The Artwork And Science Of Chart Mixing: A Complete Information To Colour Concord And Visible Impression
The Artwork and Science of Chart Mixing: A Complete Information to Colour Concord and Visible Impression
Associated Articles: The Artwork and Science of Chart Mixing: A Complete Information to Colour Concord and Visible Impression
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to The Artwork and Science of Chart Mixing: A Complete Information to Colour Concord and Visible Impression. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Artwork and Science of Chart Mixing: A Complete Information to Colour Concord and Visible Impression

Charts and graphs are the unsung heroes of information visualization. They remodel advanced numerical info into simply digestible visuals, enabling fast understanding and knowledgeable decision-making. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of a chart hinges not solely on the info it presents but additionally on its aesthetic enchantment. And a big a part of that enchantment is set by the colour palette used. Choosing the proper colours is not arbitrary; it is a nuanced course of involving understanding colour principle, contemplating your viewers, and aligning your decisions with the message you wish to convey. This text delves into the artwork and science of chart mixing, exploring varied colour schemes, their psychological affect, and sensible suggestions for creating visually compelling and informative charts.
Understanding the Colour Wheel and Primary Colour Relationships:
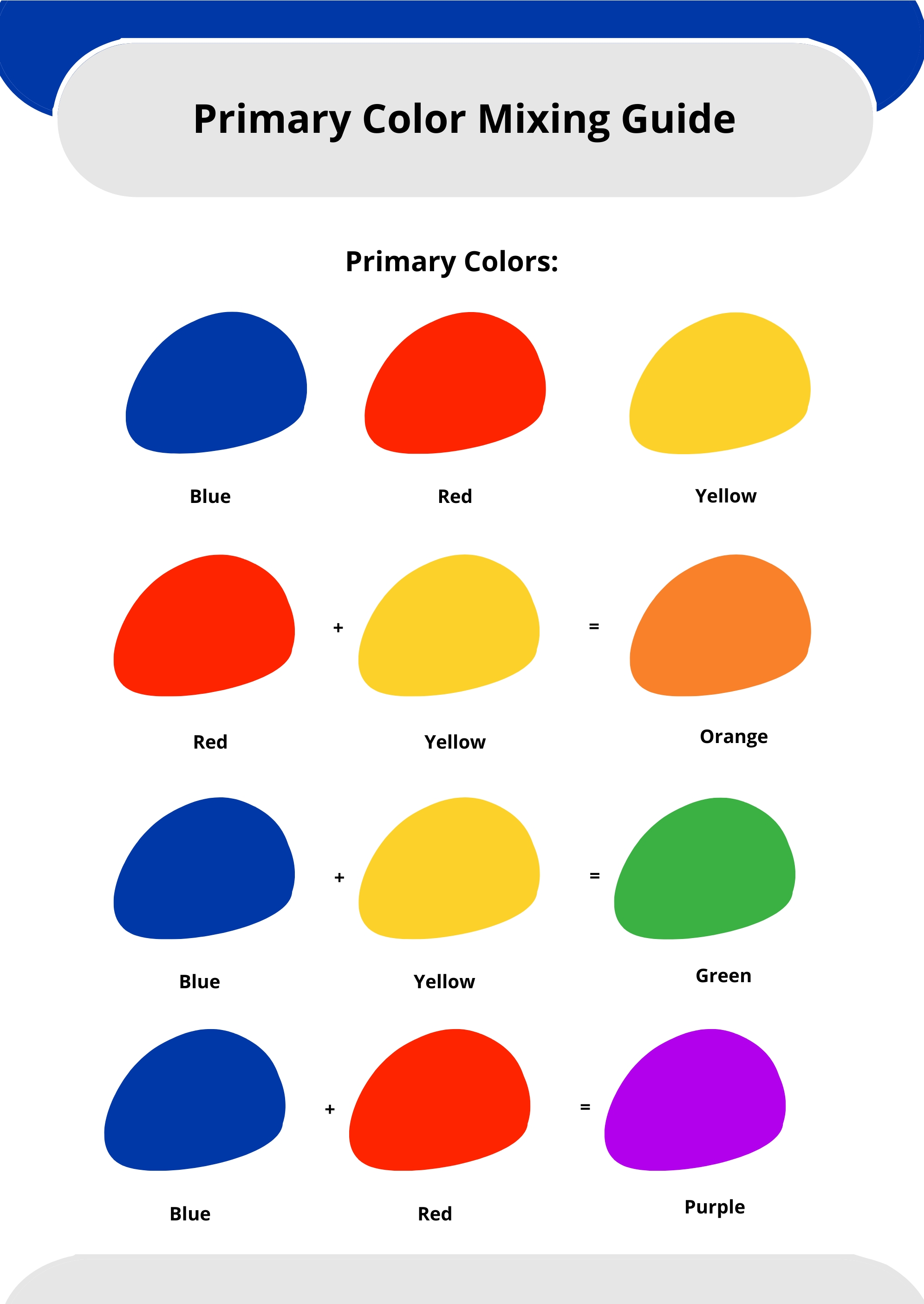
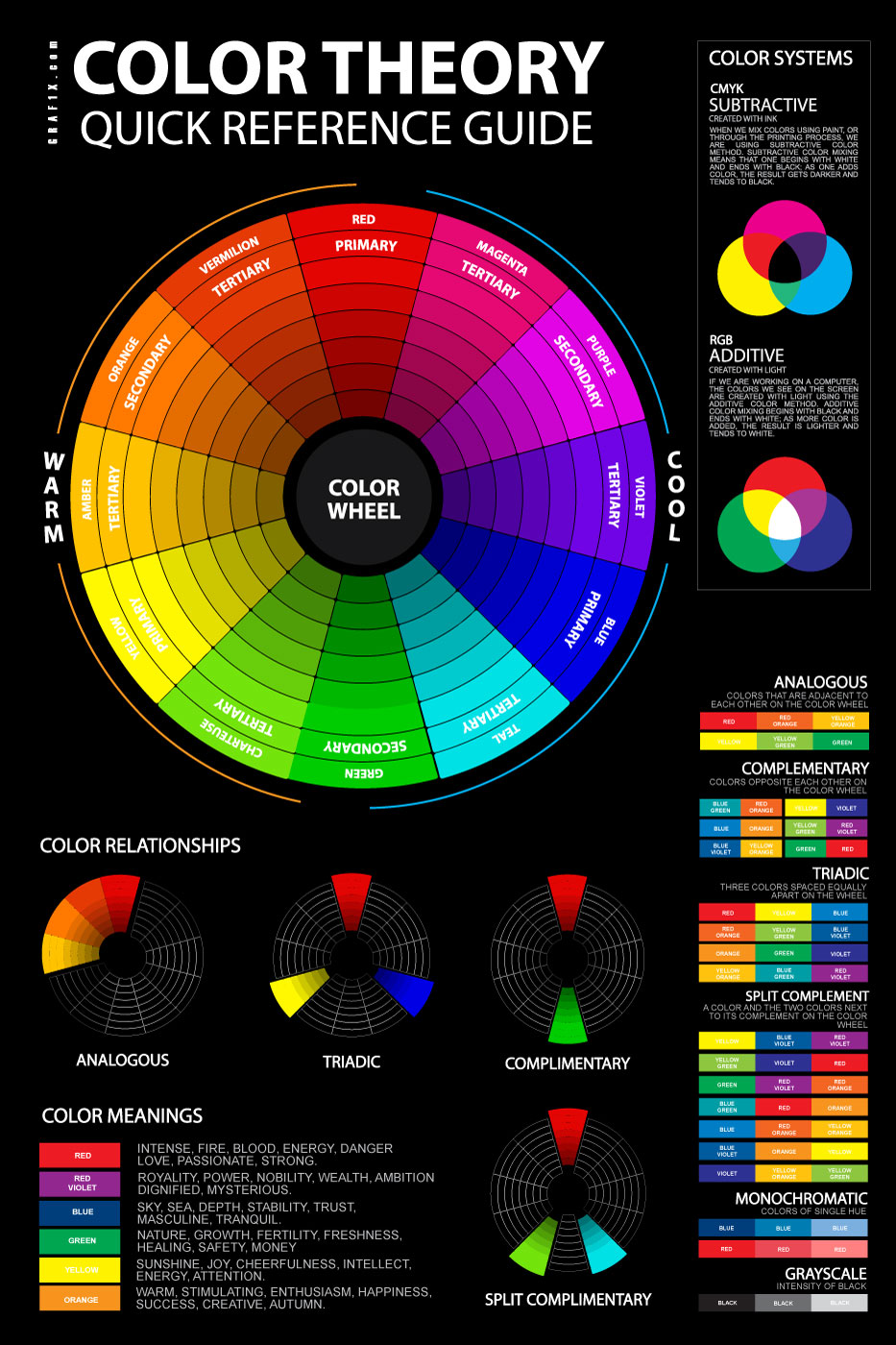
Earlier than diving into chart mixing, it is essential to know the basics of colour principle. The colour wheel, a round association of hues, is the cornerstone of this understanding. It illustrates the relationships between colours, categorized broadly into:
-
Main Colours: Crimson, Yellow, and Blue. These are the foundational colours; all different colours are derived from their mixtures.
-
Secondary Colours: Inexperienced (Yellow + Blue), Orange (Yellow + Crimson), and Violet (Crimson + Blue). Created by mixing two major colours.
-
Tertiary Colours: Crimson-Orange, Yellow-Orange, Yellow-Inexperienced, Blue-Inexperienced, Blue-Violet, and Crimson-Violet. These are shaped by mixing a major and a secondary colour.
Understanding these relationships permits us to create harmonious colour schemes based mostly on their proximity on the colour wheel:
-
Analogous Colours: These are colours that sit subsequent to one another on the colour wheel, creating a way of calm and concord. For instance, blue-green, inexperienced, and yellow-green. Analogous schemes are visually pleasing and infrequently used to create a soothing or pure really feel.
-
Complementary Colours: These are colours that lie immediately reverse one another on the colour wheel (e.g., purple and inexperienced, blue and orange). They provide excessive distinction and create a vibrant, energetic really feel. Nonetheless, utilizing them in equal proportions will be overwhelming; cautious balancing is important.
-
Triadic Colours: These are three colours evenly spaced across the colour wheel (e.g., purple, yellow, and blue; or orange, inexperienced, and violet). They provide a balanced and vibrant palette, offering an excellent degree of distinction with out being overly jarring.
-
Tetradic Colours: These contain 4 colours organized in two complementary pairs (e.g., red-orange, blue-green, blue-violet, and yellow-orange). They supply a wealthy and complicated palette, however require cautious consideration to keep away from visible chaos. Typically, one colour is used as a dominant hue, with the others performing as accents.
Colour Psychology and its Affect on Chart Design:
The selection of colours in a chart is not merely aesthetic; it has a big psychological affect on the viewer. Completely different colours evoke totally different feelings and associations:
-
Crimson: Typically related to urgency, vitality, pleasure, and typically anger or hazard. Use sparingly in charts, as it may be overwhelming. Efficient in highlighting crucial information factors or drawing consideration to damaging traits.
-
Orange: Conveys enthusiasm, creativity, and heat. It is a much less intense different to purple, appropriate for representing optimistic traits or highlighting vital info with out being overly aggressive.
-
Yellow: Related to happiness, optimism, and readability. Can be utilized to spotlight key information or characterize optimistic traits. Nonetheless, it may be troublesome to learn towards a white background, so think about using it strategically.
-
Inexperienced: Typically related to nature, development, and quietness. It is a sensible choice for representing optimistic traits or information associated to environmental points.
-
Blue: Represents belief, stability, and quietness. Incessantly utilized in company settings to convey professionalism and reliability. Might be calming however can even seem chilly if overused.
-
Violet/Purple: Typically related to luxurious, creativity, and royalty. Can add sophistication to a chart however must be used sparingly, as it may be overpowering.
-
Brown: Evokes emotions of earthiness, stability, and reliability. Appropriate for representing pure sources or historic information.
-
Grey: Represents neutrality, steadiness, and class. Typically used as a background colour or to create a way of calm. Might be efficient for highlighting information with out being distracting.
-
Black: Represents energy, sophistication, and ritual. Used sparingly as a background colour or to create distinction.
Sensible Ideas for Mixing Colours in Charts:
-
Take into account your viewers: The selection of colours must be acceptable for the meant viewers. A chart for kids would possibly use brighter, extra playful colours, whereas a chart for a enterprise presentation would possibly make the most of extra subdued {and professional} tones.
-
Preserve readability: Guarantee adequate distinction between the background and information factors. Keep away from utilizing colours which might be too related, as this may make the chart troublesome to interpret. Use colour blindness simulators to examine your chart’s accessibility.
-
Use colour strategically: Do not use too many colours. A restricted palette is mostly simpler. Use colour to spotlight key traits or information factors, quite than merely adorning the chart.
-
Select acceptable colour schemes: Choose a colour scheme that’s per the general message and tone of your chart. Analogous schemes create concord, whereas complementary schemes supply excessive distinction.
-
Use colour persistently: Preserve consistency in using colour all through the chart. The identical colour ought to all the time characterize the identical information sequence.
-
Leverage colour saturation and brightness: Adjusting the saturation and brightness of colours can considerably affect the visible affect of your chart. Brighter colours draw extra consideration, whereas muted colours create a extra refined impact.
-
Use data-driven colour decisions: As a substitute of arbitrarily assigning colours, think about using a colour scale that displays the magnitude of the info. For instance, a heatmap can use a gradient from blue (low values) to purple (excessive values).
-
Take a look at your chart: Earlier than finalizing your chart, take a look at it on totally different gadgets and display sizes to make sure that the colours stay legible and visually interesting.
Superior Methods and Instruments:
A number of superior methods can improve your chart mixing expertise:
-
Colour gradients: Utilizing clean transitions between colours can create visually interesting and informative charts, particularly for representing steady information.
-
Colour palettes from design instruments: Software program like Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and Figma supply a variety of pre-defined colour palettes, which could be a nice place to begin to your chart design.
-
Colour palette mills: Quite a few on-line instruments generate colour palettes based mostly on totally different colour schemes and enter photos, providing handy choices for locating appropriate mixtures.
-
Accessibility issues: Design charts with colour blindness in thoughts. Use colour at the side of different visible cues (e.g., patterns, shapes) to make sure that the data is accessible to everybody.
Conclusion:
Mastering chart mixing is a journey, not a vacation spot. By understanding colour principle, contemplating the psychological affect of colours, and making use of sensible suggestions, you’ll be able to create charts that aren’t solely informative but additionally visually compelling. Do not forget that the purpose is to speak your information successfully, and the suitable colour palette is an important ingredient in reaching this purpose. Experiment, iterate, and refine your method to turn into a proficient chart colour mixer, remodeling information into participating and impactful visuals.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into The Artwork and Science of Chart Mixing: A Complete Information to Colour Concord and Visible Impression. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!