Mastering Bar Charts In Tableau: A Complete Information
Mastering Bar Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Mastering Bar Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Mastering Bar Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering Bar Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information
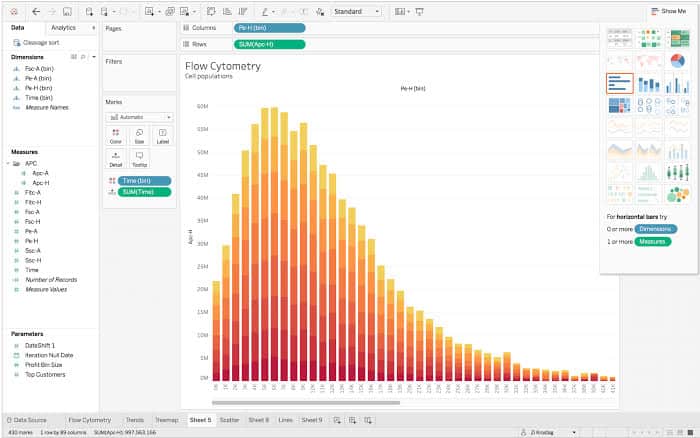
Bar charts, a cornerstone of knowledge visualization, are extremely versatile instruments for displaying categorical information and evaluating values throughout totally different classes. In Tableau, their flexibility is amplified by the software program’s highly effective options, permitting for the creation of insightful and visually interesting charts tailor-made to particular analytical wants. This text will delve into the intricacies of making, customizing, and successfully using bar charts inside the Tableau setting, protecting every thing from primary development to superior strategies.
I. Understanding the Fundamentals of Bar Charts in Tableau
At its core, a Tableau bar chart represents information utilizing rectangular bars, the place the size of every bar corresponds to the magnitude of a specific worth. The explicit information is displayed alongside one axis (often the horizontal axis), whereas the measured worth is represented alongside the opposite (often the vertical axis). This straightforward but efficient design makes it simple to match values throughout totally different classes at a look.
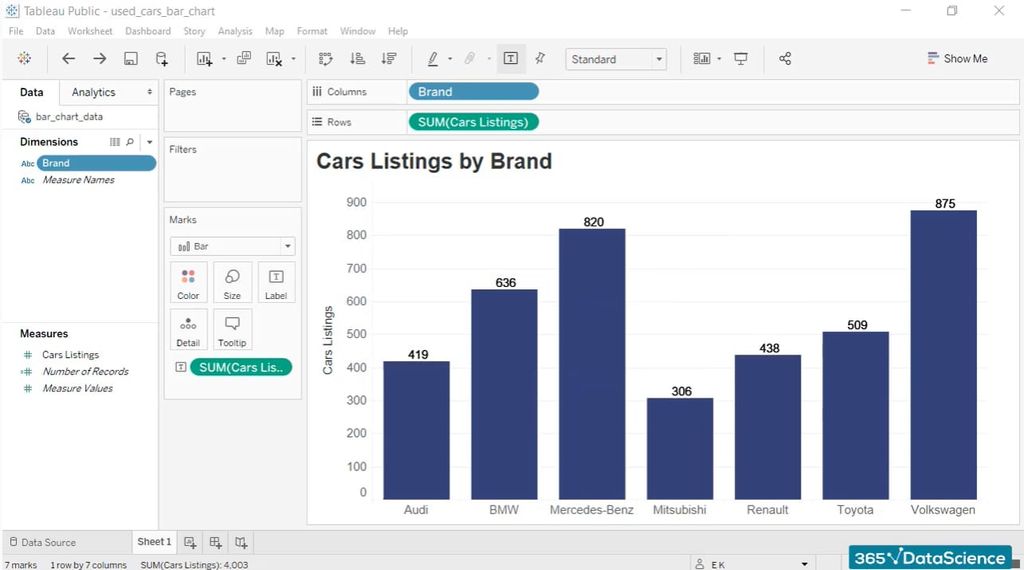
Making a primary bar chart in Tableau is easy. Assuming you’ve got already linked to your information supply, merely drag a categorical area (e.g., "Area," "Product Class," "12 months") to the Columns shelf and a numerical area (e.g., "Gross sales," "Revenue," "Models Bought") to the Rows shelf. Tableau routinely acknowledges the info sorts and constructs a bar chart, with every bar representing the aggregated worth of the numerical area for every class within the categorical area.
II. Past the Fundamentals: Customizing Your Bar Charts
Whereas a default bar chart offers a primary illustration of your information, Tableau’s energy lies in its customization choices. These choices can help you fine-tune the chart’s look and performance to boost its readability and communicative impression.
-
Aggregation: Tableau defaults to SUM for numerical fields, however you may simply change this to different aggregations like AVG (common), MIN (minimal), MAX (most), COUNT (depend of data), MEDIAN, and extra. The selection of aggregation is dependent upon the analytical query you are making an attempt to reply. For instance, you may use SUM for whole gross sales, AVG for common order worth, or COUNT for the variety of transactions.
-
Sorting: The order of bars on the chart can considerably impression its readability. Tableau permits you to kind the bars alphabetically, by the worth of the numerical area (ascending or descending), or by a customized sorting order outlined by one other area. Sorting by worth helps spotlight the very best and lowest performing classes.
-
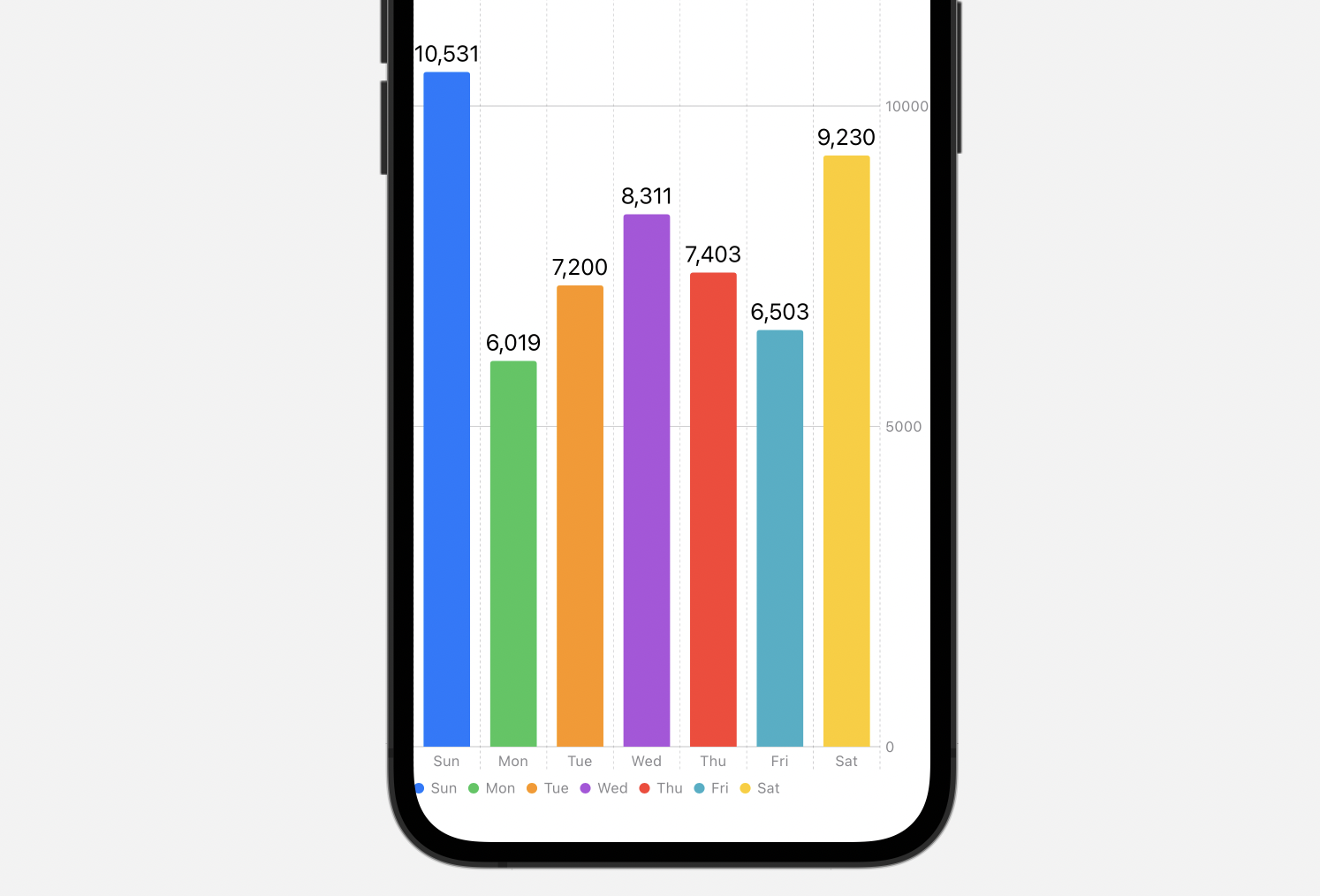
Shade: Shade coding can add one other layer of visible distinction to your bar chart. You’ll be able to coloration the bars based mostly on the specific area itself, or use a separate area to create color-coded teams inside the classes. That is significantly helpful for highlighting particular segments or developments inside your information. Cautious collection of coloration palettes is essential for accessibility and visible readability.
-
Tooltips: Tooltips present detailed details about every bar when the person hovers over it. You’ll be able to customise the tooltip to show a number of fields, offering a richer context for every information level. This enables customers to grasp not solely the worth but additionally different related attributes related to every class.
-
Labels: Including information labels straight to every bar can additional improve readability, particularly when coping with quite a few bars or carefully spaced values. You’ll be able to customise the label to show the worth, share of the full, or different calculated fields.
-
Axis Formatting: The axis labels and formatting are essential for presenting the info precisely and clearly. You’ll be able to regulate the axis ranges, intervals, titles, and formatting to make sure the chart is definitely understood. Think about using acceptable quantity codecs (e.g., foreign money, share) for enhanced readability.
III. Superior Strategies and Chart Enhancements
Tableau’s capabilities prolong far past primary customization. A number of superior strategies can elevate your bar charts to a better degree of analytical sophistication:
-
Twin Axis Charts: Combining two totally different measures on a single chart utilizing twin axes permits for direct comparability of associated metrics. For instance, you possibly can show gross sales and revenue on a twin axis bar chart to research the profitability of various product classes concurrently. Synchronization of the axes is essential to keep away from misinterpretation.
-
Stacked Bar Charts: Stacked bar charts show a number of measures inside every class, exhibiting the contribution of every measure to the full. That is helpful for visualizing proportions or compositions inside classes. For instance, you possibly can stack totally different product subcategories inside every predominant product class to see their relative contributions to total gross sales.
-
100% Stacked Bar Charts: Just like stacked bar charts, however the bars are normalized to 100%, exhibiting the share contribution of every measure inside every class. This emphasizes the proportion reasonably than absolutely the values.
-
Bar Chart with Reference Strains: Reference traces could be added to focus on key thresholds or targets. For instance, you may add a reference line to indicate the common gross sales throughout all classes, permitting for straightforward comparability of particular person class efficiency towards the common.
-
Filters and Parameters: Filters and parameters permit for interactive exploration of the info. Customers can filter the info based mostly on particular standards, dynamically altering the displayed bars and permitting for targeted evaluation. Parameters provide a extra managed strategy to work together with the chart, permitting customers to pick out particular values or ranges for evaluation.
-
Calculated Fields: Creating customized calculated fields permits for higher flexibility within the information displayed on the chart. You’ll be able to calculate ratios, percentages, or different derived metrics to create extra insightful visualizations.
-
Annotations: Including annotations to focus on particular information factors or developments can additional improve the storytelling side of your visualization. Annotations can be utilized to attract consideration to outliers, vital adjustments, or vital insights.
IV. Greatest Practices for Efficient Bar Chart Design
Creating efficient bar charts requires cautious consideration of a number of design ideas:
-
Readability and Simplicity: Keep away from cluttering the chart with pointless particulars. Give attention to conveying the important thing message clearly and concisely.
-
Applicable Scale and Axis Labels: Select an acceptable scale for the axes and make sure that the labels are clear and simple to grasp.
-
Constant Shade Palette: Use a constant coloration palette to make sure visible concord and keep away from complicated the viewers.
-
Knowledge Labels (when essential): Use information labels sparingly, solely after they improve readability and will not be redundant with the visible illustration of the bars.
-
Context and Narrative: Present adequate context for the chart, together with a transparent title, axis labels, and a short rationalization of the important thing findings. Body the chart inside a broader narrative to boost its impression.
V. Conclusion
Bar charts are a strong instrument for information visualization, and Tableau offers a complete set of options to create compelling and insightful bar charts. By understanding the basics, mastering customization choices, and using superior strategies, you may leverage the complete potential of Tableau to speak advanced information successfully and drive data-driven decision-making. Do not forget that the aim is not only to create a visually interesting chart, however to create a chart that clearly and precisely communicates your information’s story. By means of cautious planning, considerate design, and the efficient use of Tableau’s options, you may remodel uncooked information into compelling narratives that inform and encourage.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Mastering Bar Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!