NP Chart Instance Issues With Options: A Complete Information
NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: A Complete Information
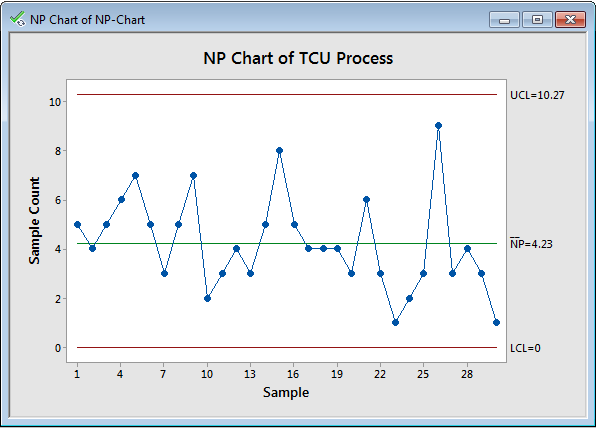
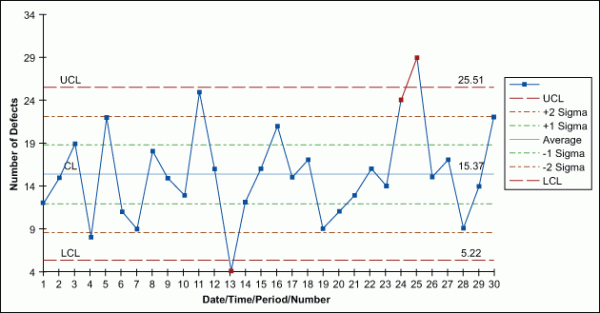
The np chart, a kind of management chart utilized in statistical course of management (SPC), is particularly designed to watch the variety of nonconforming items in a pattern of fixed dimension. Understanding its utility and interpretation is essential for sustaining constant product high quality. This text delves into numerous np chart instance issues, offering detailed options and explanations to solidify your understanding. We’ll cowl a variety of situations, highlighting widespread pitfalls and providing sensible recommendation for efficient implementation.
Understanding the np Chart
Earlier than diving into examples, let’s briefly overview the core parts of an np chart:
- n: The fixed pattern dimension. Every pattern should include the identical variety of items.
- p̂: The pattern proportion of nonconforming items (calculated because the variety of nonconforming items divided by the pattern dimension, n).
- np̂: The typical variety of nonconforming items in a pattern.
- UCL (Higher Management Restrict): The higher boundary past which the method is taken into account uncontrolled.
- LCL (Decrease Management Restrict): The decrease boundary under which the method is taken into account uncontrolled.
- Heart Line (CL): The typical variety of nonconforming items anticipated in a pattern.
The formulation for calculating the management limits are:
- Heart Line (CL) = np̄ the place p̄ is the common proportion of nonconforming items from the historic information.
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL) = np̄ + 3√(np̄(1-p̄))
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL) = np̄ – 3√(np̄(1-p̄))
Observe: If the calculated LCL is unfavorable, it is conventionally set to 0, as you can not have a unfavorable variety of nonconforming items.
Instance Issues and Options
Let’s discover a number of instance issues with detailed options:
Downside 1: Manufacturing Bolts
A producer produces bolts in batches of 100 (n=100). Knowledge from 20 earlier batches exhibits a complete of 200 faulty bolts. Assemble an np chart and analyze the information.
Resolution:
- Calculate p̄: Whole variety of faulty bolts (200) / Whole variety of bolts inspected (20 * 100 = 2000) = 0.1
- Calculate CL: np̄ = 100 * 0.1 = 10
- Calculate UCL: 10 + 3√(10 * (1-0.1)) ≈ 19.49
- Calculate LCL: 10 – 3√(10 * (1-0.1)) ≈ 0.51 (Since LCL is constructive, we preserve it.)
Now, let’s assume we acquire information from 5 new batches: 12, 8, 15, 11, 9 faulty bolts. Plot these factors on the np chart with CL=10, UCL=19.49, and LCL=0.51. If any level falls exterior the management limits, the method is taken into account uncontrolled. On this case, the purpose at 15 is above the UCL, indicating a possible downside requiring investigation.
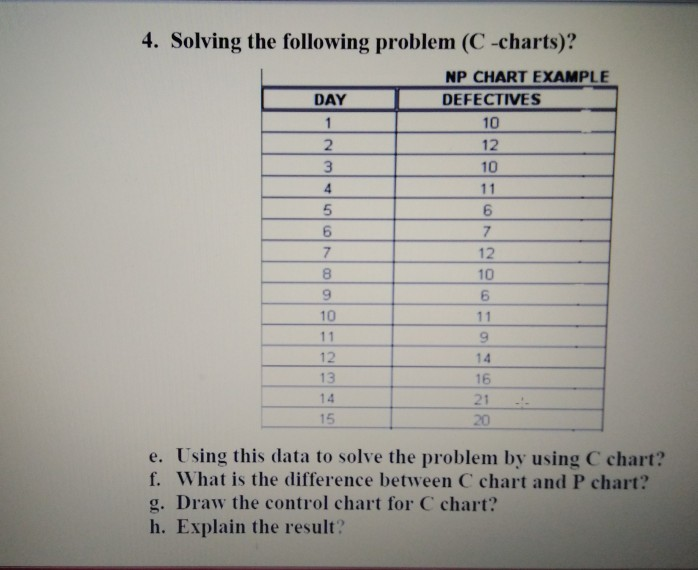
Downside 2: Software program Defects
A software program improvement group exams batches of fifty traces of code (n=50). Over 15 batches, they discover a complete of 75 defects. Assemble an np chart and analyze the information from 5 new batches: 2, 5, 3, 8, 4 defects.
Resolution:
- Calculate p̄: 75 / (15 * 50) = 0.1
- Calculate CL: np̄ = 50 * 0.1 = 5
- Calculate UCL: 5 + 3√(5 * 0.9) ≈ 10.35
- Calculate LCL: 5 – 3√(5 * 0.9) ≈ -0.35 (Set LCL to 0)
Plot the brand new batch information on the chart. The purpose representing 8 defects is above the UCL, suggesting a possible downside within the coding course of.
Downside 3: Contaminated Meals Merchandise
A meals processing plant inspects samples of 200 items (n=200) for contamination. Based mostly on historic information from 25 samples, 100 items have been discovered to be contaminated. Assemble an np chart and analyze the outcomes of 5 new samples: 3, 7, 5, 2, 8 contaminated items.
Resolution:
- Calculate p̄: 100 / (25 * 200) = 0.02
- Calculate CL: np̄ = 200 * 0.02 = 4
- Calculate UCL: 4 + 3√(4 * 0.98) ≈ 8.83
- Calculate LCL: 4 – 3√(4 * 0.98) ≈ -0.83 (Set LCL to 0)
Plotting the brand new information reveals that every one factors fall throughout the management limits. The method seems to be beneath management.
Downside 4: Dealing with Subgroups of Various Sizes
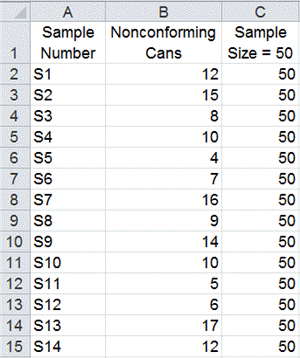
The np chart requires a continuing pattern dimension. If in case you have information with various pattern sizes, you can not immediately use an np chart. As an alternative, you need to think about using a p chart, which tracks the proportion of nonconforming items.
Downside 5: Decoding Out-of-Management Factors
When some extent falls exterior the management limits, it does not mechanically imply the method is inherently flawed. It indicators a necessity for investigation. Doable causes embrace:
- Particular Trigger Variation: A particular occasion or change within the course of (e.g., gear malfunction, operator error, uncooked materials variation).
- Sampling Error: Though unlikely with massive pattern sizes, random sampling fluctuations can often result in factors exterior the boundaries. Additional investigation is required to rule this out.
Investigating out-of-control factors includes analyzing the method for potential assignable causes. This usually contains reviewing manufacturing data, interviewing operators, and checking gear upkeep logs.
Conclusion
The np chart is a robust instrument for monitoring the variety of nonconforming items in a course of with a continuing pattern dimension. By understanding the underlying rules and making use of the formulation appropriately, you’ll be able to successfully use the np chart to determine potential issues and preserve constant product high quality. Bear in mind to all the time examine out-of-control factors to find out the basis trigger and implement corrective actions. This text has offered a strong basis for understanding and making use of np charts. Additional observe with numerous datasets will solidify your abilities in utilizing this useful statistical course of management method. Bear in mind to seek the advice of related statistical software program or assets for extra superior evaluation and interpretation. The examples offered right here provide a place to begin for mastering this important instrument in high quality management. At all times keep in mind to contemplate the context of your information and the particular necessities of your course of when deciphering the outcomes.

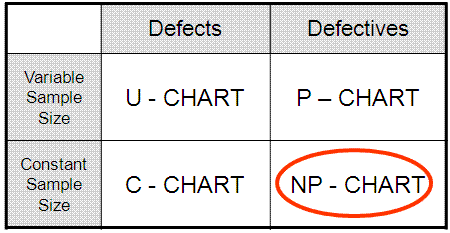

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: A Complete Information. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!