Understanding And Making use of X-bar And R Charts: A Complete Information To Course of Management
Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management
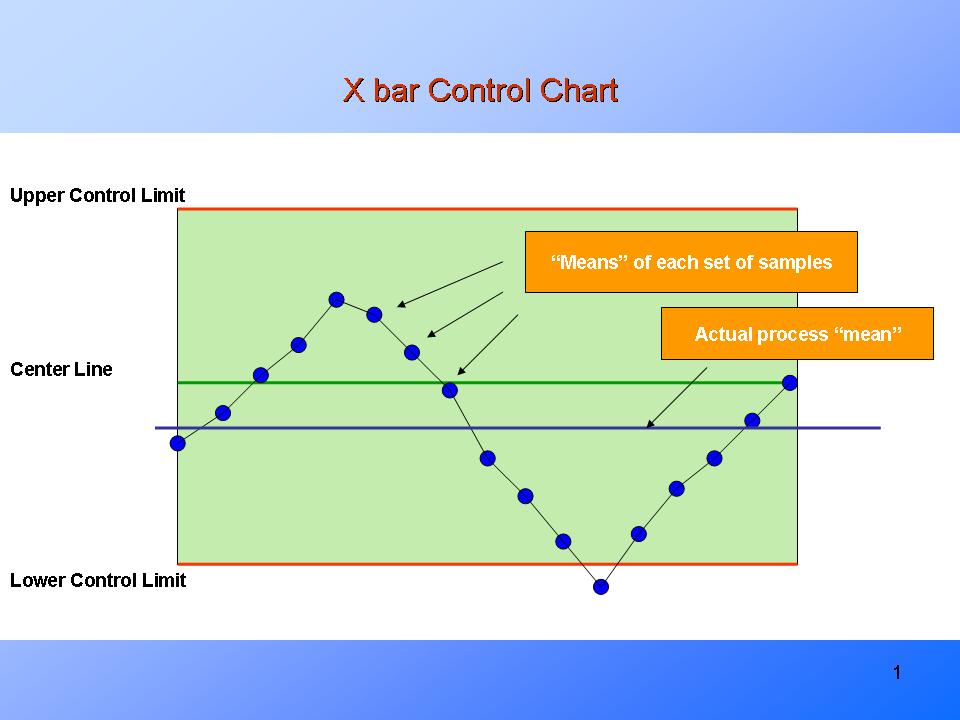
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a vital methodology for monitoring and bettering manufacturing and repair processes. Its goal is to establish and scale back variation, resulting in enhanced high quality, effectivity, and buyer satisfaction. Central to SPC are management charts, graphical instruments that show knowledge over time, permitting for the identification of tendencies and anomalies. Among the many most generally used management charts are the X-bar and R charts, a strong duo used for monitoring the common (X-bar) and vary (R) of a course of. This text offers a complete overview of X-bar and R charts, masking their software, interpretation, and limitations.
The Fundamentals of X-bar and R Charts
X-bar and R charts are used for variables knowledge, which means knowledge that may be measured on a steady scale (e.g., weight, size, temperature). They’re significantly efficient for monitoring processes the place subgroups of samples are taken at common intervals. Every subgroup sometimes consists of 4-5 samples, though the optimum subgroup dimension can range relying on the method.
-
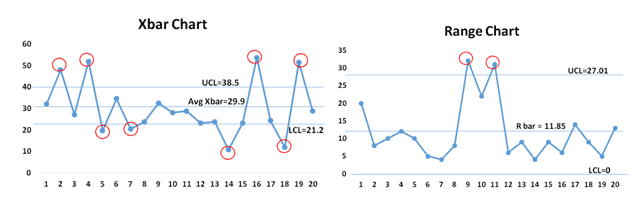
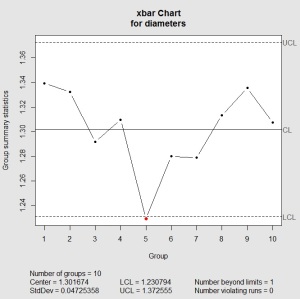
X-bar chart: This chart tracks the common (imply) of every subgroup. It displays the central tendency of the method. A secure course of will exhibit X-bar values clustered round a central line, indicating constant efficiency.
-
R chart: This chart displays the vary of every subgroup, representing the unfold or dispersion of the info inside every subgroup. It displays the variability inside the course of. A secure course of will present R values constantly beneath the higher management restrict, indicating managed variation.
These charts are used collectively as a result of they supply a holistic view of course of conduct. A course of will be thought-about below management provided that each the X-bar and R charts point out stability. An out-of-control sign on both chart suggests a possible downside requiring investigation.
Developing X-bar and R Charts: A Step-by-Step Information
Developing these charts entails a number of steps:
-
Information Assortment: Collect knowledge from the method. Gather samples in subgroups of a predetermined dimension (sometimes 4-5) at common intervals. Be certain that the sampling methodology is consultant of your entire course of.
-
Calculate Subgroup Statistics: For every subgroup, calculate the imply (X-bar) and vary (R). The vary is solely the distinction between the biggest and smallest values within the subgroup.
-
Calculate Total Statistics: Calculate the general common of the subgroup means (X-double bar) and the common of the subgroup ranges (R-bar). These are essential for establishing the central strains and management limits on the charts.
-
Decide Management Limits: Management limits are calculated utilizing management chart constants (A2, D3, D4) that are available in statistical tables or software program packages. These constants rely on the subgroup dimension. The formulation for the management limits are:
-
X-bar chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL) = X-double bar + A2 * R-bar
- Central Line (CL) = X-double bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL) = X-double bar – A2 * R-bar
-
R chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL) = D4 * R-bar
- Central Line (CL) = R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL) = D3 * R-bar (Word: D3 is 0 for subgroup sizes lower than 7)
-
-
Assemble the Charts: Plot the X-bar and R values on their respective charts, together with the calculated central strains and management limits.
Decoding X-bar and R Charts: Figuring out Out-of-Management Indicators
As soon as the charts are constructed, the following step is to interpret them. A course of is taken into account to be in statistical management if all knowledge factors fall inside the management limits and there aren’t any discernible patterns or tendencies. Nonetheless, a number of indicators point out an out-of-control course of:
-
Factors outdoors the management limits: Any level falling above the UCL or beneath the LCL is a transparent indication of an out-of-control course of. This implies a major shift within the course of imply or variability.
-
Traits: A constant upward or downward pattern within the knowledge factors suggests a gradual shift within the course of.
-
Stratification: Information factors clustering close to the management limits or exhibiting distinct layers point out potential issues.
-
Cycles: Recurring patterns or cycles recommend the presence of periodic influences on the method.
-
Runs: A sequence of consecutive factors above or beneath the central line signifies a possible shift within the course of.
Figuring out these out-of-control indicators necessitates an investigation into the foundation explanation for the variation. This entails inspecting potential sources of error, reminiscent of machine malfunction, operator error, or modifications in uncooked supplies. As soon as the foundation trigger is recognized, corrective actions will be applied to convey the method again below management.
Benefits of Utilizing X-bar and R Charts
X-bar and R charts supply a number of benefits:
-
Early detection of issues: They supply a visible illustration of course of conduct, permitting for the early detection of shifts within the imply or variability.
-
Course of enchancment: By figuring out and addressing the foundation causes of variation, these charts facilitate steady course of enchancment.
-
Lowered waste: Early detection of issues minimizes the manufacturing of faulty merchandise and reduces waste.
-
Improved high quality: By controlling variation, these charts contribute to improved product high quality and buyer satisfaction.
-
Goal evaluation: They supply an goal evaluation of course of efficiency, eliminating subjective judgments.
Limitations of X-bar and R Charts
Regardless of their effectiveness, X-bar and R charts have sure limitations:
-
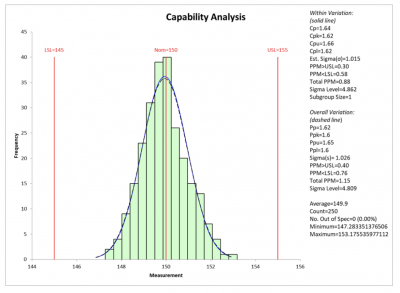
Assumption of normality: The management limits are primarily based on the belief that the info are usually distributed. If the info are considerably non-normal, the accuracy of the management limits could also be compromised. Transformations or various management charts could also be vital in such circumstances.
-
Subgroup dimension: The selection of subgroup dimension is essential. Too small a subgroup dimension could masks variation, whereas too giant a dimension could obscure short-term modifications.
-
Frequent trigger vs. particular trigger variation: Distinguishing between frequent trigger (inherent to the method) and particular trigger (assignable to particular occasions) variation will be difficult. Cautious interpretation and investigation are required.
-
Lack of knowledge on particular causes: Whereas these charts establish out-of-control conditions, they don’t instantly pinpoint the precise causes. Additional investigation is all the time wanted.
-
Information necessities: Enough knowledge are wanted to determine dependable management limits. Inadequate knowledge can result in inaccurate management limits and deceptive interpretations.
Conclusion
X-bar and R charts are invaluable instruments for monitoring and controlling processes. Their capacity to detect shifts in each the common and variability of a course of makes them important for sustaining high quality and effectivity. Nonetheless, it’s essential to know their underlying assumptions and limitations to make sure their efficient software. Correct coaching and cautious interpretation are important for maximizing the advantages of those highly effective statistical instruments. By combining the insights from X-bar and R charts with a proactive strategy to problem-solving, organizations can obtain important enhancements of their processes and general efficiency. Using statistical software program can vastly simplify the development and interpretation of those charts, making them accessible to a wider vary of customers. Moreover, integrating X-bar and R charts inside a broader high quality administration system enhances their effectiveness and contributes to a tradition of steady enchancment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!