Understanding And Making use of Management Limits In R Charts: A Complete Information
Understanding and Making use of Management Limits in R Charts: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of Management Limits in R Charts: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of Management Limits in R Charts: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of Management Limits in R Charts: A Complete Information

The R chart, a significant device in statistical course of management (SPC), is used to watch the variability inside subgroups of a course of. In contrast to the X-bar chart which tracks the common, the R chart focuses on the vary – the distinction between the most important and smallest values inside a subgroup. Understanding and appropriately making use of management limits to the R chart is essential for successfully figuring out shifts in course of variability and stopping defects. This text delves deep into the intricacies of R chart management limits, exploring their calculation, interpretation, and sensible functions.
The Basis: Understanding Course of Variability
Earlier than diving into the specifics of R chart management limits, it is important to understand the idea of course of variability. Variability is inherent in any course of, no matter how well-controlled it’s. This variability can stem from numerous sources, together with:
-
Widespread Trigger Variation: That is the inherent, pure variability inside a course of. It is the background noise, the small fluctuations which are all the time current. Widespread trigger variation is predictable and often inside acceptable limits.
-
Particular Trigger Variation: This represents uncommon or assignable causes that considerably impression the method. These are outliers, sudden shifts, or tendencies that deviate from the anticipated variability. Figuring out particular trigger variation is the first purpose of utilizing management charts just like the R chart.
The R chart helps distinguish between these two sorts of variation by visually representing the vary inside subgroups. Constant ranges recommend frequent trigger variation, whereas sudden will increase or decreases within the vary level in the direction of particular trigger variation requiring investigation.
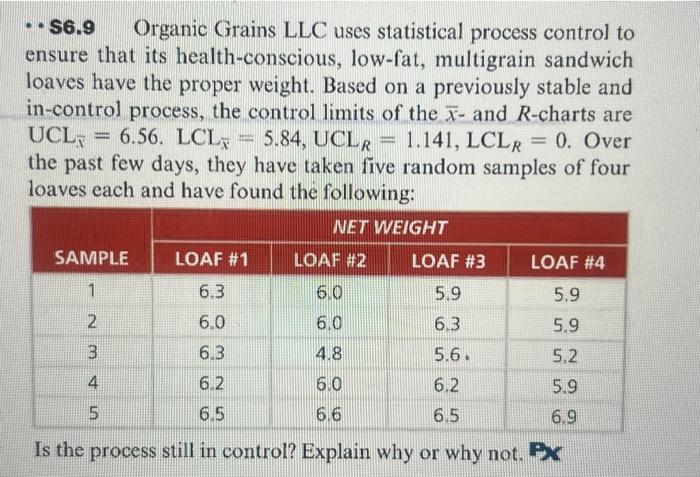
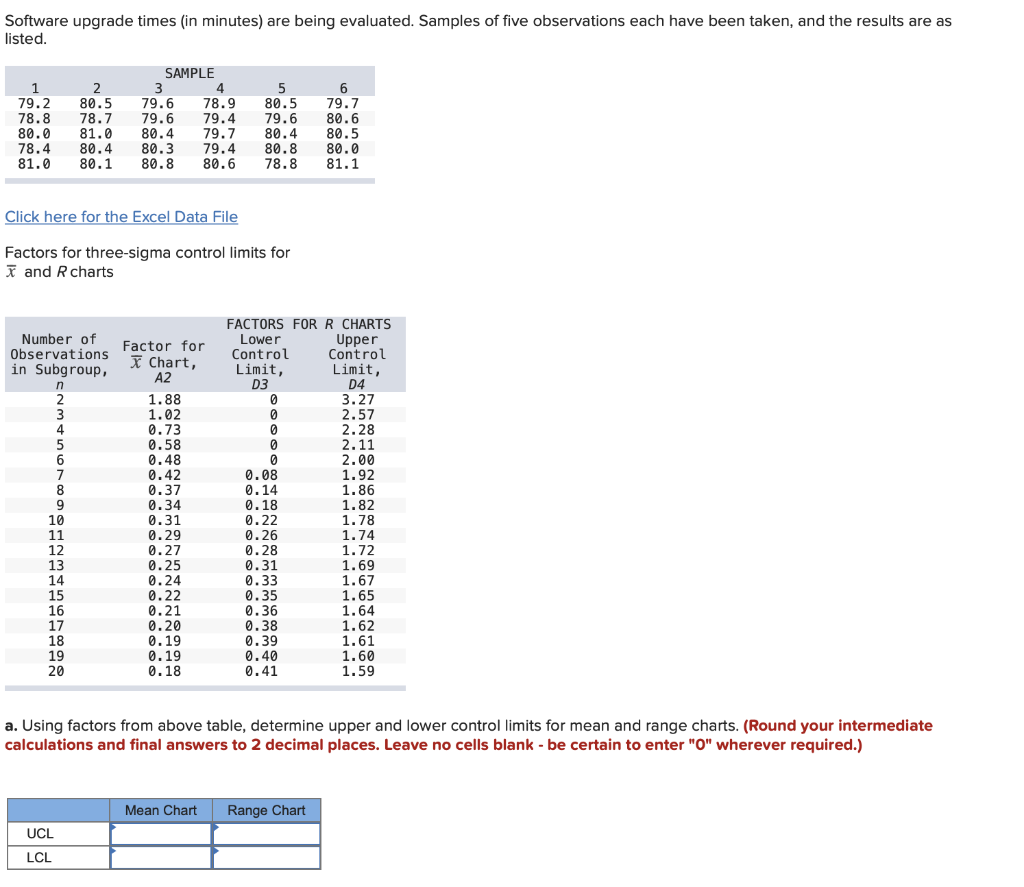
Calculating Management Limits for the R Chart
The management limits for an R chart are calculated utilizing the common vary (R-bar) and a management chart fixed (d2). The steps are as follows:
-
Accumulate Knowledge: Collect information in subgroups of dimension ‘n’. The subgroup dimension needs to be constant all through the info assortment course of. The optimum subgroup dimension will depend on the method and the frequency of knowledge assortment. Smaller subgroups are extra delicate to small shifts in variability, whereas bigger subgroups are much less delicate however present extra secure estimates of the common vary.
-
Calculate the Vary for Every Subgroup: For every subgroup, calculate the vary (R) by subtracting the smallest remark from the most important remark.
-
Calculate the Common Vary (R-bar): Sum the ranges from all subgroups and divide by the variety of subgroups (okay).
R-bar = ΣRi / okaythe place:
- R-bar is the common vary
- ΣRi is the sum of the ranges of all subgroups
- okay is the variety of subgroups
-
Decide the Management Chart Fixed (d2): The fixed d2 will depend on the subgroup dimension (n). These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The worth of d2 accounts for the connection between the vary and the usual deviation.
-
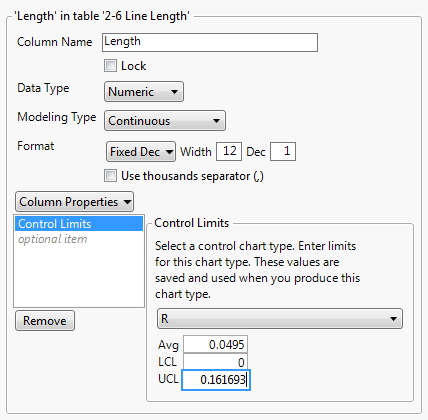
Calculate the Management Limits: The management limits are calculated as follows:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): UCL = D4 * R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): LCL = D3 * R-bar
the place:
- D4 and D3 are management chart constants that depend upon the subgroup dimension (n). These constants, like d2, are present in statistical tables or software program. Notice that D3 is usually 0 for smaller subgroup sizes.
Decoding the R Chart and Management Limits
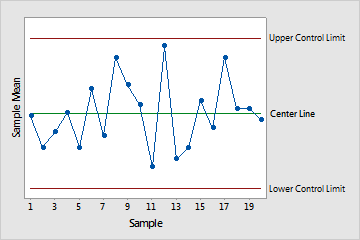
As soon as the management limits are established, plotting the vary of every subgroup on the chart permits for course of monitoring. The interpretation is easy:
-
Factors inside the Management Limits: Factors falling inside the UCL and LCL point out that the method variability is secure and inside acceptable limits. This implies that solely frequent trigger variation is current.
-
Factors Exterior the Management Limits: Factors falling exterior the UCL or LCL sign that particular trigger variation is probably going current. This warrants investigation to establish and eradicate the foundation reason behind the elevated variability.
-
Developments and Patterns: Even when all factors stay inside the management limits, the presence of tendencies (e.g., persistently rising or lowering ranges) or patterns (e.g., cyclical variations) can point out potential issues that want consideration. These patterns, though inside the limits, recommend a shift within the course of that warrants investigation.
-
Violation of the assumptions of the management chart: The R chart assumes the info follows a standard distribution. If this assumption is violated, the management limits may not be dependable. Due to this fact, checking the normality of the info is essential earlier than making use of the R chart. Transformations or various management charts is perhaps mandatory if the info isn’t usually distributed.
Selecting the Acceptable Subgroup Measurement (n)
The choice of the subgroup dimension is a crucial determination that considerably impacts the sensitivity and stability of the R chart. A number of components needs to be thought-about:
-
Course of Traits: Extremely variable processes would possibly profit from bigger subgroup sizes to offer extra secure estimates of the common vary. Conversely, processes with low variability would possibly profit from smaller subgroups to detect smaller shifts extra rapidly.
-
Knowledge Assortment Frequency: The frequency of knowledge assortment influences the subgroup dimension. Extra frequent information assortment permits for smaller subgroups.
-
Value and Time Constraints: Bigger subgroups require extra information assortment effort, doubtlessly rising prices and time.
There is not any single "greatest" subgroup dimension. The optimum dimension usually entails a trade-off between sensitivity and stability, contemplating the precise course of traits and sensible constraints.
Software program and Instruments for R Chart Evaluation
Quite a few statistical software program packages and on-line instruments can be found for creating and analyzing R charts. These instruments automate the calculations of management limits, plotting the info, and figuring out out-of-control factors. Common choices embrace:
- Minitab: A broadly used statistical software program bundle with complete SPC capabilities.
- JMP: One other sturdy statistical software program bundle providing superior statistical evaluation and visualization instruments.
- R: A robust open-source programming language with in depth statistical libraries.
- Excel: Whereas not as specialised as devoted SPC software program, Excel can be utilized to create primary R charts utilizing built-in features or add-ins.
Past the Fundamentals: Superior Concerns
Whereas the essential ideas outlined above present a stable basis, a number of superior concerns can improve the effectiveness of R chart evaluation:
-
Rational Subgrouping: Correctly defining subgroups is crucial. Subgroups needs to be homogenous, representing comparable situations below which the method operates.
-
Dealing with Out-of-Management Factors: When out-of-control factors are detected, an intensive investigation is critical to establish and proper the underlying trigger. This will contain reviewing course of parameters, tools upkeep, operator coaching, or materials specs.
-
Utilizing Different Management Charts in Conjunction: The R chart is usually used along side different management charts, such because the X-bar chart, to offer a extra complete image of course of efficiency. Combining these charts permits for a simultaneous evaluation of each the central tendency and variability of the method.
-
Course of Functionality Evaluation: As soon as the method is in statistical management, course of functionality evaluation could be carried out to evaluate whether or not the method is able to assembly predefined specs.
Conclusion
The R chart, with its give attention to course of variability, is an indispensable device for efficient SPC. Understanding the calculation and interpretation of its management limits is essential for figuring out and addressing sources of particular trigger variation. By combining cautious information assortment, acceptable subgroup choice, and an intensive understanding of the ideas outlined on this article, practitioners can leverage the R chart to enhance course of stability, scale back defects, and improve general course of efficiency. Do not forget that constant software and cautious interpretation, coupled with the suitable software program instruments, are key to unlocking the total potential of the R chart in high quality enchancment initiatives.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Understanding and Making use of Management Limits in R Charts: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!