Decoding The PH Scale: A Complete Information To The Acidity And Alkalinity Of Meals
Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information to the Acidity and Alkalinity of Meals
Associated Articles: Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information to the Acidity and Alkalinity of Meals
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information to the Acidity and Alkalinity of Meals. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information to the Acidity and Alkalinity of Meals

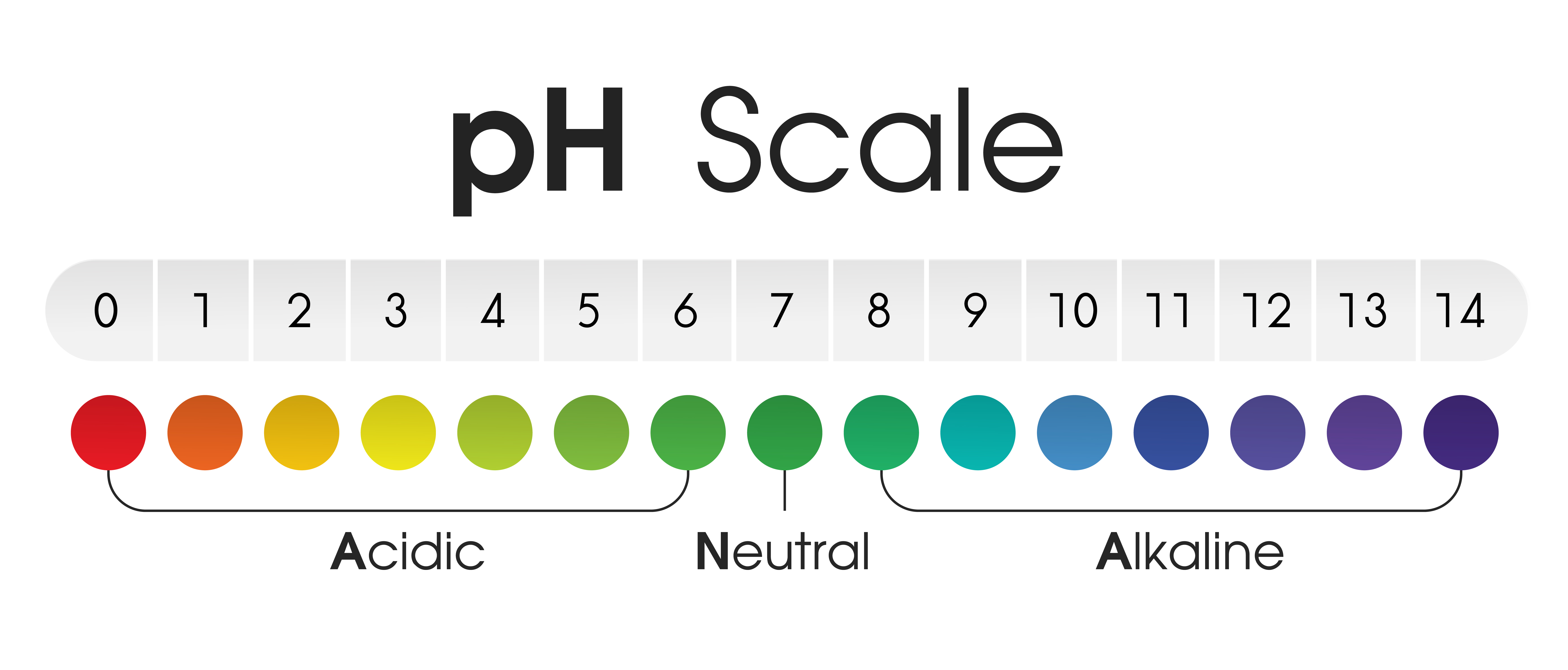
The pH scale, starting from 0 to 14, measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. A pH of seven is impartial; values under 7 point out acidity (more and more acidic because the quantity decreases), whereas values above 7 point out alkalinity (more and more alkaline because the quantity will increase). Understanding the pH of meals is essential for varied causes, from optimizing digestion and nutrient absorption to probably influencing general well being and managing sure situations. Whereas the impression of dietary pH on general physique pH is a topic of ongoing debate, the inherent acidity or alkalinity of particular person meals instantly impacts their style, preservation, and interplay with different elements. This complete article explores the pH of varied meals teams, gives an in depth chart, and discusses the implications of dietary pH.
The Significance of pH in Meals:
The pH of meals performs a important function in a number of facets:
-
Style and Taste: Acidity and alkalinity considerably affect the style profile of meals. Acids contribute to sourness (e.g., lemons, vinegar), whereas alkaline substances can impart a bitter or soapy style (though that is much less widespread in edible meals). The steadiness of acids and bases is essential for attaining fascinating taste profiles in culinary creations.
-
Meals Preservation: pH is a key consider meals preservation methods. Low pH (acidic) environments inhibit the expansion of many spoilage microorganisms, explaining why pickling and canning depend on acidic options. Conversely, excessive pH environments also can affect spoilage, albeit by means of totally different mechanisms.
-
Nutrient Availability: The pH of the gastrointestinal tract influences the absorption of sure vitamins. For example, optimum absorption of some minerals might require a selected pH vary.
-
Meals Processing: pH changes are regularly employed throughout meals processing to attain desired textures, colours, and shelf life. For instance, controlling the pH throughout cheese making is important for correct coagulation and taste growth.
-
Enzyme Exercise: Many enzymes operate optimally inside a selected pH vary. Adjustments in pH can have an effect on enzyme exercise, impacting the biochemical processes inside meals throughout digestion and processing.
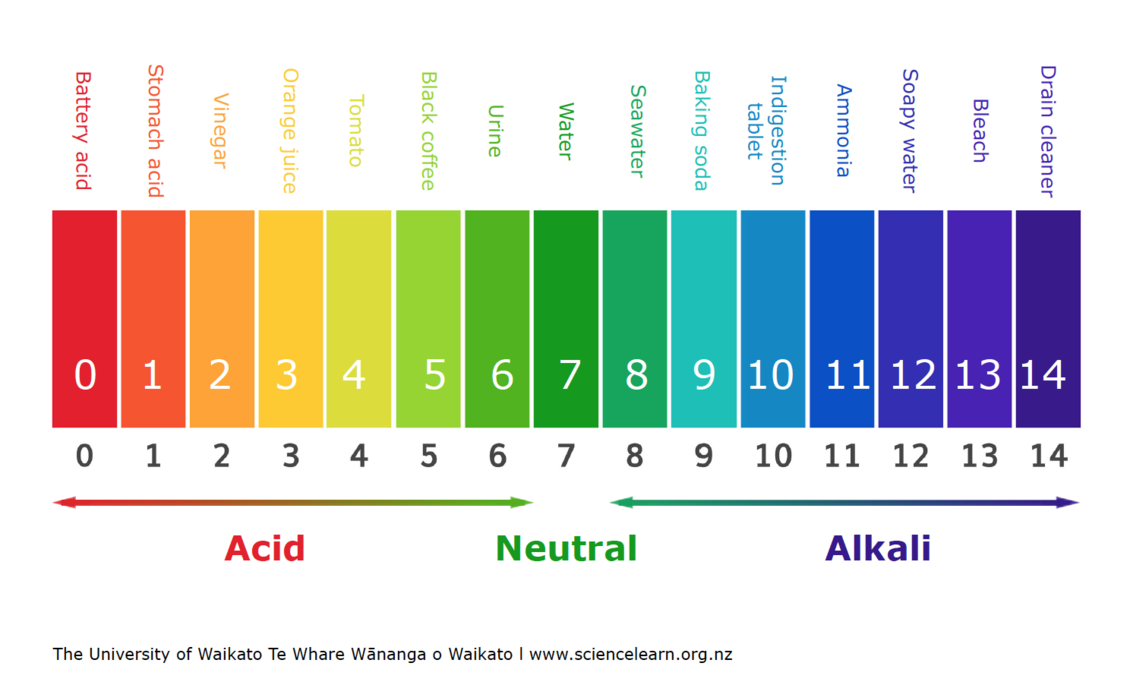
The pH of Widespread Meals Teams:
The next gives a common overview of the pH ranges of varied meals teams. It is essential to know that the precise pH worth can fluctuate based mostly on elements like ripeness, selection, processing strategies, and rising situations. Due to this fact, the values introduced right here ought to be thought-about approximations.
Extremely Acidic Meals (pH < 4.5):
- Citrus Fruits: Lemons (pH 2.0-2.6), limes (pH 1.8-2.0), oranges (pH 3.3-4.2), grapefruits (pH 3.0-3.3) are exceptionally acidic.
- Tomatoes: (pH 4.0-4.5) Although technically a fruit, tomatoes fall throughout the acidic vary.
- Vinegar: (pH 2.4-3.4) Several types of vinegar fluctuate barely in pH.
- Pickles: (pH 3.0-4.0) The pickling course of makes use of acidic options to protect the meals.
- Cranberries: (pH 2.3-2.5) Recognized for his or her excessive acidity.
- Prunes: (pH 3.0-4.0) Dried plums with important acidity.
Reasonably Acidic Meals (pH 4.5 – 6.0):
- Apples: (pH 3.0-4.0) The pH of apples can fluctuate relying on the variability.
- Grapes: (pH 3.5-4.5) Just like apples, pH varies by sort.
- Peaches: (pH 3.4-4.0)
- Plums: (pH 3.5-4.5)
- Yogurt: (pH 4.0-4.5) The acidity will depend on the kind and bacterial cultures used.
- Espresso: (pH 4.5-5.5) The pH of espresso can fluctuate based mostly on brewing strategies and bean sort.
- Tea: (pH 4.5-6.0) Just like espresso, pH varies based mostly on sort and preparation.
Impartial Meals (pH ~7.0):
- Pure Water: (pH 7.0) The benchmark for neutrality.
- Many processed meals: Some processed meals are designed to be near impartial pH. Nevertheless, this isn’t at all times constant.
Reasonably Alkaline Meals (pH 6.0 – 7.5):
- Bananas: (pH 5.0-5.6) Barely alkaline relying on ripeness.
- Potatoes: (pH 5.5-6.5)
- Asparagus: (pH 6.0-6.5)
- Broccoli: (pH 6.0-6.5)
- Carrots: (pH 5.0-6.0)
- Most greens: Many greens fall inside this vary, though particular pH varies extensively.
Extremely Alkaline Meals (pH > 7.5):
- Baking Soda: (pH 8.3-9.0) A typical alkaline ingredient in baking.
- Alkali-treated meals: Some meals bear alkali remedies throughout processing, altering their pH.
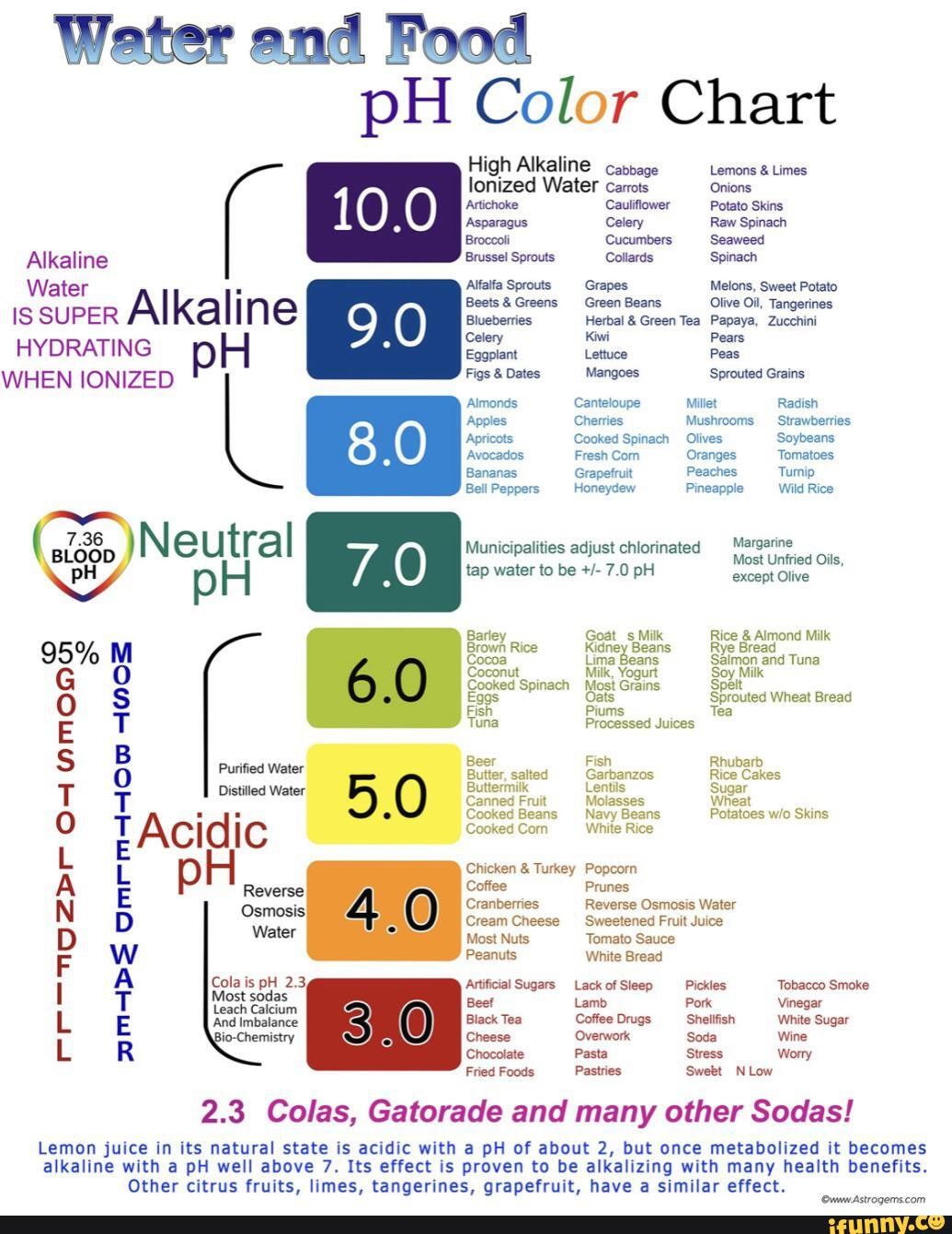
Detailed pH Chart of Widespread Meals:
| Meals | pH Vary | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Lemons | 2.0-2.6 | Extremely acidic |
| Limes | 1.8-2.0 | Extremely acidic |
| Oranges | 3.3-4.2 | Acidic |
| Grapefruits | 3.0-3.3 | Acidic |
| Tomatoes | 4.0-4.5 | Reasonably acidic |
| Apples | 3.0-4.0 | Acidic, varies by selection |
| Grapes | 3.5-4.5 | Acidic, varies by selection |
| Peaches | 3.4-4.0 | Acidic |
| Plums | 3.5-4.5 | Acidic |
| Yogurt | 4.0-4.5 | Reasonably acidic, varies by sort |
| Espresso | 4.5-5.5 | Barely acidic, varies by sort and brewing technique |
| Tea | 4.5-6.0 | Barely acidic to impartial, varies by sort and brewing technique |
| Bananas | 5.0-5.6 | Barely alkaline, varies with ripeness |
| Potatoes | 5.5-6.5 | Barely alkaline |
| Asparagus | 6.0-6.5 | Barely alkaline |
| Broccoli | 6.0-6.5 | Barely alkaline |
| Carrots | 5.0-6.0 | Barely acidic to barely alkaline |
| Baking Soda | 8.3-9.0 | Extremely alkaline |
| Pure Water | 7.0 | Impartial |
| Vinegar | 2.4-3.4 | Extremely acidic, varies by sort |
| Cranberries | 2.3-2.5 | Extremely acidic |
| Prunes | 3.0-4.0 | Acidic |
| Most Darkish Leafy Greens | 6.0-7.0 | Barely alkaline to impartial |
| Most Nuts and Seeds | 5.0-6.5 | Barely acidic to barely alkaline |
The Alkaline Weight loss program and pH Steadiness:
The idea of an "alkaline food regimen," which emphasizes consuming primarily alkaline-forming meals, has gained reputation. Proponents counsel that this food regimen may also help steadiness the physique’s pH, probably bettering well being and decreasing the chance of continual illnesses. Nevertheless, the scientific proof supporting these claims is restricted and infrequently inconclusive. The human physique possesses strong buffering techniques that tightly regulate blood pH inside a really slender vary (round 7.35-7.45). Whereas the pH of particular person meals might have an effect on the pH of urine or saliva, it has minimal impression on the tightly managed pH of blood.
Conclusion:
Understanding the pH of meals is crucial for varied facets of meals science, culinary arts, and probably, particular person dietary decisions. Whereas the impression of dietary pH on general physique pH stays a subject of ongoing analysis, the inherent acidity or alkalinity of meals instantly influences their style, preservation, and interplay with different elements. The chart supplied affords a common guideline; nevertheless, it is essential to keep in mind that the precise pH can fluctuate considerably based mostly on a number of elements. Consulting extra particular databases and contemplating the person traits of every meals merchandise is beneficial for exact pH willpower. The data on this article shouldn’t be thought-about medical recommendation; seek the advice of with a healthcare skilled or registered dietitian for personalised dietary steerage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information to the Acidity and Alkalinity of Meals. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!