Distinction Bar Chart And Histogram
distinction bar chart and histogram
Associated Articles: distinction bar chart and histogram
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to distinction bar chart and histogram. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
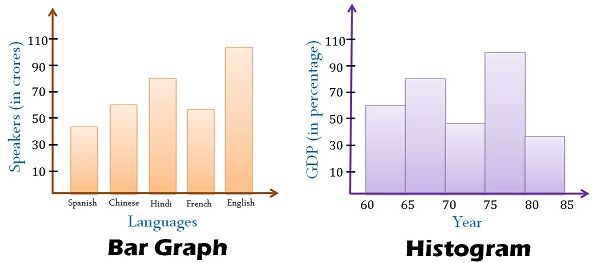
Bar Charts vs. Histograms: Unveiling the Variations in Visualizing Information
![What is the difference between a bar graph and a histogram? [SOLVED]](https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/screenshot-2021-03-01-at-9-17-06-am-1614570481.png)
Information visualization is essential for successfully speaking insights derived from datasets. Among the many many instruments out there, bar charts and histograms are steadily employed to characterize categorical and numerical information, respectively. Whereas each make the most of rectangular bars to show information, their underlying functions and interpretations differ considerably. This text delves into the nuances of bar charts and histograms, clarifying their distinct traits, functions, and limitations.
Understanding Bar Charts: Categorical Information at a Look
A bar chart is a visible illustration of categorical information, showcasing the frequency or magnitude of various classes. Every bar represents a definite class, and its size corresponds to the worth related to that class. The classes may be something from colours and types to geographical places and age teams – primarily, any information that may be grouped into discrete, non-overlapping classes.
Key Options of Bar Charts:
- Categorical Information: Bar charts are designed particularly for visualizing categorical information, the place the impartial variable is qualitative relatively than quantitative.
- Discrete Classes: The classes on the x-axis are distinct and separate, with no steady circulation between them.
- Frequency or Magnitude: The peak (or size, relying on orientation) of every bar represents the frequency (depend) or magnitude of the corresponding class.
- Straightforward Comparability: Bar charts excel at facilitating comparisons between totally different classes. The visible illustration permits for fast identification of the most important and smallest values, in addition to relative variations between classes.
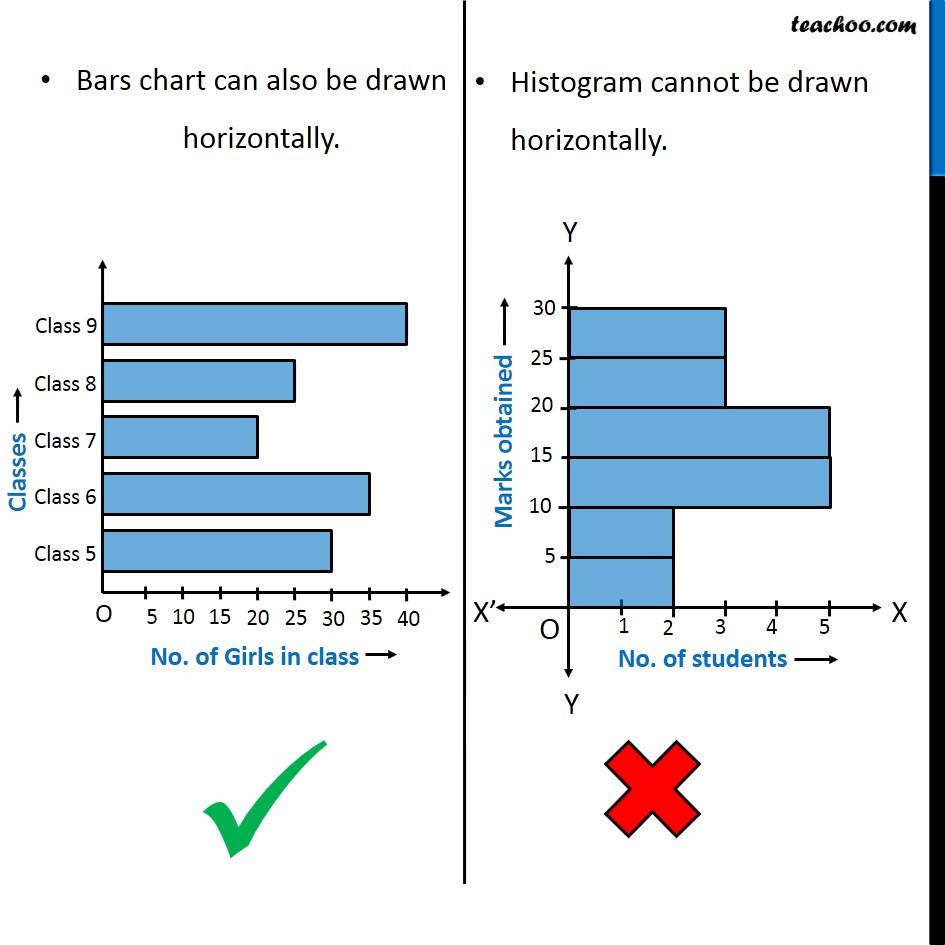
- Flexibility: Bar charts may be offered in numerous kinds, together with vertical (most typical) and horizontal orientations. They may also be grouped or stacked to show a number of variables inside the similar chart.
Varieties of Bar Charts:
- Easy Bar Chart: Shows the frequency or magnitude of a single categorical variable.
- Grouped Bar Chart: Compares the frequencies or magnitudes of a number of categorical variables throughout totally different classes.
- Stacked Bar Chart: Reveals the contribution of various sub-categories to the general worth of a essential class.
- 100% Stacked Bar Chart: A variation of the stacked bar chart the place every bar represents 100%, showcasing the proportion of every sub-category inside the principle class.
Examples of Bar Chart Functions:
- Gross sales efficiency of various product strains: Evaluating the gross sales figures for numerous merchandise over a selected interval.
- Buyer satisfaction throughout totally different demographics: Analyzing buyer suggestions categorized by age, gender, or location.
- Market share of competing manufacturers: Visualizing the market dominance of various manufacturers inside an business.
- Election outcomes: Presenting the vote counts for various candidates.
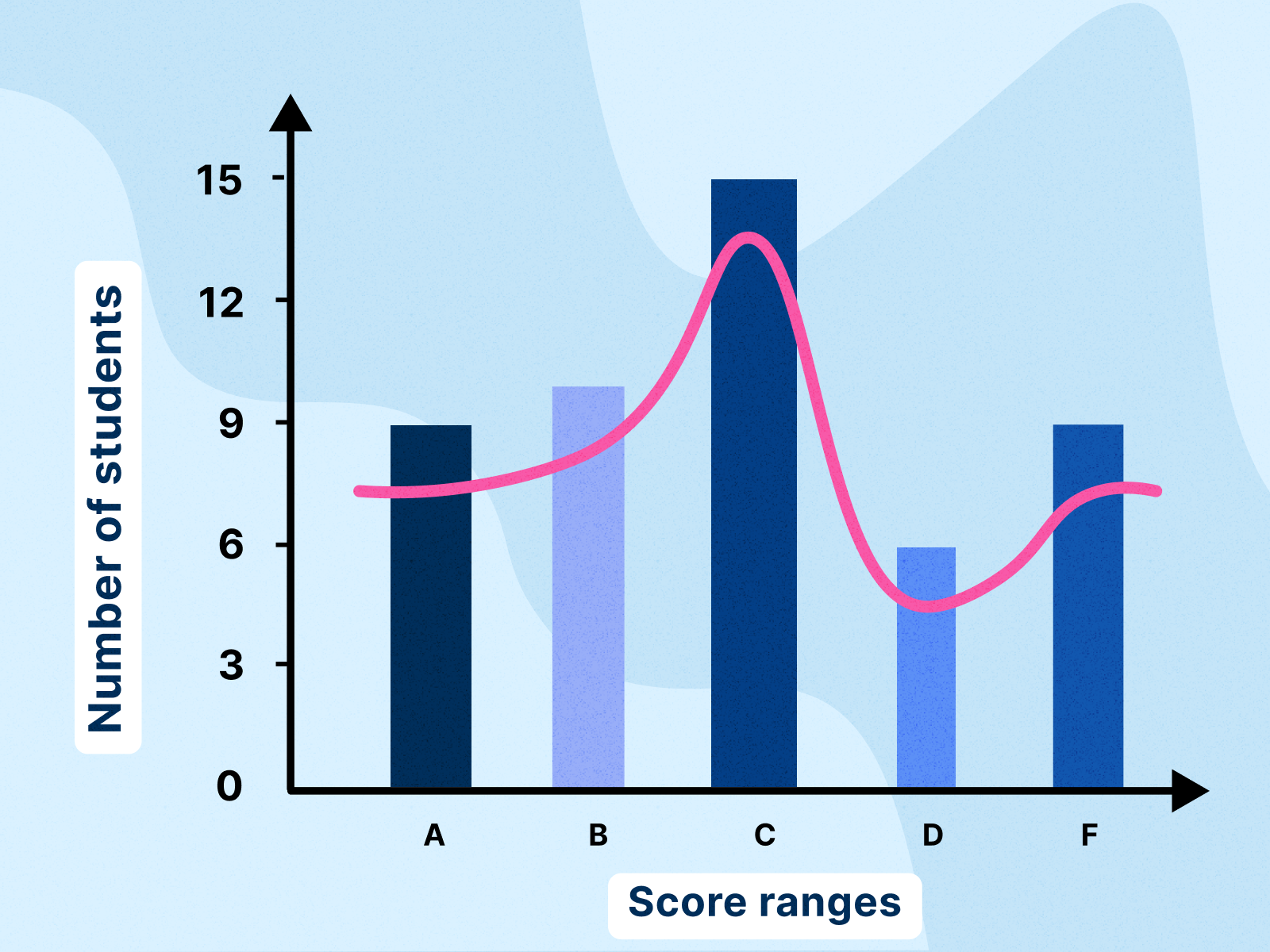
Understanding Histograms: Visualizing the Distribution of Numerical Information
Not like bar charts, histograms are used to visualise the distribution of numerical information. They show the frequency or relative frequency of knowledge factors falling inside particular intervals or bins. The information is steady, which means there is a steady circulation between values, not like the discrete classes in bar charts.
Key Options of Histograms:
- Numerical Information: Histograms are designed for visualizing numerical information, the place the impartial variable is quantitative.
- Steady Information: The information represented is steady, permitting for a variety of values inside every bin.
- Bins or Intervals: The x-axis is split into bins or intervals, every representing a variety of values.
- Frequency or Relative Frequency: The peak of every bar represents the frequency (depend) or relative frequency (proportion) of knowledge factors falling inside the corresponding bin.
- Information Distribution: Histograms reveal the form of the info distribution, indicating whether or not the info is often distributed, skewed, or has a number of peaks (modes).
- Bin Width: The selection of bin width considerably impacts the looks of the histogram. A narrower bin width offers extra element however might result in a much less clean illustration, whereas a wider bin width might obscure necessary options of the distribution.
Examples of Histogram Functions:
- Distribution of examination scores: Displaying the frequency of various rating ranges in a category.
- Evaluation of revenue ranges: Visualizing the distribution of revenue throughout a inhabitants.
- Distribution of heights or weights: Illustrating the frequency of various peak or weight ranges inside a pattern.
- High quality management in manufacturing: Monitoring the distribution of a product’s key traits to establish potential defects.
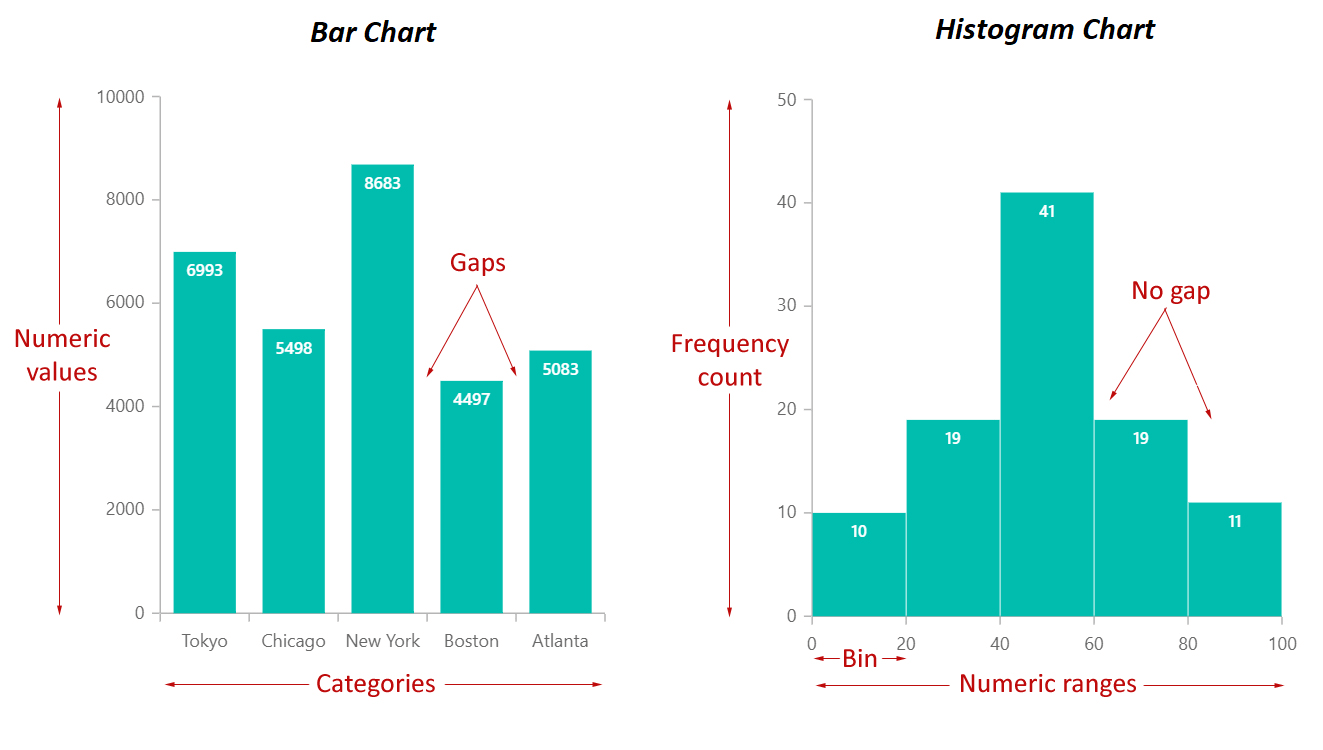
Key Variations Between Bar Charts and Histograms:
| Characteristic | Bar Chart | Histogram |
|---|---|---|
| Information Kind | Categorical | Numerical (steady) |
| X-axis | Discrete classes | Steady intervals (bins) |
| Bar Spacing | Gaps between bars | Bars are adjoining (no gaps) |
| Bar Top | Represents frequency or magnitude of class | Represents frequency or relative frequency of knowledge inside a bin |
| Goal | Examine classes | Present information distribution and establish patterns |
| Interpretation | Deal with particular person class comparisons | Deal with general information distribution and form |
Selecting Between Bar Charts and Histograms:
The selection between a bar chart and a histogram relies upon solely on the character of the info being visualized. If the info is categorical, a bar chart is the suitable alternative. If the info is numerical and steady, a histogram is critical. Utilizing the improper chart kind can result in misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions.
Limitations of Bar Charts and Histograms:
Whereas each bar charts and histograms are highly effective visualization instruments, they’ve limitations:
- Oversimplification: Each can oversimplify advanced datasets, probably hiding necessary nuances within the information.
- Deceptive Scales: Improper scaling of axes can distort the visible illustration and result in misinterpretations.
- Giant Datasets: For terribly giant datasets, each chart varieties might turn into cluttered and tough to interpret. In such circumstances, various visualization methods is likely to be more practical.
- Restricted Insights: Neither chart kind straight reveals statistical measures like imply, median, or customary deviation. These have to be calculated and reported individually.
Conclusion:
Bar charts and histograms are helpful instruments for information visualization, every serving a definite objective. Bar charts excel at evaluating categorical information, whereas histograms successfully illustrate the distribution of numerical information. Understanding the variations between these chart varieties is essential for choosing the suitable visualization methodology and precisely deciphering the info offered. Cautious consideration of knowledge kind, the specified insights, and potential limitations are important for efficient information communication. By understanding these nuances, information analysts and communicators can leverage the strengths of each bar charts and histograms to create compelling and informative visualizations that improve understanding and decision-making.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into distinction bar chart and histogram. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!