The P-T Chart And Its Utility In Refrigeration Cycles
The P-T Chart and its Utility in Refrigeration Cycles
Associated Articles: The P-T Chart and its Utility in Refrigeration Cycles
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to The P-T Chart and its Utility in Refrigeration Cycles. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The P-T Chart and its Utility in Refrigeration Cycles

The refrigeration cycle, a cornerstone of contemporary consolation and meals preservation, depends on manipulating the thermodynamic properties of a refrigerant to realize cooling. Visualizing and understanding these properties is essential for designing, optimizing, and troubleshooting refrigeration programs. One highly effective device for this goal is the pressure-temperature (P-T) chart, a graphical illustration of the refrigerant’s section equilibrium curve. This text delves into the applying of the P-T chart in analyzing the refrigeration cycle, specializing in its advantages, interpretation, and sensible implications.
Understanding the P-T Chart:
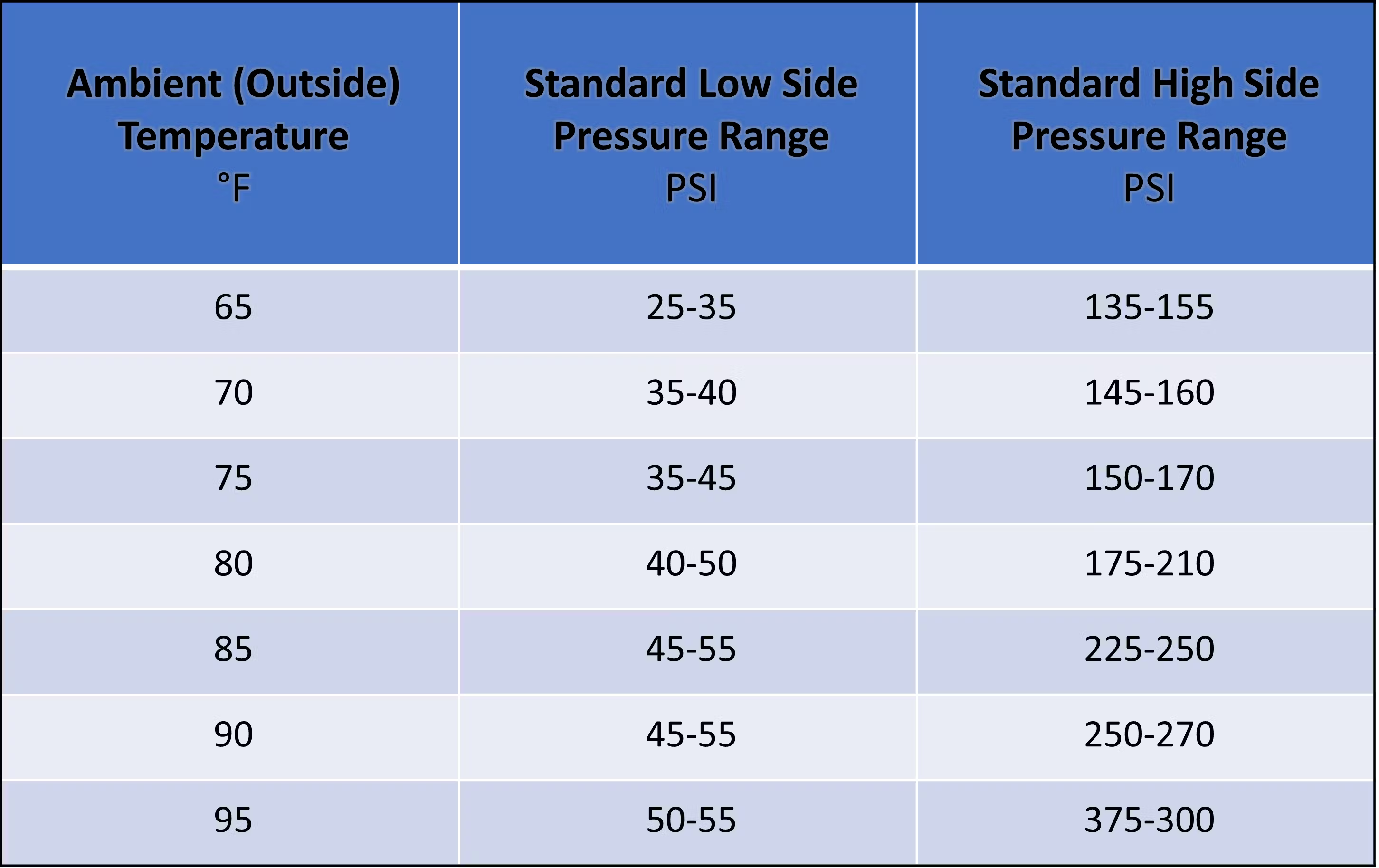
A P-T chart for a selected refrigerant shows the connection between its strain and temperature beneath numerous situations. The important thing options are:
-
Saturation Curve: This curve represents the boundary between the liquid and vapor phases. Factors on this curve point out a saturated combination of liquid and vapor. The curve is split into two components: the saturated liquid line and the saturated vapor line.
-
Saturated Liquid Line: Factors alongside this line signify the state the place the refrigerant is solely liquid and saturated, that means any additional warmth removing would trigger it to solidify.
-
Saturated Vapor Line: Factors alongside this line signify the state the place the refrigerant is solely vapor and saturated, that means any additional warmth addition would trigger it to change into superheated.
-
Superheated Vapor Area: The area above the saturated vapor line represents the superheated vapor section. On this area, the refrigerant is solely vapor and its temperature can enhance and not using a change in strain.
-
Subcooled Liquid Area: The area under the saturated liquid line represents the subcooled liquid section. Right here, the refrigerant is solely liquid and its temperature can lower and not using a change in strain.
-
Important Level: This level represents the best temperature and strain at which the liquid and vapor phases can coexist. Past this level, the excellence between liquid and vapor disappears.
-
Isobars and Isotherms: Strains of fixed strain (isobars) and fixed temperature (isotherms) may be superimposed on the chart, offering further details about the refrigerant’s state.
Making use of the P-T Chart to the Refrigeration Cycle:
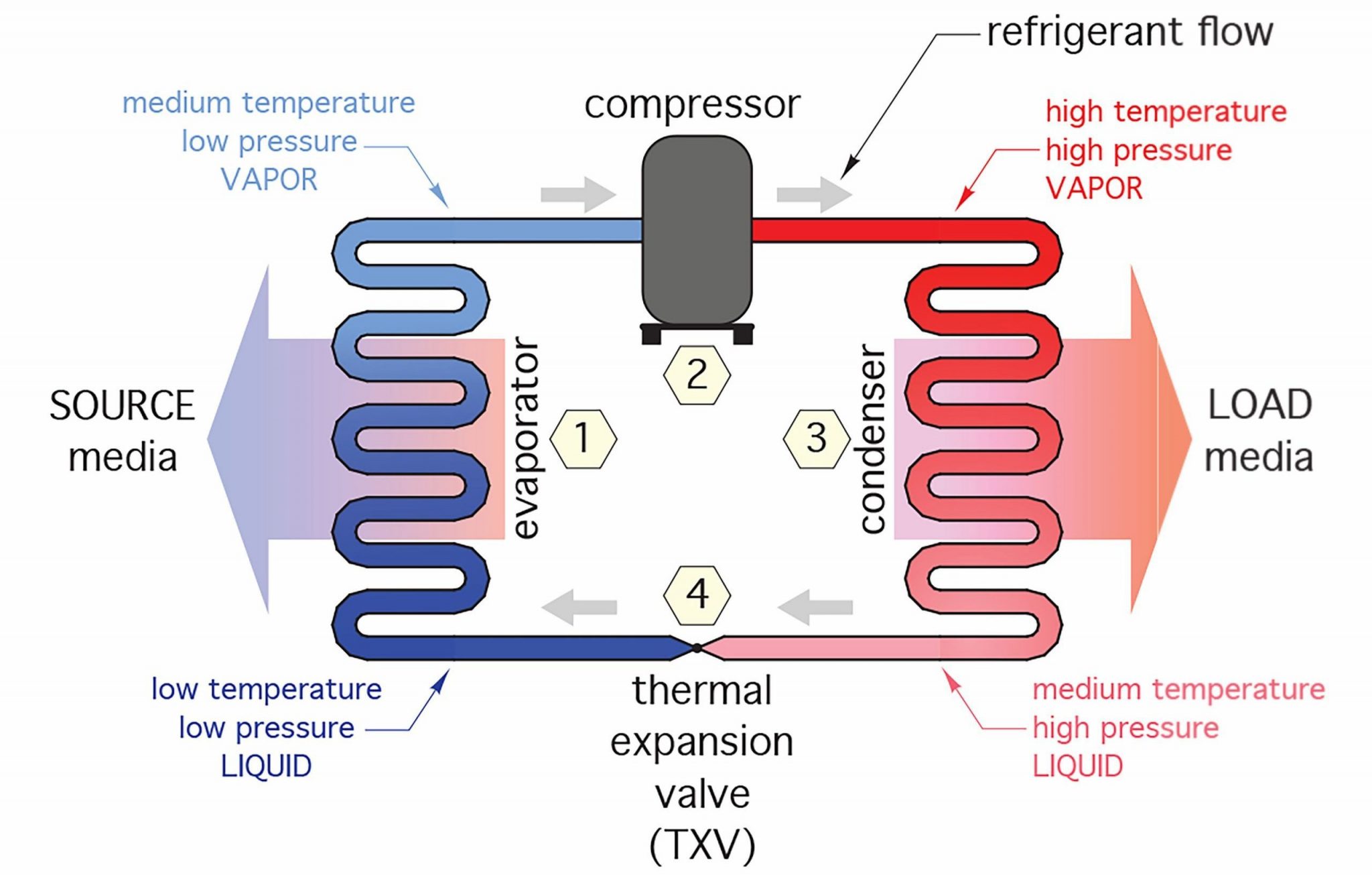
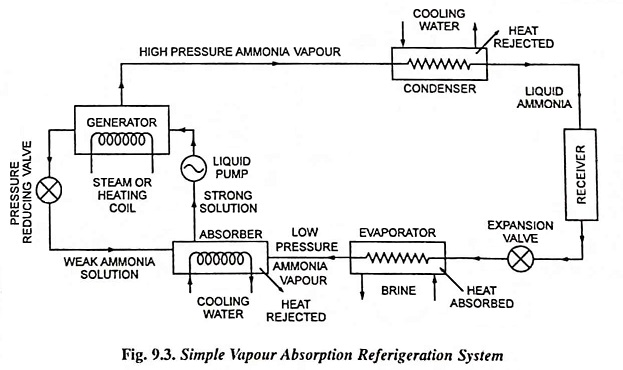
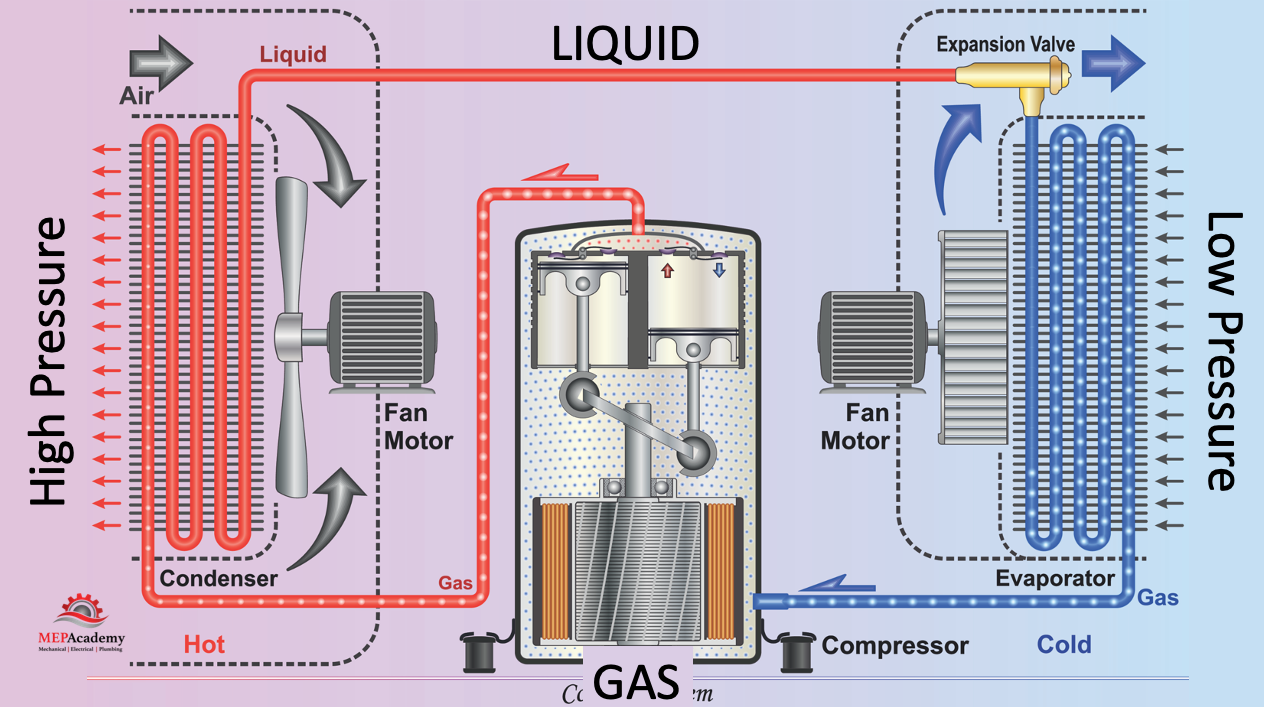
The everyday vapor-compression refrigeration cycle consists of 4 important elements: compressor, condenser, enlargement valve, and evaporator. The P-T chart permits for a transparent visualization of the refrigerant’s state adjustments all through this cycle:
-
Compression (1-2): The refrigerant enters the compressor as a low-pressure, low-temperature saturated vapor (level 1). The compressor will increase the strain and temperature considerably, leading to a superheated vapor at level 2. On the P-T chart, that is represented by a near-vertical line, reflecting the numerous strain enhance with a corresponding temperature rise.
-
Condensation (2-3): The superheated vapor enters the condenser, the place it rejects warmth to the environment. This causes the refrigerant to condense, transitioning from a superheated vapor to a saturated liquid (level 3). On the P-T chart, that is proven as a near-horizontal line at fixed strain, indicating a lower in temperature because the refrigerant releases warmth.
-
Growth (3-4): The saturated liquid passes by the enlargement valve, present process an isenthalpic (fixed enthalpy) course of. This course of reduces the strain and temperature considerably, leading to a combination of liquid and vapor (level 4). On the P-T chart, that is represented by a near-vertical line, demonstrating the sudden strain drop. The precise location of level 4 will depend on the diploma of throttling.
-
Evaporation (4-1): The low-pressure, low-temperature combination of liquid and vapor enters the evaporator, the place it absorbs warmth from the refrigerated house. This causes the refrigerant to evaporate, reworking fully right into a low-pressure, low-temperature saturated vapor (level 1). On the P-T chart, that is proven as a near-horizontal line at fixed strain, indicating a rise in temperature because the refrigerant absorbs warmth. The cycle then repeats.
Advantages of Utilizing the P-T Chart:
-
Visible Illustration: The P-T chart provides a transparent visible illustration of the refrigerant’s state adjustments all through the cycle, making it simpler to grasp the method.
-
Simplified Evaluation: It simplifies the evaluation of the refrigeration cycle, permitting for fast identification of working situations and potential issues.
-
Troubleshooting: It aids in troubleshooting by visually figuring out deviations from the perfect cycle. As an illustration, a big distinction between the precise working factors and the theoretical factors can point out inefficiencies or malfunctions.
-
Design and Optimization: The chart is invaluable in designing and optimizing refrigeration programs. Engineers can use it to pick out acceptable refrigerants and elements primarily based on desired working situations.
-
Predictive Capabilities: By analyzing the chart, engineers can predict the efficiency of the system beneath completely different working situations and make vital changes.
Limitations of the P-T Chart:
Whereas the P-T chart is a worthwhile device, it has some limitations:
-
Simplified Mannequin: It presents a simplified mannequin of the refrigeration cycle, neglecting components like strain drops in pipes and warmth losses in elements.
-
Particular to Refrigerant: Every refrigerant has its distinctive P-T chart, limiting the direct comparability between completely different refrigerants.
-
Restricted Info: It primarily exhibits strain and temperature relationships; different essential thermodynamic properties like enthalpy and entropy usually are not instantly represented. These typically require using property tables or software program along side the P-T chart.
-
Accuracy Is dependent upon Information: The accuracy of the chart will depend on the accuracy of the experimental knowledge used to generate it.
Sensible Purposes and Issues:
The P-T chart finds widespread functions in numerous refrigeration programs, together with:
-
Home Fridges: Understanding the cycle by the P-T chart helps in optimizing the efficiency and vitality effectivity of family fridges.
-
Industrial Refrigeration: Massive-scale industrial refrigeration programs, akin to these utilized in meals processing and chilly storage, rely closely on P-T charts for design, operation, and upkeep.
-
Air Conditioning Techniques: Comparable rules apply to air con programs, the place understanding the refrigerant’s state adjustments is essential for efficient cooling.
-
Warmth Pumps: Warmth pumps make the most of a reversed refrigeration cycle, and the P-T chart is crucial for analyzing their efficiency.
Conclusion:
The P-T chart serves as a basic device for understanding and analyzing refrigeration cycles. Its visible illustration of the refrigerant’s state adjustments simplifies the complicated thermodynamic processes concerned. Whereas it possesses limitations, its advantages in design, optimization, troubleshooting, and efficiency prediction are plain. Coupled with different thermodynamic instruments and knowledge, the P-T chart stays an indispensable useful resource for engineers and technicians working with refrigeration and air con programs. Its continued use ensures environment friendly and efficient cooling options throughout numerous functions. Future developments in refrigerant expertise and computational instruments will doubtless additional improve the utility and precision of P-T charts in refrigeration system evaluation and design.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into The P-T Chart and its Utility in Refrigeration Cycles. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!