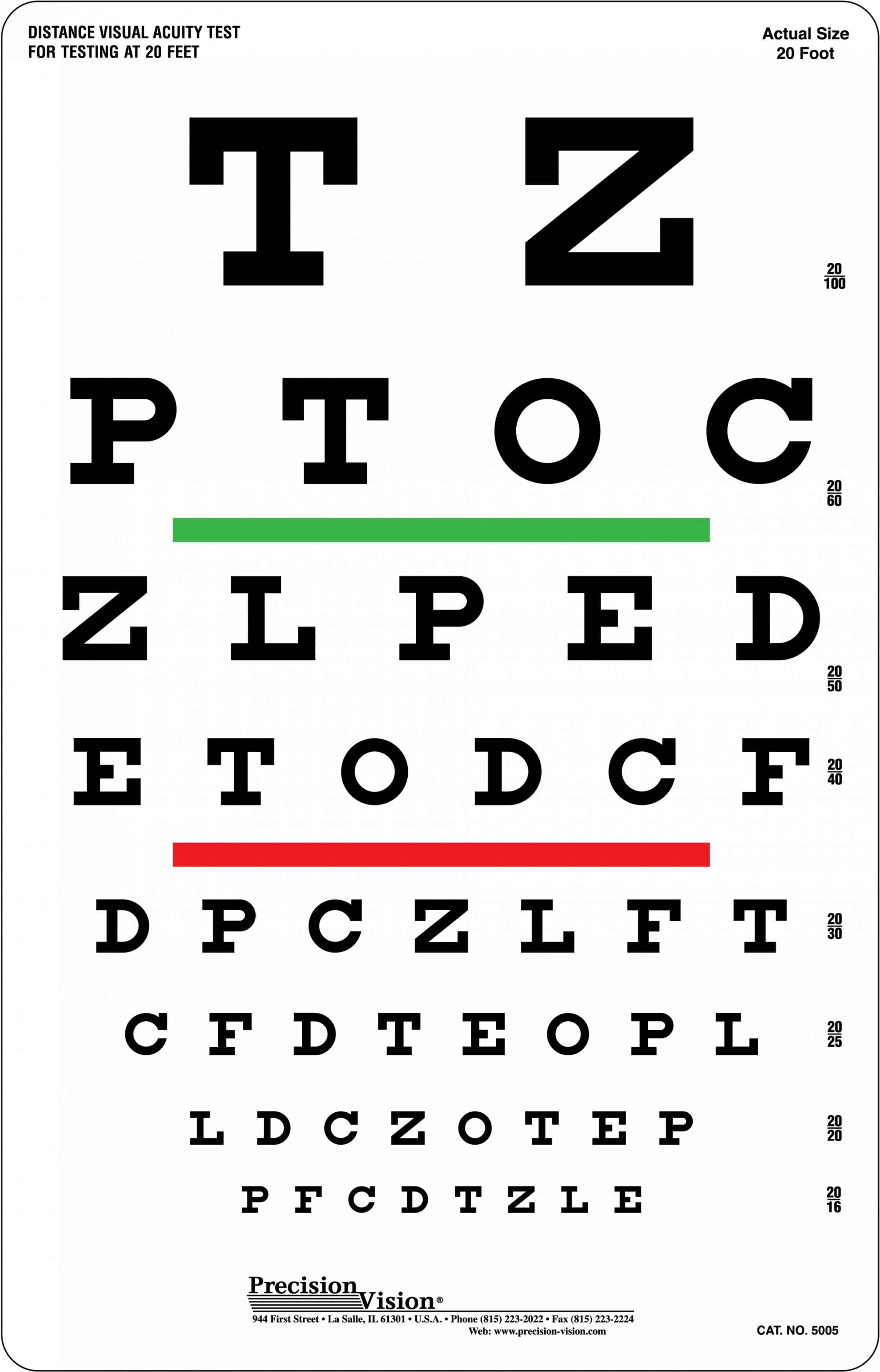
The acquainted eye chart, with its rows of progressively smaller letters, numbers, or symbols, is a cornerstone of imaginative and prescient testing. It is a easy but highly effective device that permits ophthalmologists and optometrists to evaluate visible acuity, an important measure of how clearly you see at a particular distance. Nevertheless, understanding the nuances of the attention chart, its interpretation, and the broader implications of your outcomes goes past merely studying the smallest line. This text delves into the intricacies of imaginative and prescient testing utilizing eye charts, exploring their historical past, methodology, totally different chart sorts, decoding outcomes, and what to do in case you have issues about your imaginative and prescient.
A Temporary Historical past of the Eye Chart:
The idea of standardized imaginative and prescient testing dates again centuries, with early strategies involving rudimentary visible acuity assessments. Nevertheless, the event of the fashionable eye chart is basically attributed to Hermann Snellen, a Dutch ophthalmologist, in 1862. Snellen’s chart, nonetheless broadly used at the moment, options letters of various sizes, every designed to be discernible at a particular distance. The "6/6" or "20/20" notation, frequent in lots of international locations, stems from Snellen’s system, indicating the power to learn at 6 meters (or 20 ft) what an individual with regular imaginative and prescient can learn at that distance.
Varieties of Eye Charts:
Whereas the Snellen chart stays a typical, a number of different varieties of eye charts exist, every catering to particular wants and age teams:
-
Snellen Chart: This basic chart makes use of uppercase letters organized in rows of reducing measurement. It is broadly used for adults and older kids who’re acquainted with the alphabet.
-
Landolt C Chart: This chart makes use of "C" shapes with breaks in numerous orientations. It is significantly helpful for younger kids or people who can’t learn letters, because it assesses visible acuity with out counting on letter recognition.
-
Tumbling E Chart: Much like the Landolt C chart, this chart makes use of the letter "E" rotated in varied instructions. The affected person signifies the route of the "E’s" open aspect, eliminating the necessity for studying expertise.
-
Lea Symbols Chart: This chart makes use of image symbols as an alternative of letters or shapes, making it superb for preschoolers and people with cognitive impairments.
-
Bailey-Lovie Chart: This chart improves upon the Snellen chart through the use of extra letters per line and a extra exact logarithmic development of letter sizes, resulting in a extra correct evaluation of visible acuity.
Methodology of Eye Chart Testing:
The process for eye chart testing is comparatively simple however essential for correct outcomes:
-
Distance: The affected person stands 20 ft (6 meters) away from the chart. This standardized distance ensures constant testing circumstances.
-
One Eye at a Time: The affected person covers one eye whereas the opposite is examined. This prevents using each eyes to compensate for visible impairments.
-
Studying the Chart: The affected person reads the letters or symbols aloud, ranging from the highest and continuing down.
-
Recording the Outcomes: The smallest line the affected person can learn precisely is recorded as their visible acuity. That is often expressed as a fraction (e.g., 20/20, 20/40), with the numerator representing the testing distance and the denominator representing the space at which an individual with regular imaginative and prescient may learn the identical line.
-
Each Eyes: The take a look at is repeated for the opposite eye, and eventually, each eyes are examined collectively.
Deciphering the Outcomes:
The numbers on the attention chart symbolize visible acuity. A rating of 20/20 signifies which you could see at 20 ft what an individual with regular imaginative and prescient can see at 20 ft. A rating of 20/40 means you may see at 20 ft what an individual with regular imaginative and prescient can see at 40 ft; this means decreased visible acuity. Decrease numbers within the denominator point out poorer imaginative and prescient.
Components Affecting Eye Chart Outcomes:
A number of elements can affect the accuracy of eye chart outcomes:
-
Refractive Errors: Myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism can all have an effect on visible acuity. These circumstances are often correctable with eyeglasses or contact lenses.
-
Lighting Circumstances: Inadequate or extreme lighting can impair efficiency on the attention chart.
-
Affected person Cooperation: A affected person’s attentiveness and energy can considerably have an effect on the accuracy of the take a look at, particularly with kids.
-
Chart Kind and Situation: The kind of chart used and its situation (e.g., readability, lighting) can even affect outcomes.
-
Underlying Medical Circumstances: Sure medical circumstances can have an effect on imaginative and prescient, impacting the accuracy of the attention chart take a look at.
Past Visible Acuity:
Whereas the attention chart primarily assesses visible acuity, a complete eye examination entails way more than simply studying letters. An entire eye examination contains:
-
Refraction: Figuring out the refractive error to evaluate the necessity for corrective lenses.
-
Pupil Examination: Assessing pupil measurement, form, and reactivity to gentle.
-
Eye Muscle Evaluation: Evaluating the coordination and performance of the attention muscle mass.
-
Ophthalmoscopy: Analyzing the interior buildings of the attention, together with the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels.
-
Tonometry: Measuring intraocular strain to display screen for glaucoma.
When to Search Skilled Assist:
Common eye exams are essential for sustaining eye well being. You must seek the advice of an ophthalmologist or optometrist for those who expertise:
- Blurred imaginative and prescient: Problem seeing clearly at any distance.
- Eye pressure: Discomfort or fatigue within the eyes after studying or extended visible duties.
- Double imaginative and prescient: Seeing two photos of a single object.
- Halos round lights: Rings of sunshine surrounding vibrant objects.
- Sudden modifications in imaginative and prescient: Any abrupt modifications in your capacity to see.
- Eye ache or redness: Discomfort or irritation within the eyes.
- Household historical past of eye illness: Genetic predisposition to sure eye circumstances.
Conclusion:
The attention chart is a basic device in assessing visible acuity, nevertheless it’s just one piece of the puzzle in complete eye care. Understanding how eye charts work, decoding outcomes, and recognizing when to hunt skilled assist are important steps in sustaining good eye well being. Common eye exams, coupled with a proactive method to your imaginative and prescient, will assist make sure you take pleasure in clear and wholesome imaginative and prescient all through your life. Do not underestimate the ability of a easy eye chart – it is the gateway to making sure your imaginative and prescient stays sharp and clear for years to come back.

![PDF] Comparison Of Visual Acuity Measurement Using Three, 45% OFF](http://5.imimg.com/data5/SELLER/Default/2020/12/RV/VY/WZ/111841209/71j6pildaul-sl1337-.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Decoding the Eye Chart: A Complete Information to Understanding and Utilizing Imaginative and prescient Checks. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!