The Artwork And Science Of Winemaking: A Complete Flowchart And Course of Breakdown
The Artwork and Science of Winemaking: A Complete Flowchart and Course of Breakdown
Associated Articles: The Artwork and Science of Winemaking: A Complete Flowchart and Course of Breakdown
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to The Artwork and Science of Winemaking: A Complete Flowchart and Course of Breakdown. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Artwork and Science of Winemaking: A Complete Flowchart and Course of Breakdown

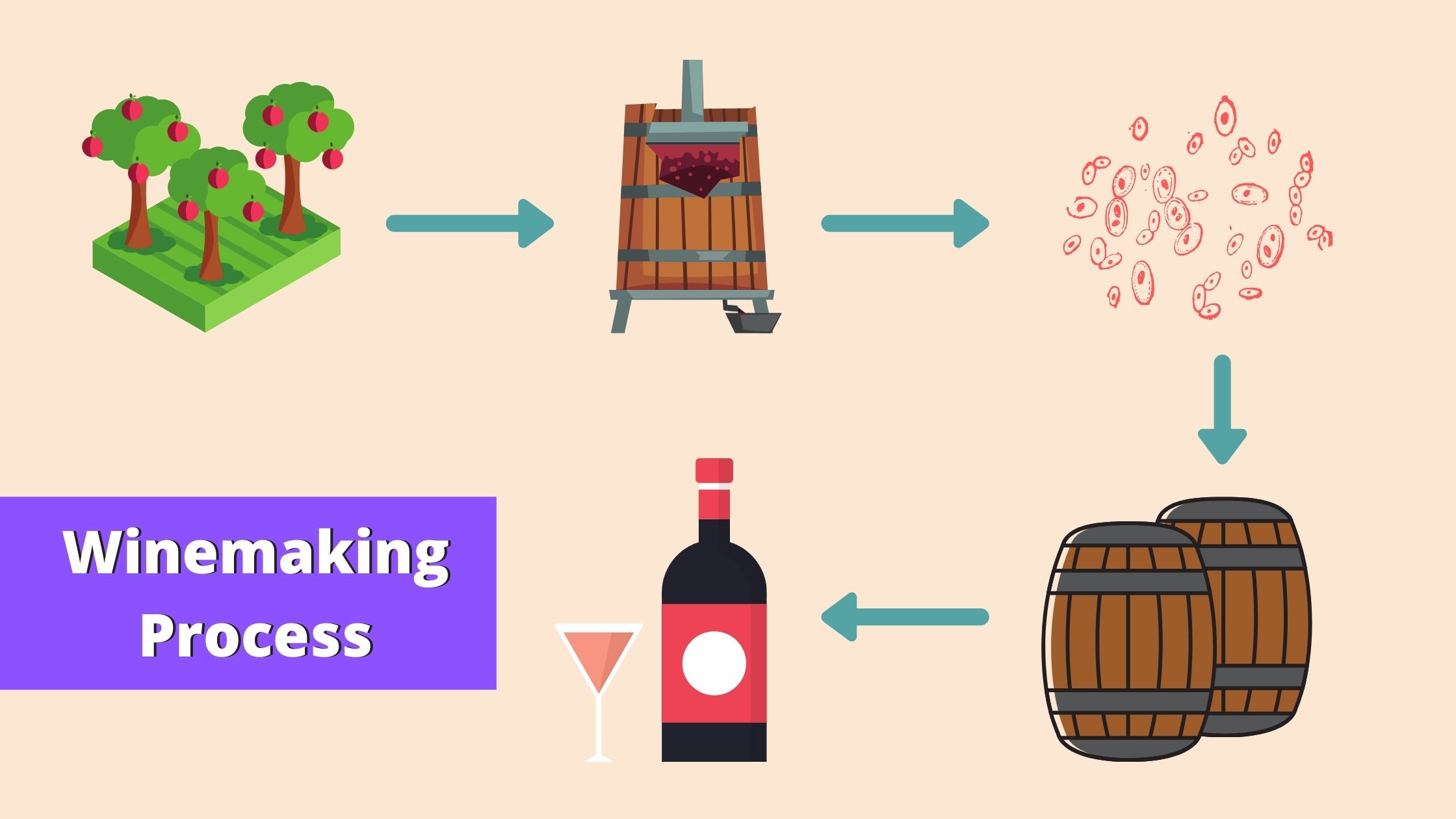
Winemaking, a follow spanning millennia, is a fragile dance between artwork and science. Reworking humble grapes into a posh and nuanced beverage requires precision, endurance, and a deep understanding of the viticultural and vinicultural processes. Whereas seemingly easy at first look – crush the grapes, ferment, age, bottle – the fact is much extra intricate. This text will delve into the excellent technique of winemaking, illustrated with an in depth flowchart, to light up the quite a few steps concerned in crafting a bottle of wine.
I. The Flowchart: A Visible Illustration of Winemaking
Earlier than diving into the detailed rationalization, let’s current a visible overview of the winemaking course of via a flowchart:
[Start] --> [Harvesting] --> [Sorting & Destemming] --> [Crushing] --> [Sulfiting (Optional)] --> [Maceration/Pre-Fermentation] --> [Fermentation (Alcoholic)] --> [Malolactic Fermentation (Optional)] --> [Pressing] --> [Racking] --> [Maturation/Aging] --> [Fining & Filtration (Optional)] --> [Bottling] --> [Aging (in Bottle)] --> [Release] --> [End]II. Detailed Breakdown of Every Stage:
A. Harvesting:
This important first step dictates the character of the ultimate wine. The timing of harvest, decided by elements like sugar ranges (brix), acidity, and phenolic ripeness, is paramount. Early harvesting yields wines with increased acidity and lighter our bodies, whereas later harvests lead to richer, extra concentrated wines with probably decrease acidity. Harvesting strategies differ from hand-picking for premium wines to mechanical harvesting for larger-scale manufacturing. The situation of the grapes upon arrival on the vineyard considerably impacts the following steps. Broken or rotten grapes should be fastidiously eliminated to forestall spoilage.
B. Sorting & Destemming:
Following harvest, the grapes endure sorting to take away any undesirable materials, together with leaves, stems, and broken or diseased berries. Destemming, the method of separating the berries from their stems, is non-obligatory and depends upon the specified wine model. Stems can contribute tannins and vegetal flavors, that are fascinating in some purple wines however undesirable in others. White wines typically don’t embody stems within the fermentation course of.
C. Crushing:
Crushing gently breaks the grape skins, releasing the juice and initiating the extraction of colour, tannins, and taste compounds. The diploma of crushing varies relying on the wine kind and desired model. Mild crushing is most well-liked for delicate white wines to attenuate the extraction of bitter compounds. Pink wines, alternatively, typically profit from a extra vigorous crush to maximise colour and tannin extraction.
D. Sulfiting (Non-obligatory):
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a standard additive used as a preservative and antioxidant. It inhibits the expansion of undesirable microorganisms and protects the wine from oxidation. The addition of SO2 is non-obligatory however extensively practiced, notably in larger-scale manufacturing, to make sure wine stability and longevity. Natural and biodynamic winemakers typically decrease or keep away from using SO2.
E. Maceration/Pre-Fermentation:
This important step, notably vital for purple wine manufacturing, includes the soaking of grape skins within the juice previous to fermentation. Throughout maceration, colour, tannins, and taste compounds are extracted from the skins, contributing to the complexity and character of the purple wine. The period of maceration varies relying on the specified model and grape selection, starting from just a few days to a number of weeks. White wine maceration is shorter and sometimes goals to extract fragrant compounds with out extreme bitterness.
F. Fermentation (Alcoholic):
Fermentation is the center of winemaking, the place yeast converts the grape sugars (glucose and fructose) into alcohol, carbon dioxide, and warmth. This course of might be spontaneous, counting on naturally occurring yeasts on the grape skins, or managed, utilizing commercially produced yeast strains to make sure constant outcomes. Pink wine fermentation sometimes happens with the skins, whereas white wine fermentation often takes place with out them. Temperature management is important throughout fermentation to handle the speed of fermentation and extract fascinating taste compounds.
G. Malolactic Fermentation (Non-obligatory):
Malolactic fermentation is a secondary fermentation the place lactic acid micro organism convert malic acid (a harsher acid) into lactic acid (a softer acid). This course of is widespread in purple wines and a few white wines, softening the acidity and including complexity. It’s typically fascinating in wines meant for growing old, because it contributes to stability and a smoother mouthfeel.
H. Urgent:
After fermentation, the wine is pressed to separate the liquid (wine) from the strong parts (skins, seeds, and pulp). The urgent method influences the ultimate wine’s character, with gentler urgent yielding lighter-bodied wines and extra forceful urgent extracting extra tannins and colour.
I. Racking:
Racking includes transferring the wine from one vessel to a different, abandoning sediment (lifeless yeast cells and different solids). This course of clarifies the wine and promotes its maturation. A number of rackings are sometimes carried out in the course of the growing old course of.
J. Maturation/Growing older:
Growing older permits the wine to develop its complexity and character. The period and technique of growing old differ tremendously relying on the wine model and grape selection. Growing older can happen in chrome steel tanks, oak barrels (contributing oaky flavors and tannins), or different vessels. Throughout growing old, chemical reactions happen, ensuing within the softening of tannins, the mixing of flavors, and the event of a extra complicated aroma profile.
Ok. Fining & Filtration (Non-obligatory):
Fining includes including substances like egg whites or bentonite clay to make clear the wine by eradicating undesirable particles. Filtration removes remaining yeast cells and different suspended solids. These processes are non-obligatory and depend upon the winemaker’s preferences and the specified readability of the ultimate product.
L. Bottling:
As soon as the wine is deemed prepared, it’s bottled beneath sterile situations to forestall spoilage. Bottling is an important step that protects the wine from oxidation and microbial contamination.
M. Growing older (in Bottle):
After bottling, many wines proceed to age and develop additional complexity. The period of bottle growing old depends upon the wine model and the winemaker’s intentions.
N. Launch:
Lastly, the wine is launched to the market, prepared for consumption and delight.
III. Conclusion:
The journey from grape to glass is a posh and multifaceted course of, requiring a mix of scientific data, creative sensibility, and meticulous consideration to element. This text, coupled with the offered flowchart, gives a complete overview of the winemaking course of. Understanding these levels permits for a deeper appreciation of the hassle and talent concerned in producing a bottle of wine, highlighting the artistry and science that converge to create this beloved beverage. Every step presents alternatives for stylistic decisions, underscoring the winemaker’s function in shaping the ultimate product and reflecting their distinctive imaginative and prescient and terroir.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into The Artwork and Science of Winemaking: A Complete Flowchart and Course of Breakdown. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!