Understanding And Making use of R-Chart Management Limits In Statistical Course of Management
Understanding and Making use of R-Chart Management Limits in Statistical Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of R-Chart Management Limits in Statistical Course of Management
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of R-Chart Management Limits in Statistical Course of Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of R-Chart Management Limits in Statistical Course of Management
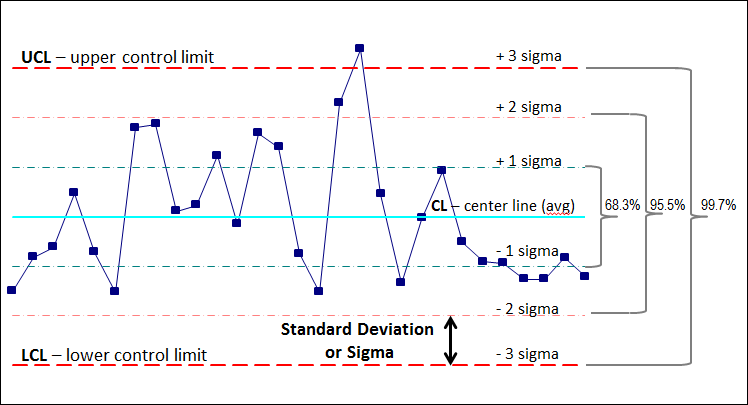
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a strong software for monitoring and bettering the consistency of processes. One key part of SPC is using management charts, graphical representations that show knowledge over time, permitting for the identification of tendencies and variations. Among the many varied management charts, the R-chart holds an important place, particularly designed for monitoring the variability inside subgroups of information. This text delves into the intricacies of R-charts, specializing in the calculation and interpretation of their management limits, and providing sensible purposes and issues.
What’s an R-Chart?
An R-chart, or vary chart, is a kind of management chart used to watch the variability inside subgroups of information. Not like X-bar charts, which monitor the typical of subgroups, R-charts deal with the vary, the distinction between the biggest and smallest values inside every subgroup. The vary gives a easy, albeit much less exact, measure of dispersion in comparison with customary deviation. Nevertheless, its simplicity makes it notably helpful in conditions the place calculations should be fast and simple, or when the pattern measurement is small.
R-charts are best when the underlying knowledge follows a traditional distribution, or no less than approximates it. It’s because the management limits are primarily based on the statistical properties of the vary distribution. Whereas deviations from normality can have an effect on the accuracy of the management limits, R-charts stay a helpful software, notably when coping with comparatively steady processes.
Calculating Management Limits for an R-Chart
The management limits for an R-chart are calculated primarily based on the typical vary (R-bar) of the subgroups. The method usually includes the next steps:
-
Information Assortment: Collect knowledge from the method being monitored. The information needs to be collected in subgroups of a constant measurement (n). The selection of subgroup measurement is essential and is dependent upon elements like the method functionality, the frequency of information assortment, and the specified sensitivity of the chart. Smaller subgroups (e.g., n=4 or n=5) are extra delicate to smaller shifts in variability, whereas bigger subgroups (e.g., n=10 or extra) are much less delicate however present extra steady estimates of the typical vary.
-
Calculating the Vary for Every Subgroup: For every subgroup, calculate the vary (R) by subtracting the smallest worth from the biggest worth.
-
Calculating the Common Vary (R-bar): Calculate the typical of the ranges from all subgroups. That is denoted as R-bar (R̄). The components is:
R̄ = ΣR / ok
the place:
- ΣR is the sum of the ranges of all ok subgroups.
- ok is the variety of subgroups.
-
Figuring out the Management Limits: The management limits are calculated utilizing elements derived from the distribution of the vary. These elements, denoted as D3 and D4, are depending on the subgroup measurement (n) and are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The management limits are:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): UCL = D4 * R̄
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): LCL = D3 * R̄
For small subgroup sizes (n<6), D3 may be zero, leading to a LCL of zero. This signifies {that a} vary of zero is virtually unimaginable and any worth beneath this suggests a possible difficulty with the information assortment or course of.
Decoding R-Chart Management Limits
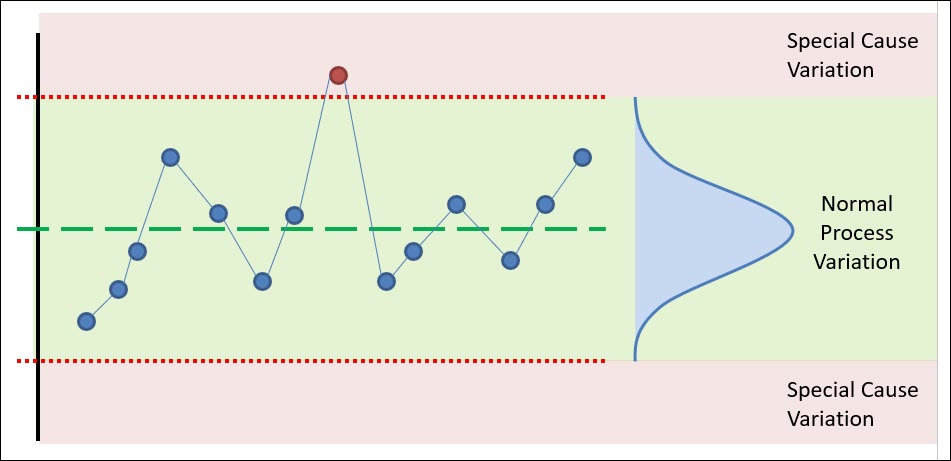
As soon as the management limits are established, the R-chart can be utilized to watch the method variability over time. Factors plotted exterior the management limits point out a big change within the course of variability. Such factors require investigation to establish the basis reason for the variation. The interpretation consists of:
-
Factors Outdoors Management Limits: Any level falling above the UCL or beneath the LCL indicators a big improve or lower in course of variability, respectively. This warrants speedy investigation to establish and rectify the reason for the variation.
-
Tendencies: A constant upward or downward pattern within the plotted factors, even when all factors stay throughout the management limits, suggests a scientific change in variability. This requires consideration and additional investigation.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors above or beneath the central line might point out underlying elements influencing the variability. This may very well be on account of totally different operators, machines, or supplies used throughout the course of.
-
Cycles: Recurring patterns or cycles within the knowledge might point out periodic influences on course of variability.
Selecting the Proper Subgroup Dimension
The number of the subgroup measurement (n) considerably impacts the effectiveness of the R-chart. Smaller subgroups are extra delicate to smaller adjustments in variability however may be extra inclined to random variation, resulting in extra false alarms. Bigger subgroups are much less delicate however present extra steady estimates of the typical vary. The optimum subgroup measurement is dependent upon the particular course of and the specified stability between sensitivity and stability. Contemplate these elements:
-
Course of Functionality: Extremely succesful processes might profit from smaller subgroups to detect refined shifts in variability.
-
Information Assortment Frequency: The frequency of information assortment influences the subgroup measurement. Extra frequent knowledge assortment permits for smaller subgroups.
-
Computational Assets: Whereas calculations for R-charts are comparatively simple, bigger subgroup sizes might require extra computational sources.
-
Sensible Issues: The practicality of gathering and analyzing knowledge must also be thought of.
Limitations of R-Charts
Whereas R-charts are helpful instruments, they’ve sure limitations:
-
Sensitivity to Outliers: Outliers can considerably affect the calculation of the typical vary and the management limits. Strong strategies for dealing with outliers needs to be thought of.
-
Assumption of Normality: The management limits are primarily based on the belief that the underlying knowledge follows a traditional distribution. Deviations from normality can have an effect on the accuracy of the management limits.
-
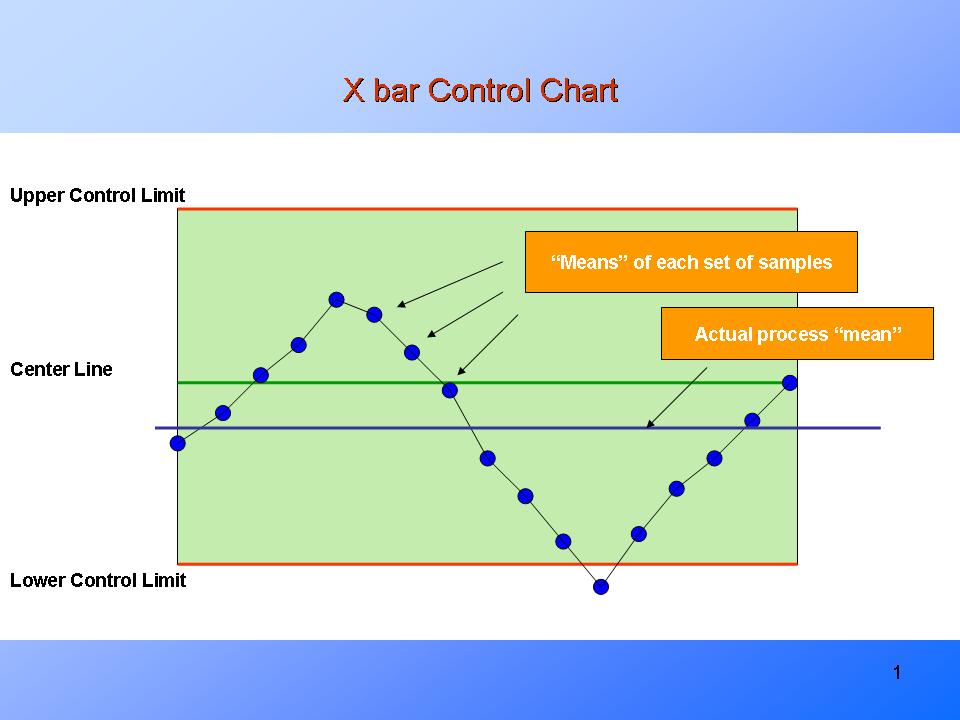
Restricted Data on the Imply: R-charts solely present data on the method variability; they don’t present direct data on the method imply. An X-bar chart is often used at the side of an R-chart to watch each the imply and variability.
-
Subgroup Dimension Dependency: The management limits are depending on the subgroup measurement, and altering the subgroup measurement requires recalculating the management limits.
Functions of R-Charts
R-charts discover purposes in a variety of industries and processes, together with:
-
Manufacturing: Monitoring the consistency of dimensions, weights, or different bodily traits of manufactured merchandise.
-
Healthcare: Monitoring the variability in affected person wait instances, laboratory check outcomes, or remedy dosages.
-
Service Industries: Monitoring the variability in service instances, buyer satisfaction scores, or error charges.
-
Software program Growth: Monitoring the variability in bug charges, code complexity, or testing instances.
Conclusion
R-charts are a helpful software in statistical course of management for monitoring course of variability. Understanding the ideas of calculating and decoding management limits is essential for successfully utilizing R-charts to establish and handle sources of variation. By fastidiously contemplating elements resembling subgroup measurement and potential limitations, practitioners can leverage the ability of R-charts to reinforce course of consistency and enhance general high quality. Combining R-charts with X-bar charts gives a complete method to monitoring each the central tendency and variability of a course of, resulting in extra knowledgeable decision-making and steady enchancment. Bear in mind to all the time take into account the particular context of your course of and select the suitable statistical strategies accordingly. Consulting with a statistician or high quality management knowledgeable may be extremely useful in advanced conditions.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Understanding and Making use of R-Chart Management Limits in Statistical Course of Management. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!