Understanding And Making use of The P-Chart System For Management Limits: A Complete Information
Understanding and Making use of the p-Chart System for Management Limits: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of the p-Chart System for Management Limits: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Making use of the p-Chart System for Management Limits: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of the p-Chart System for Management Limits: A Complete Information
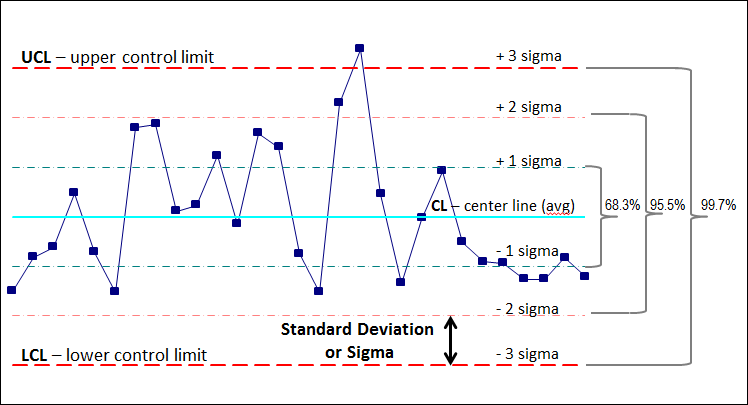
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a vital instrument for monitoring and bettering the standard of processes throughout numerous industries. Probably the most extensively used SPC charts is the p-chart, designed for controlling the proportion (or proportion) of nonconforming items in a pattern. Understanding the p-chart’s method for management limits is significant for efficient course of monitoring and figuring out potential sources of variation. This text offers a complete exploration of the p-chart, its underlying rules, the calculation of its management limits, and the interpretation of its outcomes, accompanied by sensible examples.
What’s a p-Chart?
A p-chart is a graphical illustration of the proportion of faulty gadgets in a sequence of samples taken from a course of over time. It is notably helpful when the method attribute being measured is attribute information – information that’s categorical, representing the presence or absence of a attribute moderately than a steady measurement. Examples embody:
- The share of faulty elements in a batch of manufactured elements.
- The proportion of buyer complaints obtained every week.
- The speed of errors in an information entry course of.
The p-chart makes use of management limits to find out whether or not the method is working inside acceptable limits of variation or if it is exhibiting instability or particular trigger variation. These limits assist distinguish between frequent trigger variation (inherent to the method) and particular trigger variation (as a result of assignable causes like machine malfunction or operator error).
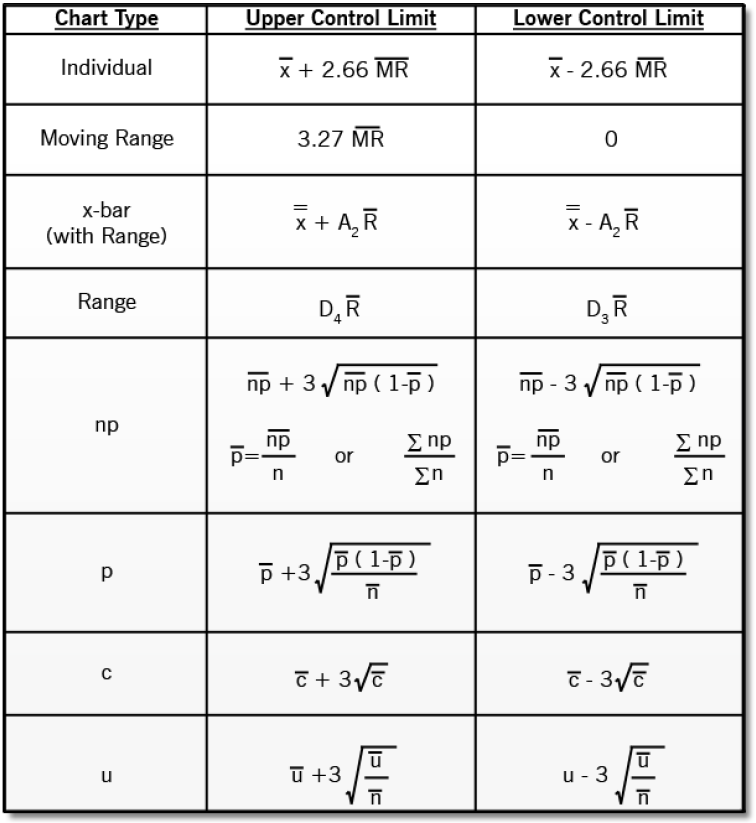
The p-Chart System for Management Limits
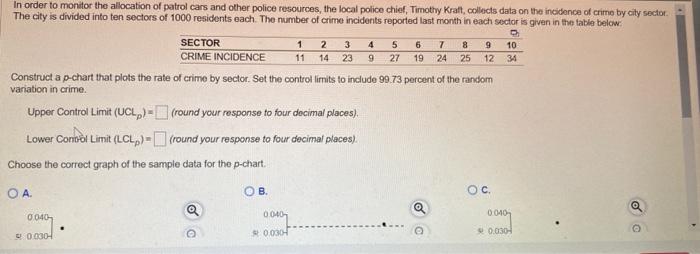
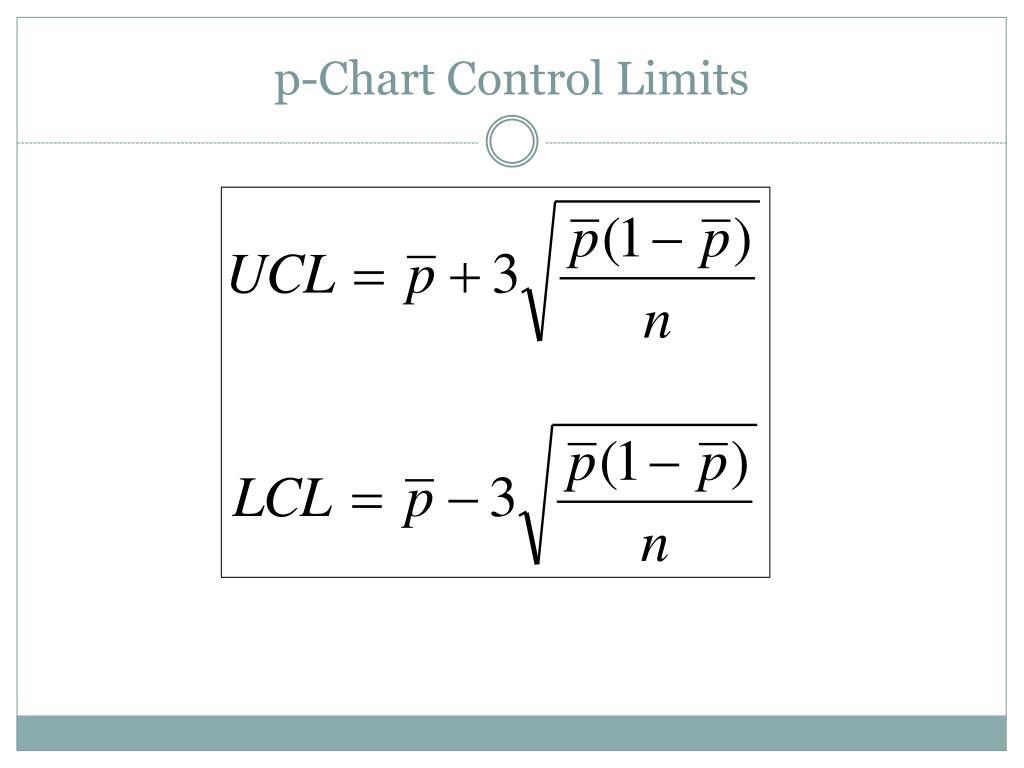
The management limits for a p-chart are calculated based mostly on the typical proportion of nonconforming items and the pattern dimension. The method for the management limits is:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): p̄ + 3√(p̄(1-p̄)/n)
- Central Line (CL): p̄
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): p̄ – 3√(p̄(1-p̄)/n)
The place:
- p̄ (p-bar): The typical proportion of nonconforming items throughout all samples. That is calculated by summing the proportions of nonconforming items in every pattern and dividing by the variety of samples.
- n: The pattern dimension (variety of items inspected in every pattern). This could stay fixed for all samples for correct interpretation.
The "3" within the method represents three normal deviations from the central line. It is a frequent conference in SPC, representing a 99.73% confidence interval. Factors falling exterior these limits recommend the method is uncontrolled and requires investigation.
Steps for Establishing a p-Chart:
-
Outline the Course of Attribute: Clearly establish the attribute you’re measuring (e.g., faulty gadgets, errors).
-
Decide the Pattern Dimension (n): Select a constant pattern dimension for every pattern. The pattern dimension must be giant sufficient to offer statistically significant outcomes, sometimes a minimum of 25-30 items. Bigger pattern sizes present extra exact estimates however require extra assets.
-
Acquire Information: Acquire information on the variety of nonconforming items in every pattern. Make sure the samples are consultant of the method and picked up persistently over time.
-
Calculate p̄ (p-bar): For every pattern, calculate the proportion of nonconforming items (p = variety of nonconforming items / pattern dimension). Then, calculate the typical proportion (p̄) throughout all samples.
-
Calculate Management Limits: Use the method above to calculate the UCL and LCL utilizing the calculated p̄ and the pattern dimension (n).
-
Assemble the Chart: Plot the proportion of nonconforming items (p) for every pattern on a chart, together with the central line (p̄) and the UCL and LCL.
-
Interpret the Chart: Analyze the chart for any factors falling exterior the management limits or patterns that recommend the method is uncontrolled.
Instance:
Let’s contemplate a producing course of producing digital elements. We gather information from 20 samples, every with a pattern dimension of fifty items. The variety of faulty items in every pattern is recorded:
| Pattern | Faulty Models | Proportion (p) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 0.06 |
| 2 | 2 | 0.04 |
| 3 | 4 | 0.08 |
| … | … | … |
| 20 | 5 | 0.10 |
After accumulating information from all 20 samples, we discover that the typical proportion of faulty items is p̄ = 0.065. With n = 50, we will calculate the management limits:
- UCL: 0.065 + 3√(0.065(1-0.065)/50) ≈ 0.156
- CL: 0.065
- LCL: 0.065 – 3√(0.065(1-0.065)/50) ≈ -0.026 (Since LCL is unfavorable, we set it to 0)
We might then plot the proportion of faulty items for every pattern on a chart, together with the central line (0.065), UCL (0.156), and LCL (0). Any pattern with a proportion above 0.156 would point out the method is uncontrolled.
Deciphering the p-Chart:
A p-chart offers beneficial insights into course of stability. Listed here are some key interpretations:
- Factors exterior the management limits: Point out particular trigger variation. Examine the causes of those factors to establish and proper issues.
- Tendencies: A constant upward or downward pattern suggests a scientific shift within the course of.
- Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low proportions point out a cyclical variation within the course of.
- Stratification: Clustering of factors round particular values suggests the presence of subgroups inside the information.
- All factors close to the central line: Signifies a secure and constant course of.
Limitations of the p-Chart:
- Fixed Pattern Dimension: The p-chart assumes a relentless pattern dimension for all samples. Variations in pattern dimension can have an effect on the accuracy of the management limits.
- Independence of Samples: The samples must be unbiased of one another. If samples are taken too shut collectively, they might not be really unbiased.
- Enough Information: A adequate variety of samples is required to acquire a dependable estimate of p̄. Too few samples can result in inaccurate management limits.
Conclusion:
The p-chart is a strong instrument for monitoring and bettering processes the place the attribute of curiosity is attribute information. Understanding the p-chart method for management limits and its interpretation is crucial for successfully utilizing this instrument. By rigorously accumulating information, calculating management limits precisely, and deciphering the chart appropriately, organizations can establish and deal with sources of variation, resulting in improved course of stability and high quality. Do not forget that the p-chart is only one instrument in a broader high quality administration system, and its use must be complemented by different methods for root trigger evaluation and course of enchancment. Cautious consideration of the assumptions and limitations of the p-chart is essential for its efficient and dependable utility.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Understanding and Making use of the p-Chart System for Management Limits: A Complete Information. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!