The Energy Of The Vertical: Charting Information For Readability And Perception
The Energy of the Vertical: Charting Information for Readability and Perception
Associated Articles: The Energy of the Vertical: Charting Information for Readability and Perception
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to The Energy of the Vertical: Charting Information for Readability and Perception. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Energy of the Vertical: Charting Information for Readability and Perception

Charts are ubiquitous. From the every day information to complicated scientific publications, charts current information in a visually digestible format, reworking uncooked numbers into compelling narratives. Whereas numerous chart sorts exist, the vertical chart, encompassing bar charts, column charts, and variations thereof, stays a cornerstone of information visualization, providing a strong and versatile instrument for understanding and speaking info. This text delves into the intricacies of the vertical chart, exploring its strengths, limitations, and various functions throughout numerous fields.
Understanding the Vertical Format: A Basis of Readability
The elemental energy of the vertical chart lies in its intuitive design. People are naturally inclined to understand verticality as representing magnitude or amount. Taller bars or columns immediately convey a bigger worth in comparison with shorter ones. This inherent visible hierarchy simplifies the method of evaluating information factors, permitting for speedy comprehension of relative sizes and traits. Not like horizontal charts, which might typically be much less intuitive for representing magnitude, the vertical orientation aligns naturally with our spatial reasoning, making information interpretation extra environment friendly and fewer susceptible to misinterpretation.
Key Kinds of Vertical Charts:
The umbrella time period "vertical chart" encompasses a number of distinct sorts, every suited to particular information illustration wants:
-
Bar Charts: These are arguably the most typical sort of vertical chart. They use rectangular bars of various heights to characterize information values, sometimes categorical information alongside the horizontal axis (e.g., months, product classes) and numerical information alongside the vertical axis (e.g., gross sales figures, inhabitants counts). Bar charts excel at exhibiting comparisons between totally different classes, making it simple to determine the best and lowest values and spot important variations.
-
Column Charts: Primarily the rotated model of bar charts, column charts show information with columns extending vertically. They serve the identical objective as bar charts, evaluating totally different classes, however their orientation might be preferable in sure contexts, significantly when coping with longer class labels that may muddle a horizontal axis in a bar chart.
-
Stacked Bar/Column Charts: These charts lengthen the essential bar/column chart by stacking segments representing totally different sub-categories inside every fundamental class. This enables for visualizing the composition of every class, exhibiting each the general worth and the contribution of particular person parts. For instance, a stacked bar chart might present the gross sales breakdown of a product throughout totally different areas, with every area’s contribution stacked on prime of one another.
-
Clustered Bar/Column Charts: As a substitute of stacking, clustered charts place bars or columns representing sub-categories side-by-side for every fundamental class. This method facilitates direct comparability of sub-categories throughout totally different fundamental classes. For instance, a clustered column chart might examine gross sales of various merchandise throughout totally different months.
-
100% Stacked Bar/Column Charts: A variation of stacked charts, these normalize the info to 100%, representing every section as a share of the whole for every class. This emphasizes the proportion of every sub-category inside the entire, relatively than absolutely the values.
Functions Throughout Disciplines:
The flexibility of vertical charts makes them indispensable throughout a variety of fields:
-
Enterprise and Finance: Monitoring gross sales figures, market share, earnings, bills, and funding returns. Vertical charts are essential for presenting monetary information clearly to stakeholders, enabling knowledgeable decision-making.
-
Science and Analysis: Presenting experimental outcomes, statistical analyses, and scientific findings. Vertical charts facilitate comparisons between remedy teams, showcasing the impression of various variables.
-
Healthcare: Visualizing affected person demographics, illness prevalence, remedy outcomes, and healthcare useful resource allocation. Charts are essential for understanding well being traits and enhancing healthcare companies.
-
Schooling: Illustrating pupil efficiency, check scores, enrollment charges, and commencement statistics. Vertical charts assist educators and directors observe progress and determine areas needing enchancment.
-
Advertising and Promoting: Analyzing marketing campaign efficiency, web site site visitors, buyer demographics, and model consciousness. Charts present essential insights into the effectiveness of selling methods.
-
Authorities and Public Coverage: Presenting demographic information, financial indicators, crime charges, and social welfare statistics. Vertical charts are important for speaking complicated info to the general public and policymakers.
Designing Efficient Vertical Charts:
Creating a transparent and efficient vertical chart requires cautious consideration of a number of design components:
-
Selecting the Proper Chart Sort: Choose the chart sort that most closely fits the info and the message you wish to convey. Take into account whether or not it’s good to present absolute values, proportions, or the composition of classes.
-
Clear Axis Labels: Label each the horizontal and vertical axes clearly and concisely, specifying the items of measurement. Keep away from ambiguous or deceptive labels.
-
Applicable Scaling: Select a scale that precisely represents the info with out distorting the visible impression. Keep away from deceptive scales that exaggerate or reduce variations.
-
Constant Colour Scheme: Use a constant colour scheme to differentiate totally different classes or sub-categories. Keep away from overly vibrant or distracting colours.
-
Legible Font: Use a legible font dimension and elegance that’s simple to learn from a distance.
-
Information Labels: Take into account including information labels on to the bars or columns to offer exact values, particularly when the size is compressed or the variations between bars are small.
-
**





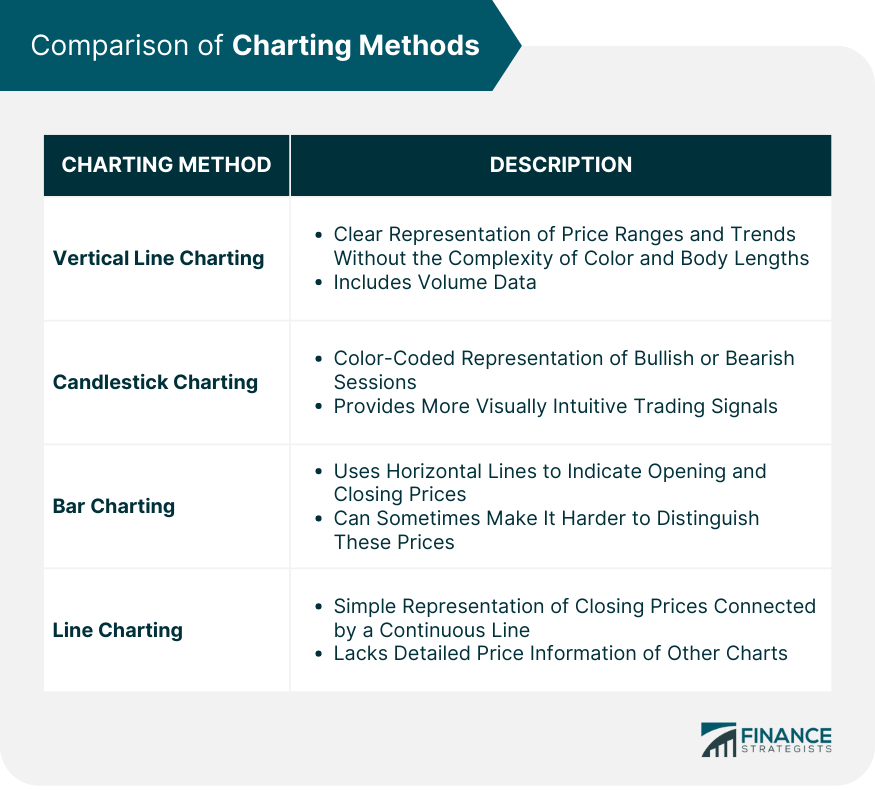
Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into The Energy of the Vertical: Charting Information for Readability and Perception. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!