Understanding And Making use of The R Chart: A Complete Information To Course of Variability Management
Understanding and Making use of the R Chart: A Complete Information to Course of Variability Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of the R Chart: A Complete Information to Course of Variability Management
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Making use of the R Chart: A Complete Information to Course of Variability Management. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of the R Chart: A Complete Information to Course of Variability Management

The R chart, a cornerstone of statistical course of management (SPC), is a strong instrument used to observe the variability inside subgroups of information. In contrast to the X-bar chart, which tracks the typical of those subgroups, the R chart focuses particularly on the vary – the distinction between the best and lowest values inside every subgroup. By charting the vary over time, the R chart helps establish shifts in course of variability, permitting for well timed intervention and prevention of defects. This text delves into the intricacies of R charts, explaining their development, interpretation, and sensible purposes.
Understanding Course of Variability:
Earlier than diving into the specifics of the R chart, it is essential to understand the idea of course of variability. In any manufacturing or service course of, some degree of variation is inevitable. This variation can stem from varied sources, together with:
- Frequent Trigger Variation: That is inherent to the method and is usually random and predictable. It is the background noise of the system, representing the traditional fluctuations anticipated beneath secure working situations.
- Particular Trigger Variation: That is sudden and sometimes vital variation that arises from identifiable sources. These sources may very well be machine malfunctions, operator errors, adjustments in uncooked supplies, or environmental components. Figuring out and eliminating particular trigger variation is important to course of enchancment.
The R chart’s major objective is to detect particular trigger variation by monitoring the vary inside subgroups. A big change within the vary means that one thing has altered the inherent variability of the method, doubtlessly indicating an issue requiring consideration.
Establishing an R Chart:
The development of an R chart includes a number of steps:
-
Subgroup Choice: Knowledge should be collected in subgroups, sometimes consisting of 4 to five consecutive items of output. The subgroup measurement must be constant all through the info assortment interval. The selection of subgroup measurement is a important choice; bigger subgroups are extra delicate to detecting shifts within the common however much less delicate to detecting shifts in variability. Smaller subgroups are extra delicate to detecting shifts in variability however much less delicate to shifts within the common. The optimum subgroup measurement typically is determined by the particular course of being monitored.
-
Knowledge Assortment: For every subgroup, accumulate knowledge on the attribute being measured. This attribute must be a steady variable, equivalent to weight, size, temperature, or time. Guarantee correct and constant knowledge assortment strategies are employed.
-
Vary Calculation: For every subgroup, calculate the vary (R) by subtracting the smallest worth from the most important worth.
-
Common Vary Calculation: Calculate the typical vary (R-bar) by averaging the ranges of all subgroups. It is a essential statistic representing the typical variability inside the subgroups.
-
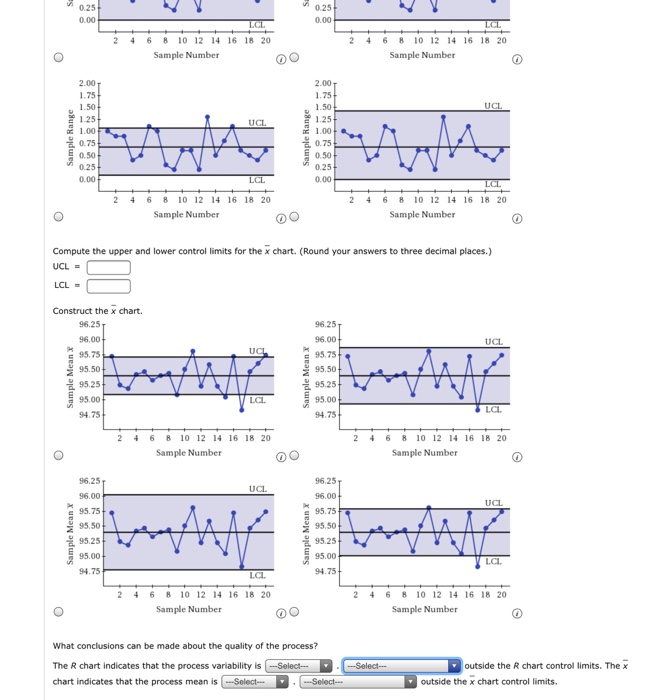
Management Limits Calculation: Management limits are calculated utilizing management chart constants, that are based mostly on the subgroup measurement (n). These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The higher management restrict (UCL) and decrease management restrict (LCL) are calculated as follows:
- *UCL = R-bar UCLR**
- *LCL = R-bar LCLR**
The place UCLR and LCLR are the higher and decrease management restrict components respectively, depending on the subgroup measurement (n). For instance, for n=5, UCLR is roughly 2.115 and LCLR is roughly 0.
-
Chart Development: Plot the person ranges (R) for every subgroup on a chart with a central line at R-bar, an higher management restrict (UCL), and a decrease management restrict (LCL).
Deciphering an R Chart:
As soon as the R chart is constructed, decoding the info is essential for efficient course of monitoring. The next conditions point out potential issues:
-
Factors exterior the management limits: Any level falling above the UCL or under the LCL alerts a possible particular trigger variation. This warrants investigation into the underlying causes of the elevated or decreased variability.
-
Traits: A constant upward or downward pattern within the ranges suggests a gradual shift in course of variability. Even when factors stay inside the management limits, a pattern signifies a possible downside that must be addressed earlier than it results in out-of-control factors.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors above or under the central line, even inside the management limits, can point out underlying patterns or subgroups that want additional investigation.
-
Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low ranges recommend cyclical variations within the course of that must be understood and addressed.
Purposes of R Charts:
R charts discover huge purposes throughout varied industries and processes, together with:
-
Manufacturing: Monitoring the variability of dimensions, weights, or different important traits of manufactured merchandise.
-
Healthcare: Monitoring the variability in affected person wait instances, laboratory take a look at outcomes, or medicine dosages.
-
Service Industries: Monitoring the variability in service instances, buyer satisfaction scores, or transaction processing instances.
-
High quality Management: Figuring out and correcting sources of variation in any course of the place consistency is important.
-
Course of Enchancment: Utilizing the knowledge from the R chart to establish and remove sources of particular trigger variation, resulting in improved course of stability and lowered defects.
Limitations of R Charts:
Whereas R charts are invaluable instruments, they do have some limitations:
-
Sensitivity to Outliers: Excessive values inside a subgroup can considerably inflate the vary, masking different variations inside the knowledge. Strong strategies, equivalent to utilizing the median vary as a substitute of the vary, can mitigate this problem.
-
Assumption of Normality: Whereas not strictly required, the effectiveness of R charts is enhanced when the underlying knowledge is roughly usually distributed. Transformations or various management charts could also be essential for non-normal knowledge.
-
Subgroup Dimension: The selection of subgroup measurement considerably impacts the chart’s sensitivity to various kinds of variation. Cautious consideration is required to pick out an acceptable subgroup measurement based mostly on the particular course of and targets.
R Charts in Conjunction with X-bar Charts:
R charts are sometimes used at the side of X-bar charts, which monitor the typical of the subgroups. This mix supplies a complete image of each the central tendency and variability of the method. A simultaneous evaluation of each charts permits for a extra nuanced understanding of course of efficiency and the identification of each shifts within the common and adjustments in variability.
Conclusion:
The R chart is an important instrument for monitoring course of variability and making certain constant high quality. By monitoring the vary inside subgroups, it helps establish and tackle sources of particular trigger variation, resulting in improved course of stability and lowered defects. Understanding its development, interpretation, and limitations is essential for successfully using this highly effective approach in varied purposes. Whereas its simplicity makes it accessible, a radical understanding of its underlying ideas and acceptable utility are key to its profitable implementation and the achievement of improved course of management. Do not forget that the R chart is simplest when used as a part of a broader high quality administration system, incorporating different statistical strategies and steady enchancment practices.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Understanding and Making use of the R Chart: A Complete Information to Course of Variability Management. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!
