Mastering English And Hindi Tenses: A Complete Chart And Examples
Mastering English and Hindi Tenses: A Complete Chart and Examples
Associated Articles: Mastering English and Hindi Tenses: A Complete Chart and Examples
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Mastering English and Hindi Tenses: A Complete Chart and Examples. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering English and Hindi Tenses: A Complete Chart and Examples

The mastery of tenses is essential for fluency and correct communication in each English and Hindi. Whereas the grammatical constructions differ considerably, understanding the core ideas of time – previous, current, and future – stays basic. This text offers an in depth comparability of English and Hindi tenses, providing a complete chart and quite a few examples to solidify your understanding.
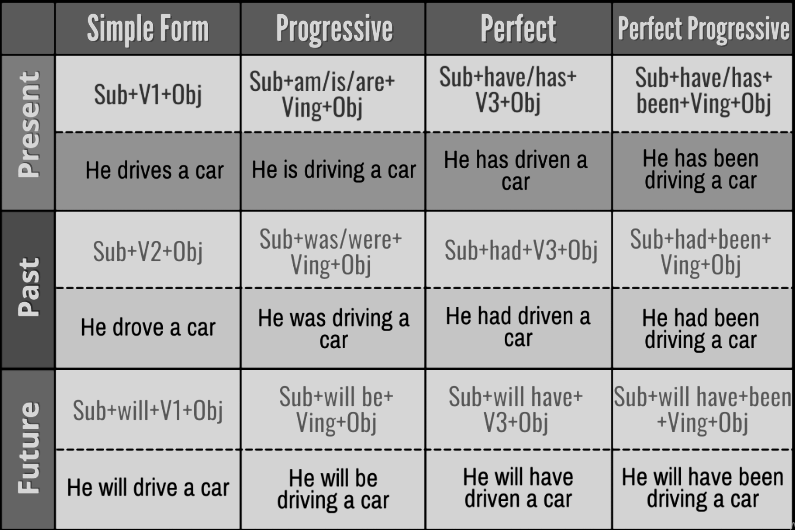
I. English Tenses: A Detailed Overview
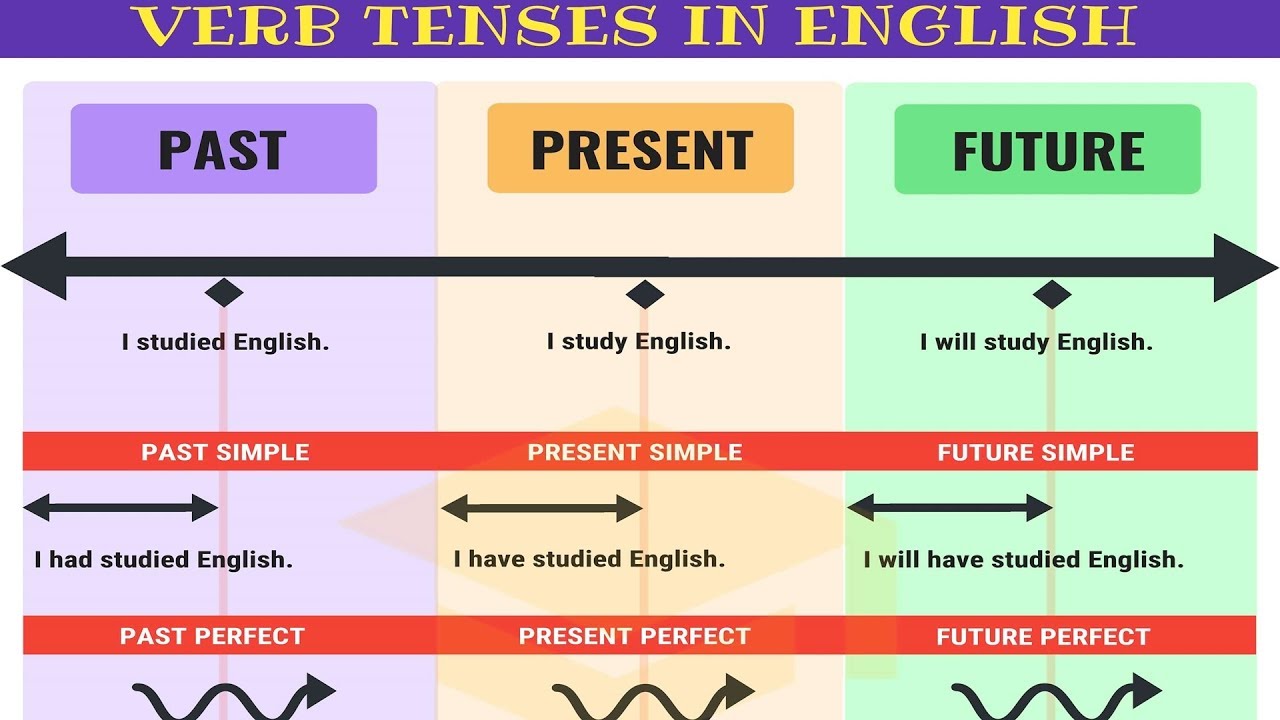
English tenses are shaped utilizing auxiliary verbs (serving to verbs) like be, have, and do, together with the primary verb’s inflection (modifications in type). We categorize English tenses primarily into three predominant teams: current, previous, and future, every additional subdivided into easy, steady (progressive), excellent, and ideal steady facets.
A. Current Tenses:
-
Easy Current: Expresses routine actions, basic truths, and everlasting states.
- Type: Base type of the verb (add -s/-es for third-person singular).
- Instance: She eats breakfast each morning. The solar rises within the east.
-
Current Steady (Progressive): Expresses actions occurring for the time being of talking, non permanent actions, or future plans.
- Type: Am/is/are + current participle (-ing type of the verb).
- Instance: He is watching tv. They are going to the get together tonight.
-
Current Good: Expresses actions accomplished at an unspecified time prior to now, or actions persevering with as much as the current.
- Type: Has/have + previous participle.
- Instance: I have completed my work. She has lived in London for 5 years.
-
Current Good Steady (Progressive): Emphasizes the period of an motion that began up to now and continues as much as the current.
- Type: Has/have + been + current participle.
- Instance: They have been taking part in soccer for 2 hours. We have been ready for the bus since 8 am.
B. Previous Tenses:
-
Easy Previous: Expresses accomplished actions up to now.
- Type: Previous tense type of the verb (usually including -ed, however irregular verbs have distinctive types).
- Instance: He walked to highschool. She ate a sandwich.
-
Previous Steady (Progressive): Expresses actions in progress at a selected time up to now.
- Type: Was/have been + current participle.
- Instance: They have been taking part in cricket when it began raining. I was learning if you referred to as.
-
Previous Good: Expresses an motion accomplished earlier than one other motion up to now.
- Type: Had + previous participle.
- Instance: I had eaten dinner earlier than he arrived. She had completed her homework by 8 pm.
-
Previous Good Steady (Progressive): Expresses an motion persevering with up to a degree up to now.
- Type: Had + been + current participle.
- Instance: They had been working on the venture for months earlier than it was lastly accomplished. He had been ready for hours earlier than the physician noticed him.
C. Future Tenses:
-
Easy Future: Expresses actions that can occur sooner or later.
- Type: Will/shall + base type of the verb. (Shall is much less widespread now, largely used with I/we in formal contexts expressing dedication or obligation).
- Instance: We will go to the seaside tomorrow. He will end his research subsequent 12 months.
-
Future Steady (Progressive): Expresses actions that might be in progress at a selected time sooner or later.
- Type: Will/shall + be + current participle.
- Instance: They might be taking part in tennis at 3 pm. She might be working late tonight.
-
Future Good: Expresses actions that might be accomplished earlier than a selected time sooner or later.
- Type: Will/shall + have + previous participle.
- Instance: I can have completed my task by Friday. They can have arrived by then.
-
Future Good Steady (Progressive): Expresses actions that can have been in progress as much as a selected time sooner or later.
- Type: Will/shall + have + been + current participle.
- Instance: We can have been dwelling right here for ten years subsequent month. He can have been learning for 5 years by the point he graduates.
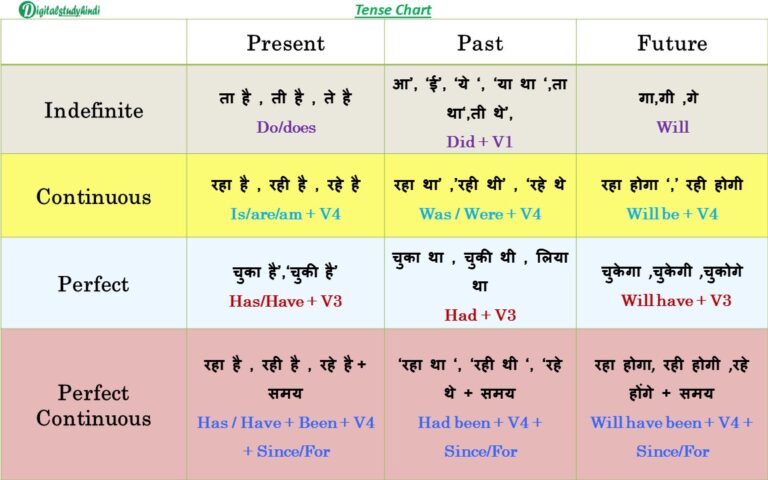
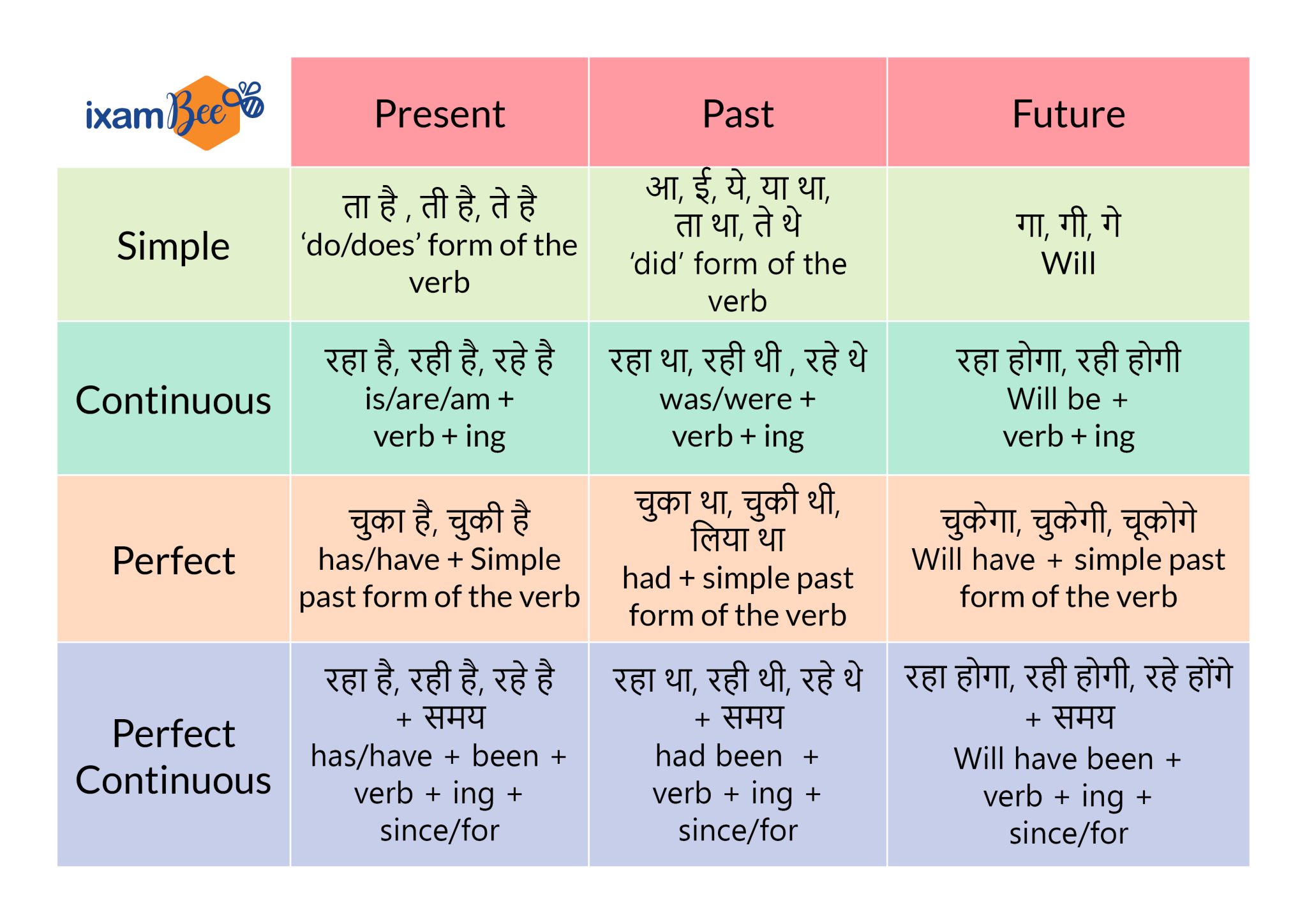
II. Hindi Tenses: A Comparative Evaluation
Hindi tense system, whereas conceptually related, differs considerably in its grammatical construction. It primarily depends on verb conjugations to point tense and facet. There is no direct equal of the continual facet in the identical method English makes use of "-ing" types. As an alternative, Hindi makes use of totally different verb types and generally auxiliary verbs to convey related meanings.
Hindi tenses are broadly categorized as:
-
Current Tense: Makes use of current tense verb conjugations. The precise type is determined by the topic pronoun and the verb. It could possibly categorical routine actions, ongoing actions, or states.
-
Instance: मैं खाता हूँ (Fundamental khāta hūn) – I eat (routine)
मैं खा रहा हूँ (Fundamental khā rahā hūn) – I’m consuming (ongoing)
-
Instance: मैं खाता हूँ (Fundamental khāta hūn) – I eat (routine)
-
Previous Tense: Makes use of previous tense verb conjugations. Once more, the particular type varies with the topic and verb. It could possibly categorical easy previous actions, previous steady actions (utilizing auxiliary verbs), or previous excellent actions (additionally utilizing auxiliary verbs).
-
Instance: मैंने खाया (Maine khāyā) – I ate (easy previous)
मैं खा रहा था (Fundamental khā rahā thā) – I used to be consuming (previous steady)
मैंने खा लिया था (Maine khā liyā thā) – I had eaten (previous excellent)
-
Instance: मैंने खाया (Maine khāyā) – I ate (easy previous)
-
Future Tense: Makes use of future tense verb conjugations or auxiliary verbs like "jāūngā" (will go) to precise future actions.
- Instance: मैं खाऊँगा (Fundamental khāūngā) – I’ll eat
III. Comparative Tense Chart: English vs. Hindi
| English Tense | English Instance | Hindi Tense | Hindi Instance (with Translation) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy Current | He eats. | वर्तमान काल (Current Tense) | वह खाता है (vah khātā hai) – He eats | Ordinary motion |
| Current Steady | He’s consuming. | वर्तमान काल (Current Tense) | वह खा रहा है (vah khā rahā hai) – He’s consuming | Ongoing motion |
| Current Good | He has eaten. | पूर्ण वर्तमान काल (Good Current Tense) | उसने खा लिया है (usne khā liyā hai) – He has eaten | Motion accomplished at an unspecified time prior to now |
| Current Good Steady | He has been consuming. | (No direct equal) | वह खाता आ रहा है (vah khātā ā rahā hai) – He has been consuming (approx.) | Requires a extra descriptive phrasing in Hindi. |
| Easy Previous | He ate. | भूतकाल (Previous Tense) | उसने खाया (usne khāyā) – He ate | Accomplished motion up to now |
| Previous Steady | He was consuming. | भूतकाल (Previous Tense) | वह खा रहा था (vah khā rahā thā) – He was consuming | Motion in progress at a selected time up to now |
| Previous Good | He had eaten. | भूतकाल (Previous Tense) | उसने खा लिया था (usne khā liyā thā) – He had eaten | Motion accomplished earlier than one other motion up to now |
| Previous Good Steady | He had been consuming. | (No direct equal) | वह बहुत देर से खा रहा था (vah bahut der se khā rahā thā) – He had been consuming for a very long time (approx.) | Requires extra context and descriptive phrasing. |
| Easy Future | He’ll eat. | भविष्य काल (Future Tense) | वह खाएगा (vah khāegā) – He’ll eat | Easy future motion |
| Future Steady | He might be consuming. | भविष्य काल (Future Tense) | वह खा रहा होगा (vah khā rahā hogā) – He might be consuming (approx.) | Makes use of a modal verb to precise the continual facet. |
| Future Good | He can have eaten. | भविष्य काल (Future Tense) | वह खा चुका होगा (vah khā chukā hogā) – He can have eaten (approx.) | Makes use of a perfective participle to point completion earlier than future time. |
| Future Good Steady | He can have been consuming. | (No direct equal) | वह काफी देर से खा रहा होगा (vah kāfī der se khā rahā hogā) – He can have been consuming for some time (approx.) | Requires a extra elaborate building in Hindi. |
Conclusion:
This complete information offers a foundational understanding of English and Hindi tenses. Whereas the constructions differ, the underlying ideas of time stay constant. By diligent examine and apply utilizing the examples supplied, you may considerably enhance your grammatical accuracy and fluency in each languages. Do not forget that nuances exist inside every tense, and mastering them requires steady studying and utility. Consulting grammar books and working towards with native audio system will additional improve your understanding and proficiency.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Mastering English and Hindi Tenses: A Complete Chart and Examples. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!