Decoding The Gaze: A Complete Information To Eye Muscle Motion And Charts
Decoding the Gaze: A Complete Information to Eye Muscle Motion and Charts
Associated Articles: Decoding the Gaze: A Complete Information to Eye Muscle Motion and Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Gaze: A Complete Information to Eye Muscle Motion and Charts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Gaze: A Complete Information to Eye Muscle Motion and Charts

Our eyes, seemingly easy orbs, are marvels of intricate engineering. Their means to swiftly and exactly give attention to objects close to and much, observe shifting targets, and keep a steady visible subject is orchestrated by a fancy interaction of six extraocular muscle mass (EOMs). Understanding the perform of those muscle mass and their coordinated actions is essential in diagnosing and treating a variety of ophthalmological situations, from strabismus to double imaginative and prescient. This text explores the anatomy and performance of the EOMs, presents varied strategies of charting eye actions, and discusses the medical significance of those charts.
The Six Extraocular Muscle mass: Anatomy and Operate
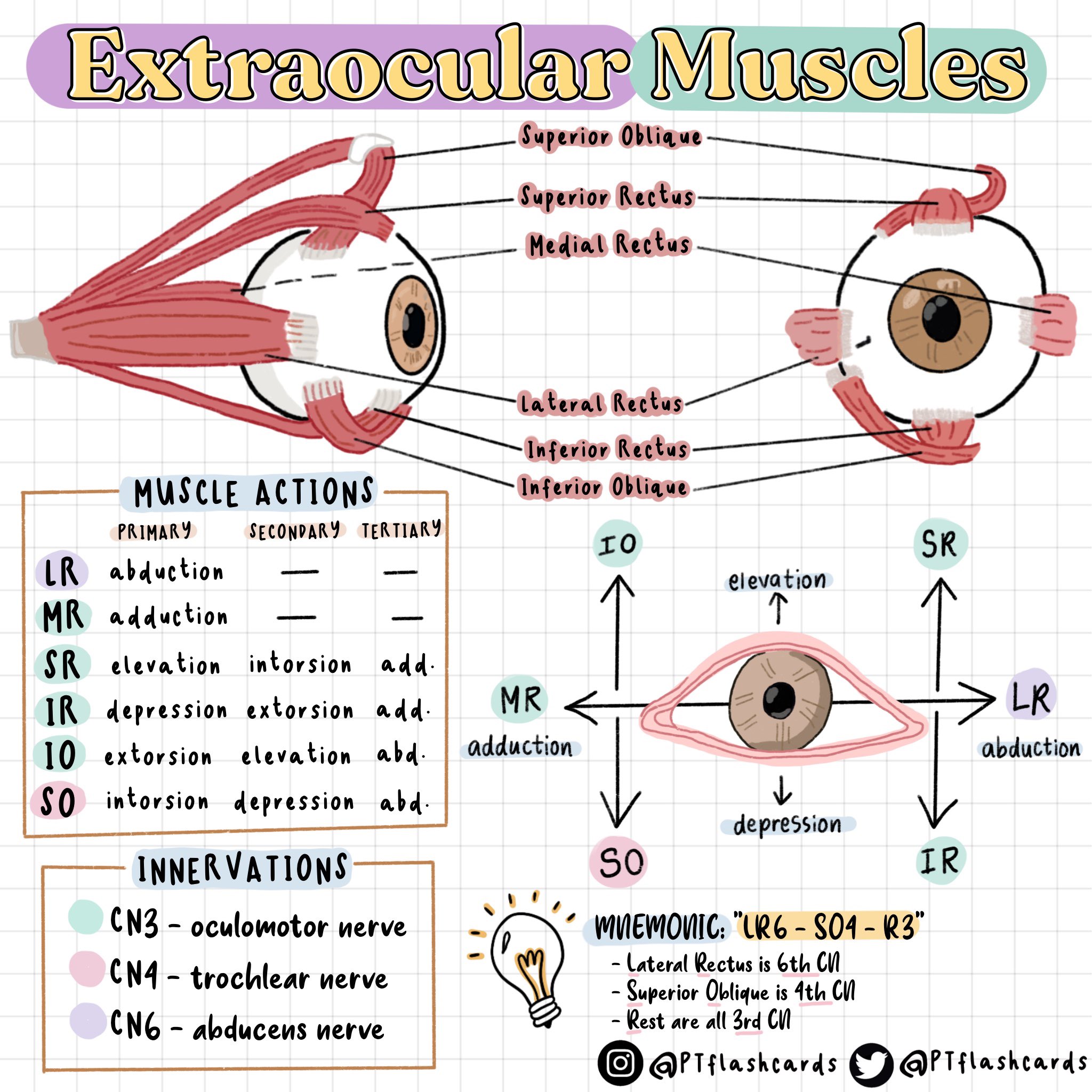
Six muscle mass, working in live performance, management the motion of every eye. They’re:
-
Superior Rectus: Originating from the widespread tendinous ring, this muscle inserts into the superior facet of the eyeball. Its main motion is elevation (trying up), but it surely additionally contributes to intorsion (rotating the highest of the attention in direction of the nostril) and adduction (turning the attention inward in direction of the nostril).
-
Inferior Rectus: Additionally originating from the widespread tendinous ring, this muscle inserts into the inferior facet of the eyeball. Its main motion is melancholy (trying down), but it surely additionally contributes to extorsion (rotating the highest of the attention away from the nostril) and adduction.
-
Medial Rectus: This muscle originates from the widespread tendinous ring and inserts into the medial facet of the eyeball. Its sole main motion is adduction (shifting the attention inward).
-
Lateral Rectus: This muscle originates from the lateral facet of the orbit and inserts into the lateral facet of the eyeball. Its sole main motion is abduction (shifting the attention outward).
-
Superior Indirect: Originating from the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, this muscle passes by way of the trochlea (a cartilaginous pulley) earlier than inserting into the supero-temporal facet of the eyeball. Its main motion is intorsion and melancholy, but it surely additionally contributes to abduction.
-
Inferior Indirect: Originating from the medial facet of the orbit close to the lacrimal fossa, this muscle inserts into the infero-temporal facet of the eyeball. Its main motion is extorsion and elevation, but it surely additionally contributes to abduction.
Understanding Synergistic and Antagonistic Muscle Actions
The EOMs do not work in isolation. They function synergistically (working collectively) and antagonistically (working towards one another) to realize exact eye actions. For instance, seeking to the proper entails the proper lateral rectus (abduction) and the left medial rectus (adduction) working synergistically. Concurrently, the left lateral rectus and proper medial rectus act as antagonists, inhibiting motion in the other way. This intricate steadiness ensures clean, coordinated eye actions. Disruptions on this steadiness, attributable to muscle weak point, paralysis, or neurological problems, can result in varied eye motion problems.
Strategies of Charting Eye Actions
A number of strategies exist for charting eye actions, every providing completely different ranges of element and medical utility. These strategies are essential for documenting the vary of movement, figuring out limitations, and assessing the presence of strabismus (misalignment of the eyes) or different problems.
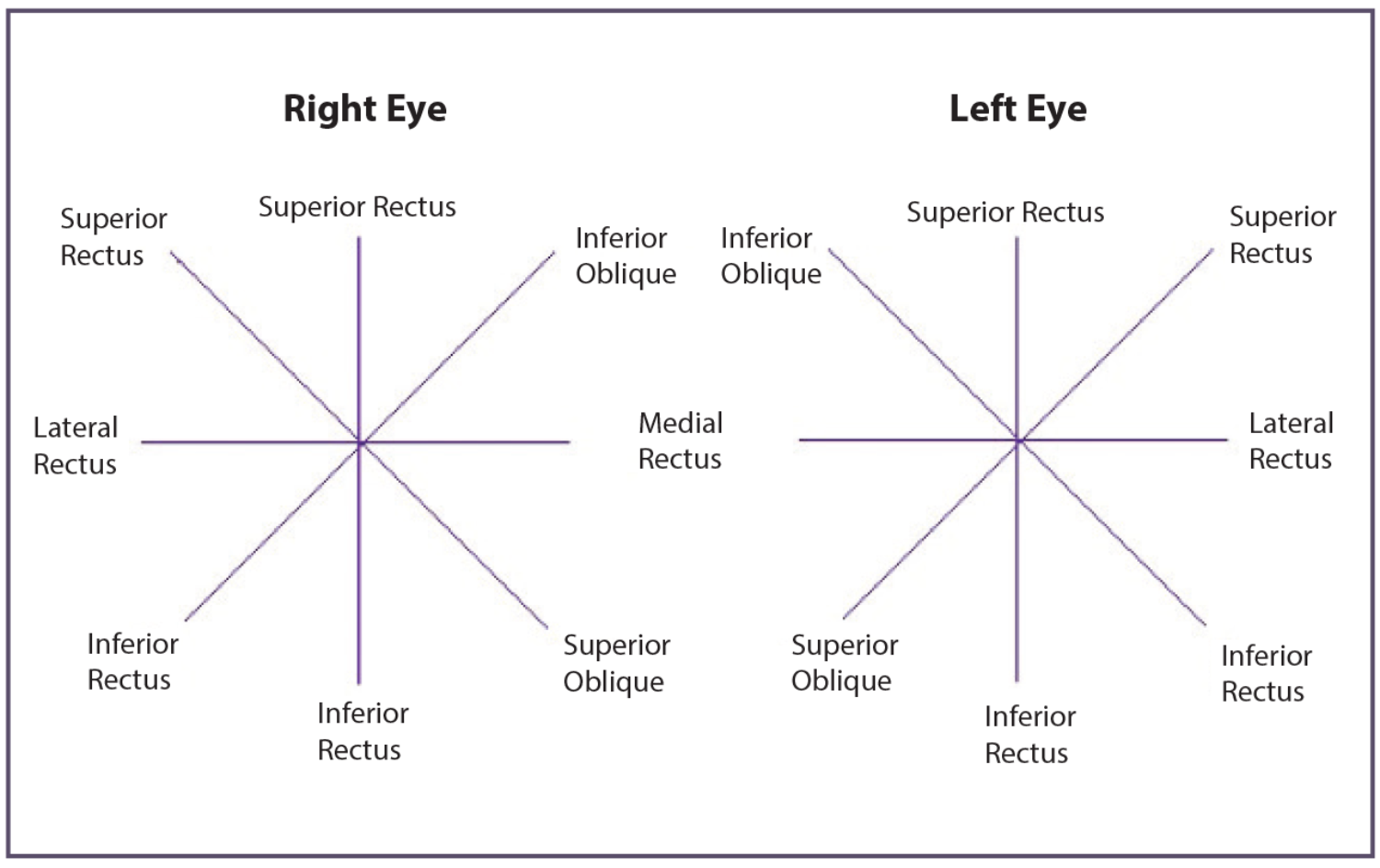
1. Easy Vary of Movement Chart: This chart entails a easy schematic illustration of the attention and its six cardinal positions of gaze (up, down, proper, left, and the intermediate indirect positions). The examiner assesses the power of the attention to maneuver absolutely into every place and notes any limitations or restrictions. It is a primary methodology, primarily used for screening functions.
2. Ductions and Variations Chart: This extra detailed chart differentiates between ductions (monocular eye actions) and variations (binocular, coordinated eye actions). Ductions assess the motion of every eye individually, whereas variations assess the coordinated actions of each eyes collectively in numerous instructions. This chart gives a extra complete analysis of eye muscle perform, figuring out potential imbalances or weaknesses.
3. Quantitative Measurement of Eye Motion: Superior strategies use subtle gear, reminiscent of infrared oculography or electro-oculography, to quantify eye actions with precision. These strategies measure the velocity, amplitude, and accuracy of saccades (speedy eye actions) and pursuits (clean, following actions). These measurements are significantly helpful in diagnosing and monitoring situations affecting saccadic or pursuit eye actions, reminiscent of cerebellar problems.
4. Hess Chart and Lancaster Crimson-Inexperienced Check: These are specialised charts used to quantify and visualize the extent of strabismus. The Hess chart makes use of a sequence of lights organized in a grid sample, whereas the Lancaster Crimson-Inexperienced check employs purple and inexperienced filters to evaluate the place of every eye independently. These charts assist decide the sort and magnitude of strabismus, guiding therapy choices.
Medical Significance of Eye Motion Charts
Eye motion charts play an important function in varied medical settings:
-
Strabismus Analysis and Administration: Charts are important for diagnosing and monitoring the therapy of strabismus. They assist decide the sort (esotropia, exotropia, hypertropia, hypotropia), magnitude, and any related limitations in eye motion.
-
Neurological Problems: Abnormalities in eye actions can point out neurological issues affecting the cranial nerves controlling the EOMs (III, IV, VI) or the brainstem pathways concerned in coordinating eye actions. Charts may help determine the particular neurological lesion primarily based on the sample of eye motion deficits. Situations like internuclear ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus, and gaze palsies could be identified and characterised utilizing these charts.
-
Myasthenia Gravis: This autoimmune dysfunction impacts neuromuscular junctions, resulting in fluctuating weak point of voluntary muscle mass, together with the EOMs. Eye motion charts, particularly these involving repetitive eye actions, can reveal attribute fatigability and worsening of eye motion deficits with sustained effort.
-
Myopathies: Muscle ailments can have an effect on the EOMs, inflicting limitations in eye actions. Charts may help assess the extent of muscle involvement and information the prognosis and administration of those situations.
-
Trauma and Orbital Illness: Eye accidents or orbital ailments may cause restrictions in eye actions. Charts are essential for documenting the extent of those limitations and monitoring restoration.
Deciphering Eye Motion Charts: Key Concerns
Deciphering eye motion charts requires experience and an intensive understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the EOMs. A number of elements want consideration:
-
Affected person Age: Regular eye actions fluctuate with age, significantly in infants and younger youngsters.
-
Affected person Cooperation: Correct evaluation is determined by the affected person’s means to cooperate and comply with directions.
-
Presence of different medical situations: Underlying medical situations can have an effect on eye motion evaluation.
-
Consistency of findings: A number of assessments could also be essential to verify the findings and rule out transient results.
Conclusion
Eye motion charts are indispensable instruments in ophthalmology and neurology. They supply a visible illustration of advanced eye muscle interactions, permitting clinicians to diagnose and handle a variety of situations affecting eye motion. Whereas easy charts provide a primary evaluation, superior strategies present quantitative measurements for a extra exact prognosis. The interpretation of those charts requires experience and cautious consideration of assorted elements. In the end, understanding the intricate mechanics of eye muscle motion and the efficient utilization of charting strategies are essential for offering optimum affected person care.
![]()





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Decoding the Gaze: A Complete Information to Eye Muscle Motion and Charts. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!