Mastering Pie Charts In Tableau: A Complete Information
Mastering Pie Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Mastering Pie Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Mastering Pie Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering Pie Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information

Pie charts, regardless of their sometimes-maligned status, stay a robust visualization device in knowledge evaluation, notably when successfully utilized. In Tableau, the creation and customization of pie charts are surprisingly simple, but the nuances of their design and interpretation can considerably impression the readability and effectiveness of your knowledge storytelling. This text will delve into the creation, optimization, and finest practices for utilizing pie charts throughout the Tableau atmosphere, equipping you with the information to leverage their strengths whereas mitigating their limitations.
Understanding the Strengths and Weaknesses of Pie Charts
Earlier than diving into the technical elements of Tableau’s pie chart performance, it is essential to grasp the inherent strengths and weaknesses of this visualization kind.
Strengths:
- Intuitive Illustration of Proportions: Pie charts excel at visually representing the proportion of various classes inside an entire. At a look, viewers can grasp the relative sizes of every section in comparison with the general dataset. This makes them splendid for showcasing market share, finances allocation, or demographic breakdowns.
- Straightforward to Perceive: Their round format is inherently acquainted and readily understood, even by people with restricted knowledge evaluation expertise. This simplicity makes them efficient for displays to numerous audiences.
- Fast Comparability of Classes: Direct comparability of particular person classes is comparatively simple. Bigger slices instantly stand out, highlighting essentially the most important parts.
Weaknesses:
- Issue in Evaluating Small Segments: Because the variety of classes will increase, or when classes signify small proportions, the chart turns into cluttered and tough to interpret. Nice distinctions between small slices change into almost inconceivable to discern.
- Restricted Variety of Classes: Pie charts are finest suited to datasets with a comparatively small variety of classes (typically lower than 6-7). Past this restrict, the chart turns into visually overwhelming and loses its effectiveness.
- Poor at Displaying Exact Values: Whereas pie charts successfully illustrate proportions, they aren’t splendid for conveying exact numerical values. Readers typically must confer with accompanying knowledge labels for correct figures.
- Troublesome to Evaluate Throughout A number of Datasets: Evaluating proportions throughout a number of pie charts may be difficult, notably if the general sizes of the datasets differ.
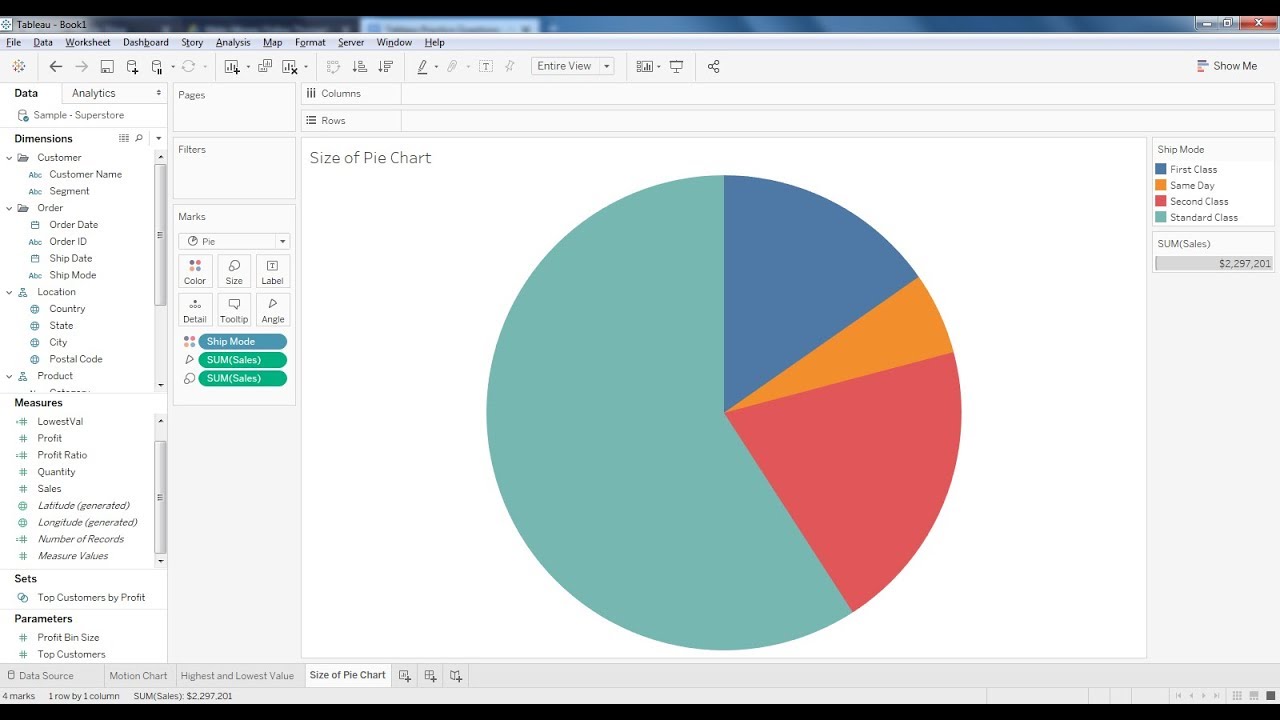
Creating Pie Charts in Tableau:
Making a pie chart in Tableau is a remarkably easy course of. The core steps contain dragging and dropping fields onto the suitable cabinets throughout the Tableau interface.
-
Connecting to your Knowledge: Start by connecting to your knowledge supply. This may very well be an Excel file, a database, or another knowledge supply appropriate with Tableau.
-
Dragging Fields to the View: As soon as linked, drag the sector representing the classes (e.g., "Product Class," "Area") to the "Angle" shelf on the Marks card. This determines which segments comprise the pie chart. Then, drag the sector representing the values (e.g., "Gross sales," "Variety of Clients") to the "Dimension" shelf. This dictates the dimensions of every section, reflecting its proportion inside the entire.
-
Formatting and Customization: Tableau gives intensive customization choices. You may regulate colours, add labels (displaying percentages or values), change the title, and add filters to refine the displayed knowledge. Experiment with totally different colour palettes to reinforce visible enchantment and knowledge readability. Think about using a colorblind-friendly palette for broader accessibility.
Optimizing Pie Charts in Tableau:
Whereas making a primary pie chart is simple, optimizing it for readability and impression requires cautious consideration:
-
Labeling: At all times embody knowledge labels. These labels ought to clearly point out the proportion or worth every slice represents. Keep away from overly cluttered labels; if vital, use a smaller font measurement or regulate label placement. Tableau means that you can select between share and worth labels, and even each.
-
Coloration Choice: Select colours which can be visually distinct and straightforward to distinguish. Keep away from utilizing too many colours, particularly when you have many classes. Think about using a constant colour scheme that aligns along with your general model or report design.
-
Sorting: Type the slices in a logical order (e.g., largest to smallest) to enhance readability. This helps viewers rapidly establish essentially the most important classes.
-
Filtering: Make the most of filters to permit customers to work together with the chart and give attention to particular subsets of the information. This may be notably useful when coping with quite a few classes.
-
Including Tooltips: Allow tooltips to supply extra detailed data when customers hover over a particular slice. This lets you show further knowledge factors with out cluttering the chart itself.
-
Contemplate Alternate options: In case your dataset comprises many classes or requires exact worth comparisons, take into account various visualizations like bar charts or treemaps, that are higher suited to these eventualities.
Superior Methods and Concerns:
-
Twin-Axis Pie Charts: Whereas not a regular function, you’ll be able to create the visible impact of a dual-axis pie chart through the use of two separate pie charts side-by-side or stacked, rigorously coordinating their sizes and scales. This may be helpful for evaluating proportions throughout totally different datasets.
-
Interactive Pie Charts: Tableau’s interactive options assist you to create dynamic pie charts that reply to person alternatives. Filters, parameters, and actions can be utilized to create partaking and informative visualizations.
-
Accessibility: Guarantee your pie charts are accessible to customers with visible impairments. Use adequate colour distinction, present various textual content descriptions, and think about using auditory cues.
-
Knowledge Density: Keep away from overloading the pie chart with an excessive amount of data. Preserve the variety of classes manageable and give attention to conveying crucial insights.
Troubleshooting Widespread Points:
-
Overlapping Labels: If labels overlap, regulate their place or font measurement. Think about using a unique label placement possibility inside Tableau’s formatting settings.
-
Inconsistent Colours: Guarantee your colour palette is constant and visually interesting. Tableau gives a variety of pre-defined colour palettes, or you’ll be able to create your personal customized palette.
-
Deceptive Proportions: Rigorously evaluation your knowledge to make sure the pie chart precisely represents the proportions. Errors in knowledge aggregation or calculation can result in deceptive visualizations.
Conclusion:
Pie charts, when used judiciously and successfully, could be a priceless asset in your knowledge visualization toolkit. Tableau offers the instruments to create visually interesting and informative pie charts, however their effectiveness hinges on considerate design and a transparent understanding of their strengths and limitations. By following the very best practices outlined on this article, you’ll be able to leverage Tableau’s capabilities to create compelling pie charts that successfully talk your knowledge insights. Bear in mind to at all times prioritize readability, accuracy, and accessibility in your visualizations to make sure your viewers can readily perceive and interpret the knowledge offered. Contemplate the context of your knowledge and your viewers when selecting between a pie chart and various visualization strategies. Finally, the purpose is to inform a compelling story along with your knowledge, and the proper chart alternative is essential to reaching that purpose.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into Mastering Pie Charts in Tableau: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!