Figuring out Pattern Measurement With Morgan’s Charts: A Complete Information
Figuring out Pattern Measurement with Morgan’s Charts: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Figuring out Pattern Measurement with Morgan’s Charts: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Figuring out Pattern Measurement with Morgan’s Charts: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Figuring out Pattern Measurement with Morgan’s Charts: A Complete Information
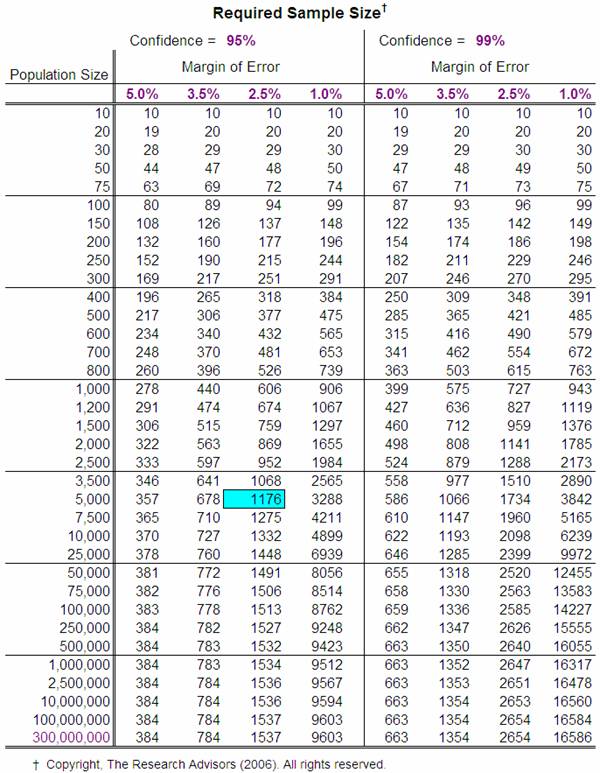
Choosing the proper pattern measurement is essential for any analysis challenge. An inadequate pattern measurement can result in inaccurate conclusions and a waste of sources, whereas an excessively massive pattern measurement is expensive and inefficient. Morgan’s charts provide a handy and readily accessible technique for figuring out acceptable pattern sizes, significantly for estimating inhabitants proportions with a specified stage of confidence and precision. This text supplies an in depth rationalization of Morgan’s charts, their software, limitations, and concerns for efficient pattern measurement willpower.
Understanding Morgan’s Charts
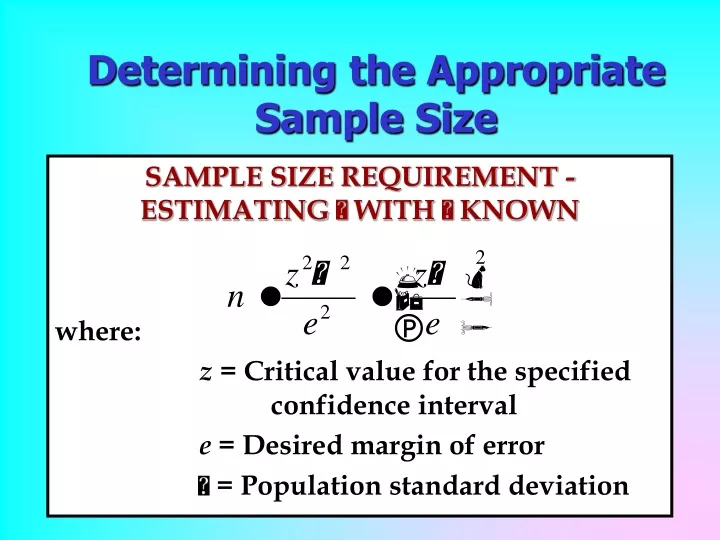
Morgan’s charts, also referred to as Morgan’s pattern measurement tables, are visible aids that simplify the method of figuring out the pattern measurement required for estimating a inhabitants proportion. These charts are primarily based on the formulation for calculating pattern measurement, incorporating elements like the specified confidence stage, margin of error (precision), and an estimated proportion of the attribute of curiosity inside the inhabitants.
Not like advanced statistical software program or formulation that require intricate calculations, Morgan’s charts current the knowledge in a user-friendly desk format. The charts sometimes show pattern sizes for varied combos of:
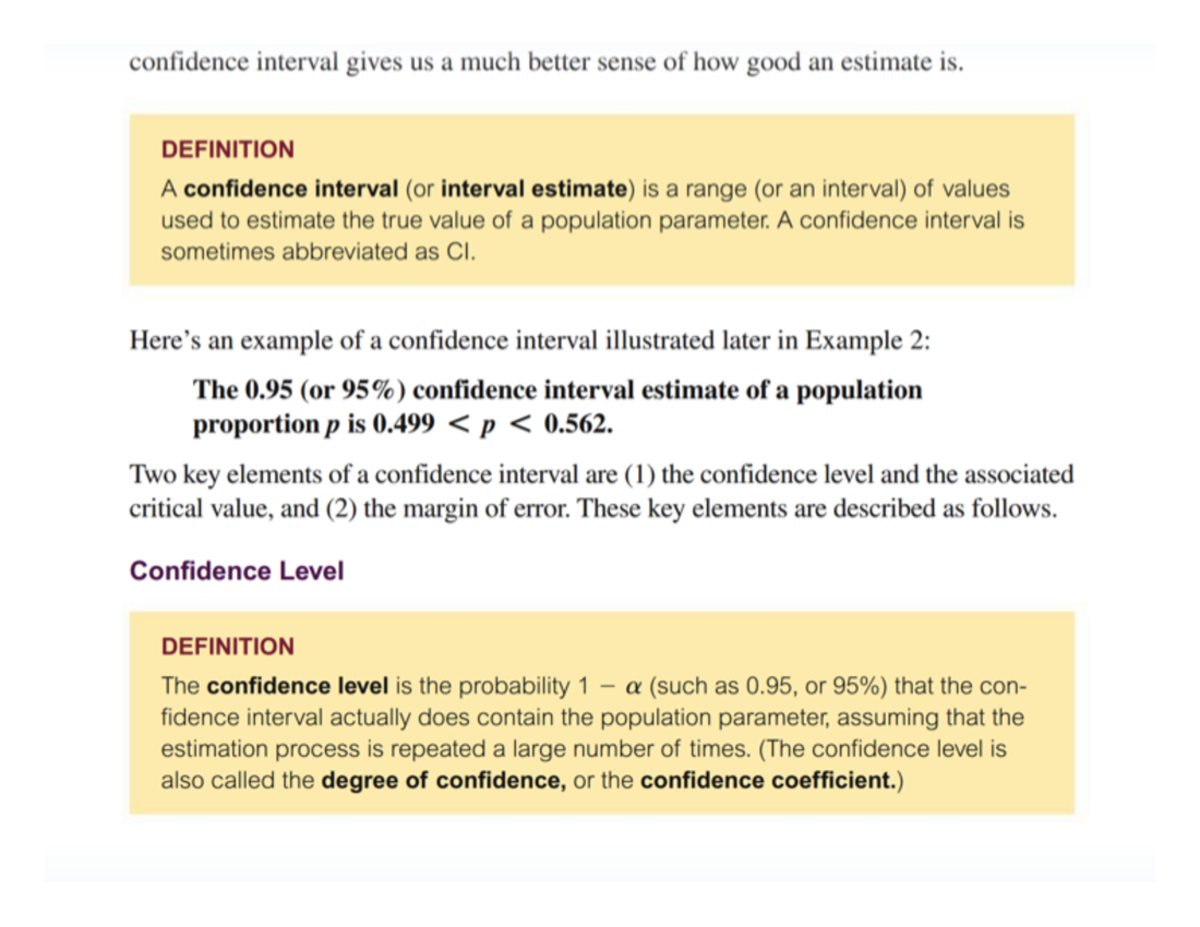
- Confidence Stage: The chance that the true inhabitants proportion lies inside the calculated confidence interval (e.g., 95%, 99%).
- Margin of Error: The appropriate vary of error across the estimated proportion (e.g., ±5%, ±3%). A smaller margin of error requires a bigger pattern measurement.
- Estimated Inhabitants Proportion (p): That is an informed guess concerning the proportion of the inhabitants possessing the attribute of curiosity. This guess impacts the pattern measurement wanted. In case you have no prior data, a conservative estimate of 0.5 (50%) is commonly used, as this maximizes the required pattern measurement.
The right way to Use Morgan’s Charts
Utilizing Morgan’s charts is simple:
-
Decide the Desired Confidence Stage: Select the arrogance stage that aligns with the analysis goals. A 95% confidence stage is usually used, however larger ranges (e.g., 99%) present larger certainty however require bigger pattern sizes.
-
Specify the Margin of Error: Resolve on the suitable margin of error. This represents the precision of the estimate. A smaller margin of error implies a extra exact estimate however necessitates a bigger pattern measurement.
-
Estimate the Inhabitants Proportion (p): If prior data or pilot research present an estimate of the inhabitants proportion, use that worth. If not, utilizing 0.5 (50%) is essentially the most conservative method, guaranteeing a sufficiently massive pattern measurement.
-
Find the Applicable Pattern Measurement: Utilizing the chosen confidence stage, margin of error, and estimated inhabitants proportion, find the corresponding pattern measurement within the Morgan chart.
Instance: Utilizing Morgan’s Charts
As an instance we need to estimate the proportion of adults in a metropolis who assist a selected political candidate, with a 95% confidence stage and a margin of error of ±3%. We now have no prior data of the inhabitants proportion, so we use the conservative estimate of p = 0.5.
Referring to a Morgan chart with these parameters, we might discover the corresponding pattern measurement. The chart would seemingly present a pattern measurement of roughly 1068 people. This implies we have to survey no less than 1068 adults to acquire an estimate of the inhabitants proportion with the desired confidence stage and margin of error.
Limitations of Morgan’s Charts
Whereas Morgan’s charts present a handy technique for figuring out pattern measurement, they’ve some limitations:
-
Finite Inhabitants Correction: Morgan’s charts sometimes assume an infinitely massive inhabitants. For smaller populations, a finite inhabitants correction issue must be utilized to regulate the pattern measurement. This correction reduces the pattern measurement required because the inhabitants measurement decreases.
-
Assumptions of Easy Random Sampling: The charts are primarily based on the idea of easy random sampling. If different sampling strategies (e.g., stratified sampling, cluster sampling) are used, the calculated pattern measurement may not be acceptable. Extra advanced calculations are essential for these strategies.
-
Homogeneity of the Inhabitants: The charts assume homogeneity inside the inhabitants. If the inhabitants is very heterogeneous, a bigger pattern measurement may be wanted to make sure enough illustration of all subgroups.
-
Non-response Bias: Morgan’s charts don’t account for non-response bias. If a good portion of the pattern doesn’t reply, the outcomes may be biased, and a bigger preliminary pattern measurement must be thought-about to compensate for potential non-response.
-
Precision of the Estimated Proportion: The accuracy of the pattern measurement relies on the accuracy of the estimated inhabitants proportion (p). An inaccurate estimate of p can result in an under- or overestimation of the required pattern measurement.
Software program and On-line Calculators
Whereas Morgan’s charts are helpful, many statistical software program packages (like SPSS, R, SAS) and on-line calculators present extra subtle pattern measurement calculations. These instruments typically incorporate corrections for finite populations, totally different sampling strategies, and permit for extra exact management over varied parameters. They’ll additionally deal with extra advanced eventualities, similar to estimating pattern measurement for a number of proportions or means.
Past Inhabitants Proportions
Morgan’s charts primarily deal with estimating inhabitants proportions. For different statistical parameters, similar to means or variances, totally different formulation and strategies are required to find out the suitable pattern measurement. These calculations typically contain contemplating the inhabitants normal deviation or variance and the specified stage of precision for the imply.
Conclusion
Morgan’s charts provide a user-friendly method to figuring out pattern measurement for estimating inhabitants proportions. Their simplicity makes them accessible to researchers with restricted statistical experience. Nevertheless, it is essential to concentrate on their limitations and take into account the particular traits of the analysis challenge. When coping with advanced eventualities or requiring larger precision, using statistical software program or on-line calculators is really helpful to make sure correct and dependable pattern measurement willpower, resulting in sturdy and significant analysis findings. The selection between utilizing Morgan’s charts and extra subtle strategies relies on the complexity of the analysis design, the out there sources, and the specified stage of accuracy. Keep in mind that a well-defined pattern measurement is a cornerstone of dependable and impactful analysis.



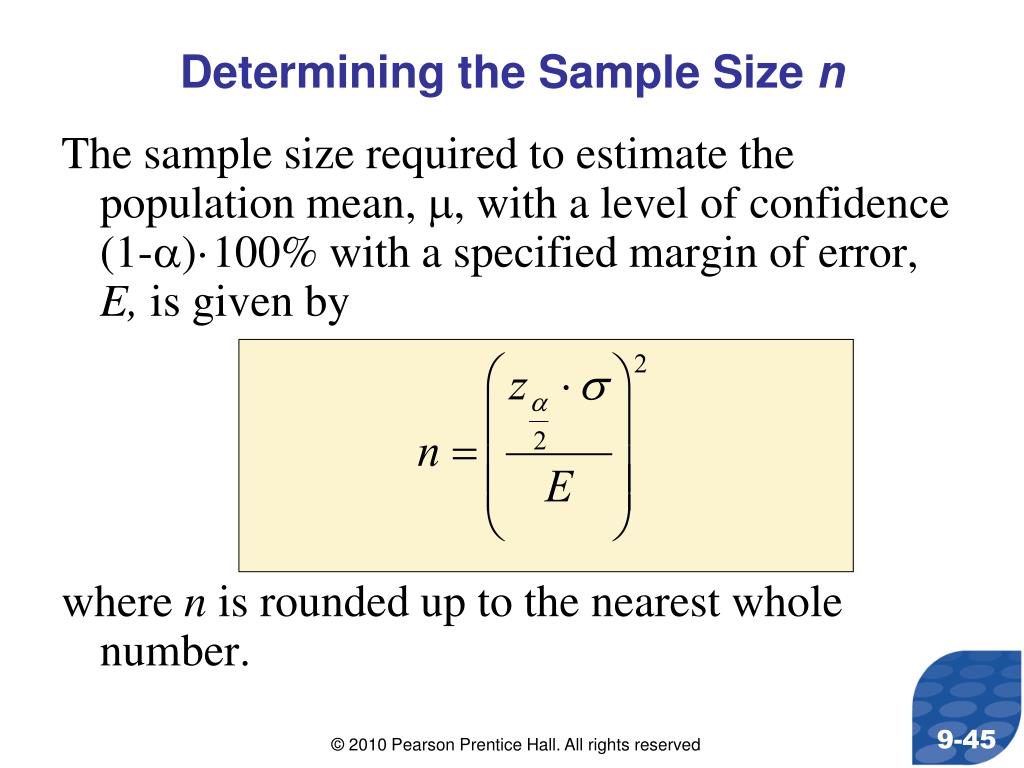
Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Figuring out Pattern Measurement with Morgan’s Charts: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!