Decoding The T-Distribution Chart: A Complete Information
Decoding the t-Distribution Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the t-Distribution Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the t-Distribution Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the t-Distribution Chart: A Complete Information

The t-distribution, a vital instrument in statistical inference, is incessantly used when coping with small pattern sizes or unknown inhabitants commonplace deviations. Not like the conventional distribution, the t-distribution is characterised by its levels of freedom (df), influencing its form and unfold. Understanding easy methods to interpret a t-distribution chart is prime for accurately conducting speculation assessments and developing confidence intervals. This text gives a complete information to navigating t-distribution charts, demystifying their use and empowering you to confidently apply them in your statistical analyses.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Levels of Freedom and the t-Distribution
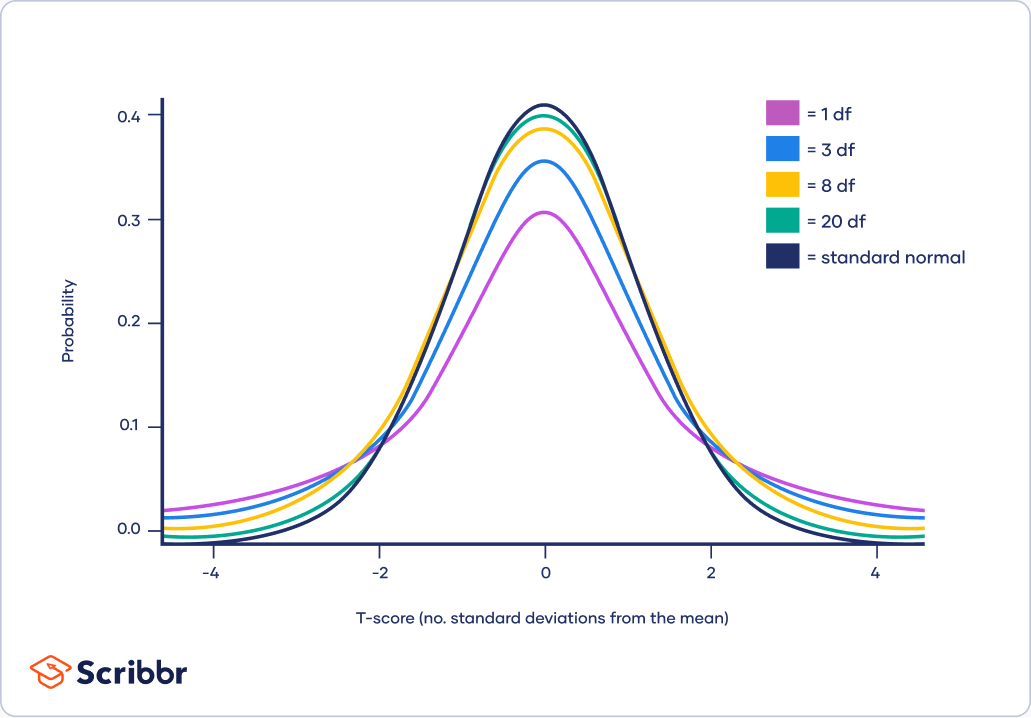
Earlier than delving into chart interpretation, let’s solidify our understanding of the important thing ideas. The t-distribution’s form is decided by its levels of freedom (df). The levels of freedom signify the variety of impartial items of data obtainable to estimate a parameter. In easy phrases, for a pattern of measurement ‘n’, the levels of freedom are usually calculated as (n-1). It’s because one diploma of freedom is misplaced when estimating the pattern imply, which is utilized in calculating the pattern commonplace deviation.
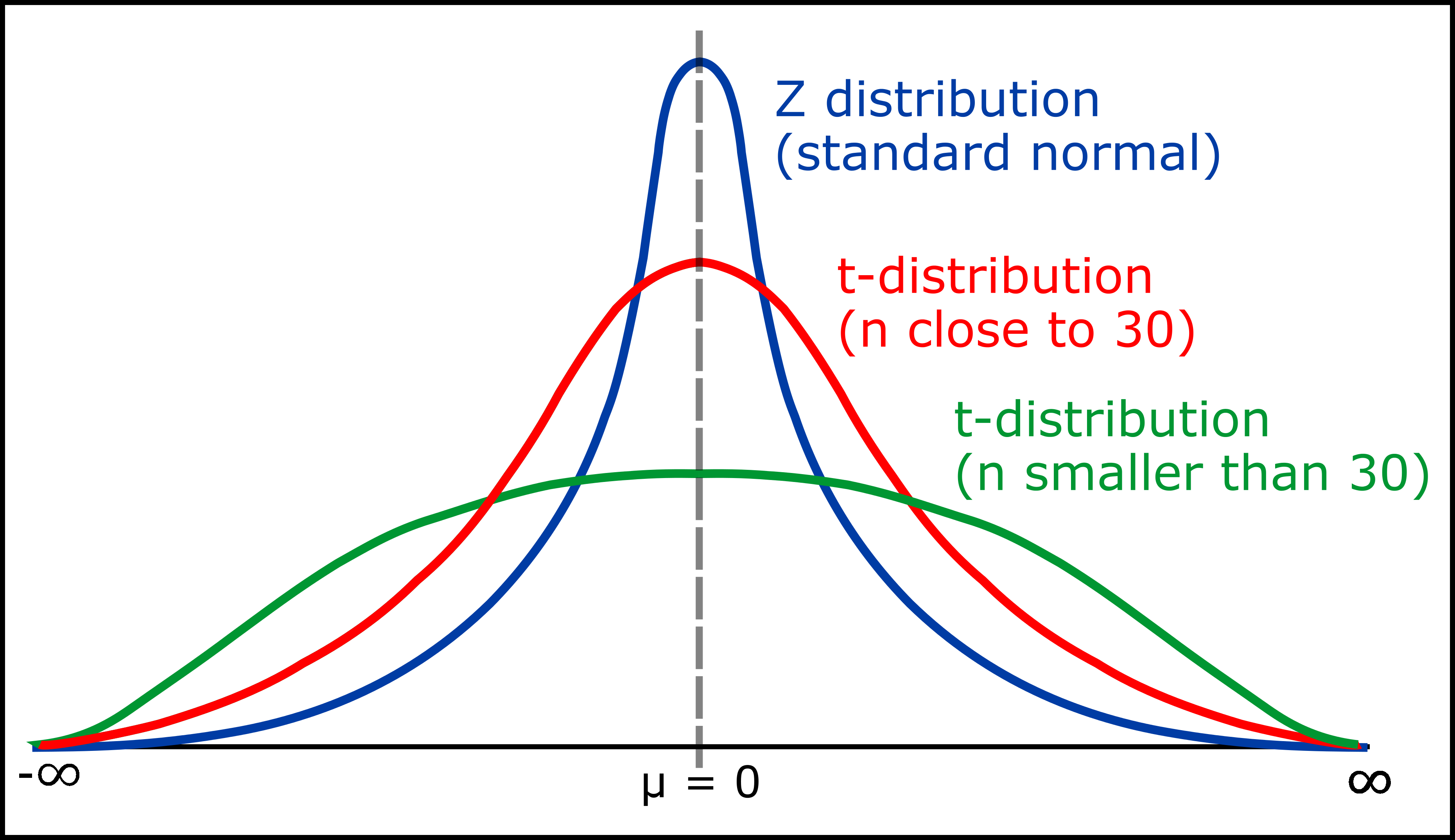
Because the levels of freedom improve, the t-distribution approaches the usual regular distribution (z-distribution). It’s because with bigger pattern sizes, the pattern commonplace deviation turns into a extra dependable estimator of the inhabitants commonplace deviation, decreasing the uncertainty related to the t-statistic. Conversely, with smaller levels of freedom, the t-distribution has heavier tails than the conventional distribution, reflecting the elevated uncertainty resulting from restricted pattern data. This implies excessive values usually tend to happen within the t-distribution, particularly with low levels of freedom.
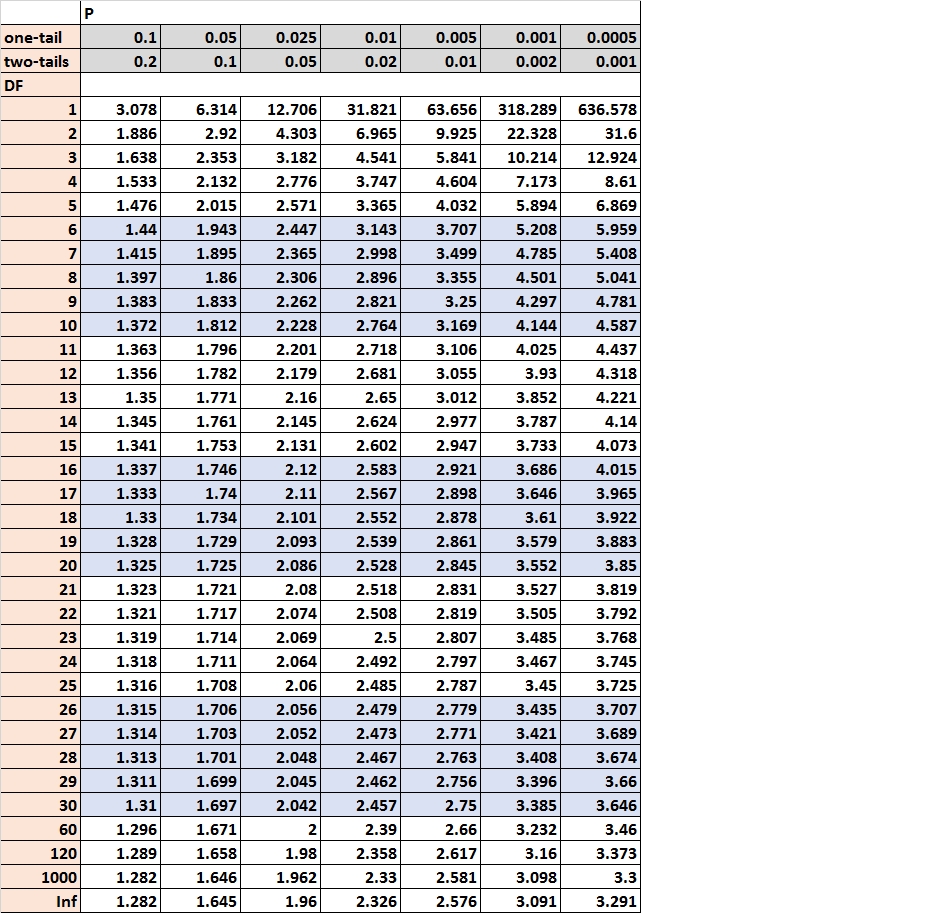
Construction of a t-Distribution Chart (Desk):
A typical t-distribution chart, typically present in statistical textbooks or software program packages, is offered as a desk. This desk organizes vital t-values based mostly on two major inputs:
-
Levels of Freedom (df): That is often listed within the leftmost column of the desk. It ranges from 1 to a big quantity (typically as much as infinity, representing the usual regular distribution).
-
Significance Stage (α): This represents the likelihood of rejecting the null speculation when it’s really true (Kind I error). Significance ranges are generally offered as column headers, usually together with values like 0.10, 0.05, 0.025, 0.01, and 0.005 (or their corresponding percentages: 10%, 5%, 2.5%, 1%, and 0.5%). These values correspond to one-tailed or two-tailed assessments.
Deciphering the Chart for One-Tailed Assessments:
A one-tailed take a look at examines whether or not a parameter is considerably larger than (right-tailed) or lower than (left-tailed) a hypothesized worth. To seek out the vital t-value for a one-tailed take a look at:
-
Find the levels of freedom (df) within the leftmost column. This corresponds to your pattern measurement (n-1).
-
Determine the importance stage (α) column that corresponds to your chosen alpha stage. Keep in mind, that is the likelihood of rejecting the null speculation when it’s true. For a right-tailed take a look at, use the α worth straight. For a left-tailed take a look at, the vital t-value would be the destructive of the worth discovered at this α stage.
-
The cell the place the df row and α column intersect comprises the vital t-value. In case your calculated t-statistic (out of your pattern information) exceeds this vital worth (for a right-tailed take a look at) or is lower than the destructive of this vital worth (for a left-tailed take a look at), you reject the null speculation.
Instance: One-Tailed Check
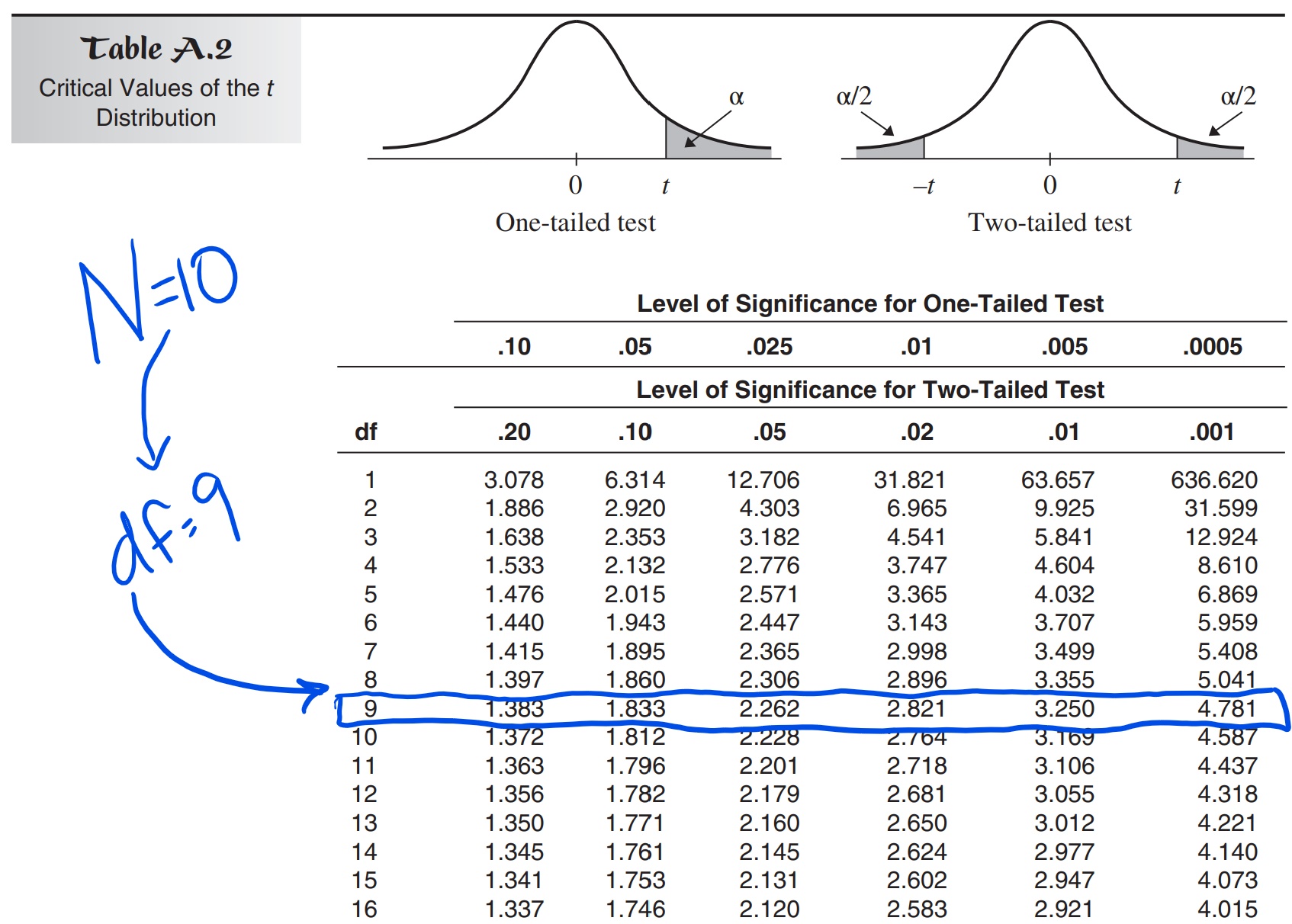
Suppose you may have a pattern of 16 observations (n=16), leading to df = 15. You’re conducting a right-tailed take a look at with a significance stage of α = 0.05. Find df = 15 within the leftmost column and the α = 0.05 column. The intersecting cell will present the vital t-value. In case your calculated t-statistic is bigger than this vital worth, you reject the null speculation.
Deciphering the Chart for Two-Tailed Assessments:
A two-tailed take a look at examines whether or not a parameter is considerably totally different from (both larger or lower than) a hypothesized worth. The method is barely totally different:
-
Find the levels of freedom (df) within the leftmost column.
-
Determine the importance stage (α) column similar to half your chosen alpha stage (α/2). It’s because the α stage is cut up between the 2 tails of the distribution. For instance, in case your α = 0.05, you’ll search for the α = 0.025 column.
-
The cell the place the df row and α/2 column intersect comprises the vital t-value. Nonetheless, keep in mind that that is the optimistic vital worth. You should have two vital values: the optimistic worth from the desk and its destructive counterpart. In case your calculated t-statistic falls exterior this vary (i.e., lower than the destructive vital worth or larger than the optimistic vital worth), you reject the null speculation.
Instance: Two-Tailed Check
To illustrate you may have a pattern of 21 observations (n=21), giving df = 20. You are conducting a two-tailed take a look at with α = 0.01. You’d search for the df = 20 row and the α/2 = 0.005 column. The intersecting cell offers you the optimistic vital t-value. Your calculated t-statistic have to be both larger than this worth or lower than its destructive to reject the null speculation.
Coping with Lacking Values within the Desk:
Some t-distribution charts may not have entries for all levels of freedom. In case your df just isn’t straight listed, you possibly can both:
-
Use interpolation: Estimate the vital t-value by averaging the values from the closest df values above and under your df. That is an approximation, however typically sufficiently correct.
-
Use statistical software program: Software program packages like R, SPSS, Python (with SciPy), or Excel can calculate exact vital t-values for any df.
-
Seek the advice of a extra in depth desk: Extra complete t-distribution tables are available on-line or in superior statistical texts.
Relationship to Confidence Intervals:
The t-distribution can also be essential in developing confidence intervals. The vital t-value from the chart is used to calculate the margin of error, which determines the width of the boldness interval. For a (1-α) confidence interval, you’ll use the vital t-value similar to α/2 for a two-tailed take a look at.
Conclusion:
Mastering the interpretation of a t-distribution chart is crucial for anybody working with statistical inference. By understanding the roles of levels of freedom and significance ranges, and by following the steps outlined above, you possibly can precisely decide vital t-values for each one-tailed and two-tailed assessments. Keep in mind to at all times take into account the context of your evaluation, guaranteeing you choose the suitable take a look at (one-tailed or two-tailed) and significance stage based mostly in your analysis query and the character of your information. Whereas t-distribution charts present a useful instrument, using statistical software program for exact calculations, notably when coping with much less widespread levels of freedom, is extremely really useful for accuracy and effectivity. This complete information ought to equip you with the information and confidence to successfully make the most of t-distribution charts in your statistical endeavors.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding the t-Distribution Chart: A Complete Information. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!