Understanding And Using Pareto Charts In Challenge Administration (PMP)
Understanding and Using Pareto Charts in Challenge Administration (PMP)
Associated Articles: Understanding and Using Pareto Charts in Challenge Administration (PMP)
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Using Pareto Charts in Challenge Administration (PMP). Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Using Pareto Charts in Challenge Administration (PMP)
The Challenge Administration Skilled (PMP) certification emphasizes the significance of data-driven decision-making. Among the many varied analytical instruments obtainable to challenge managers, the Pareto chart stands out as a strong visible illustration of the important few versus the trivial many. This text delves deep into the idea of Pareto charts, their software in PMP contexts, and the way they contribute to environment friendly challenge administration.
What’s a Pareto Chart?
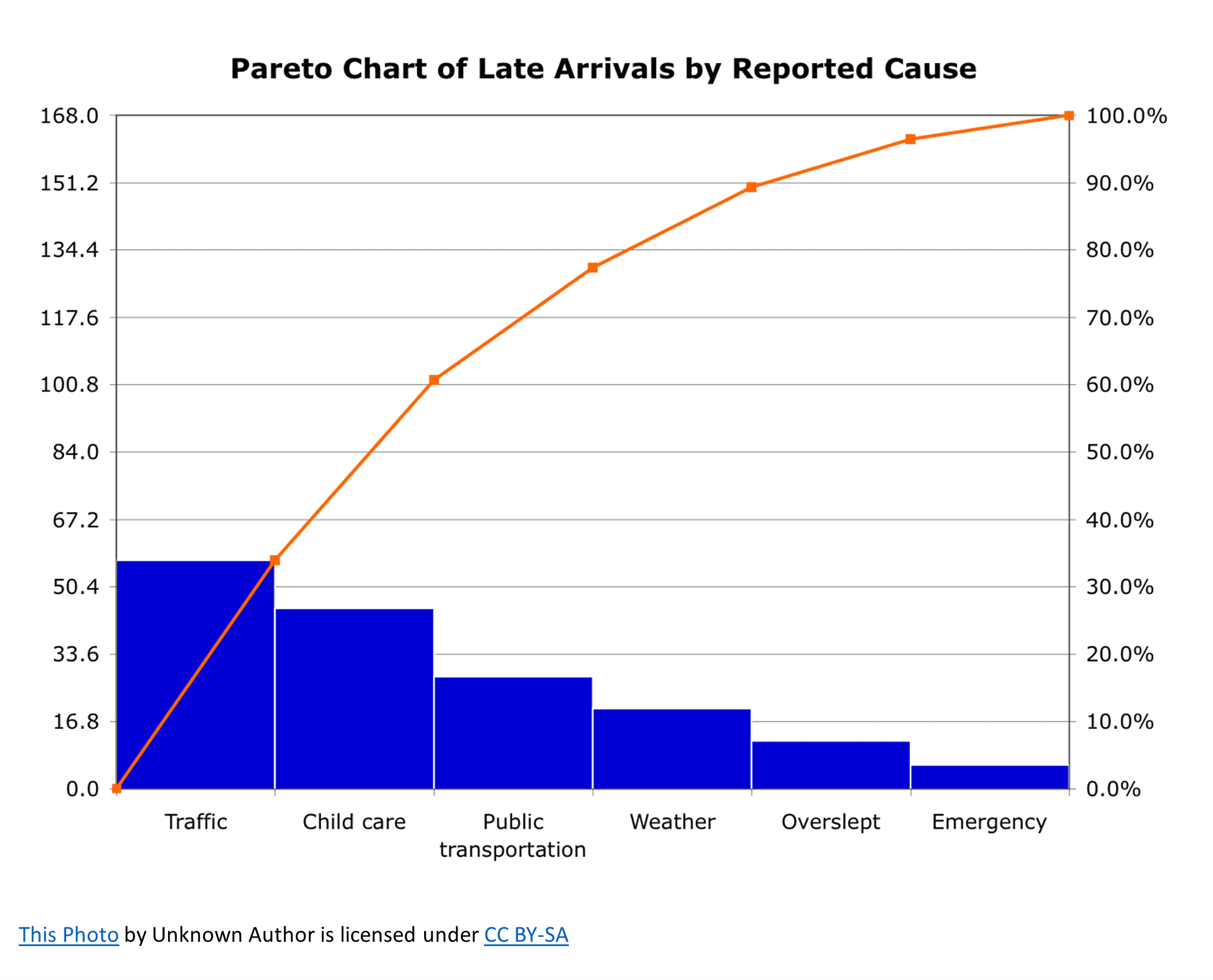
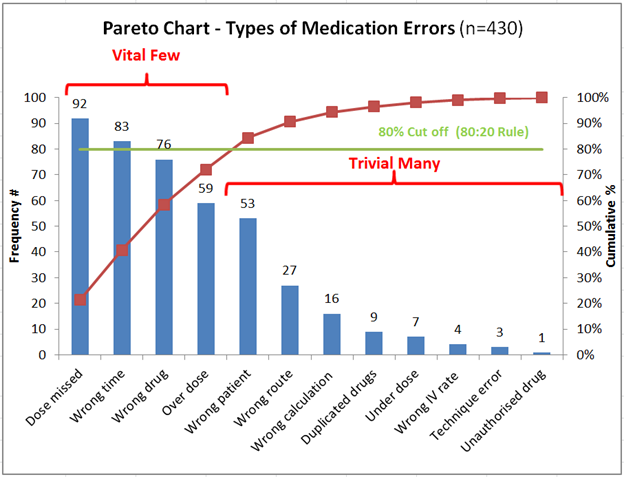
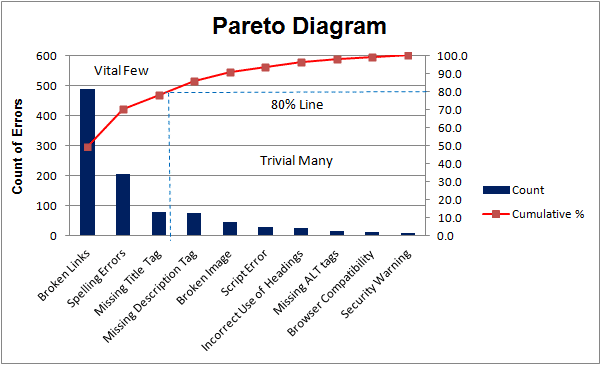
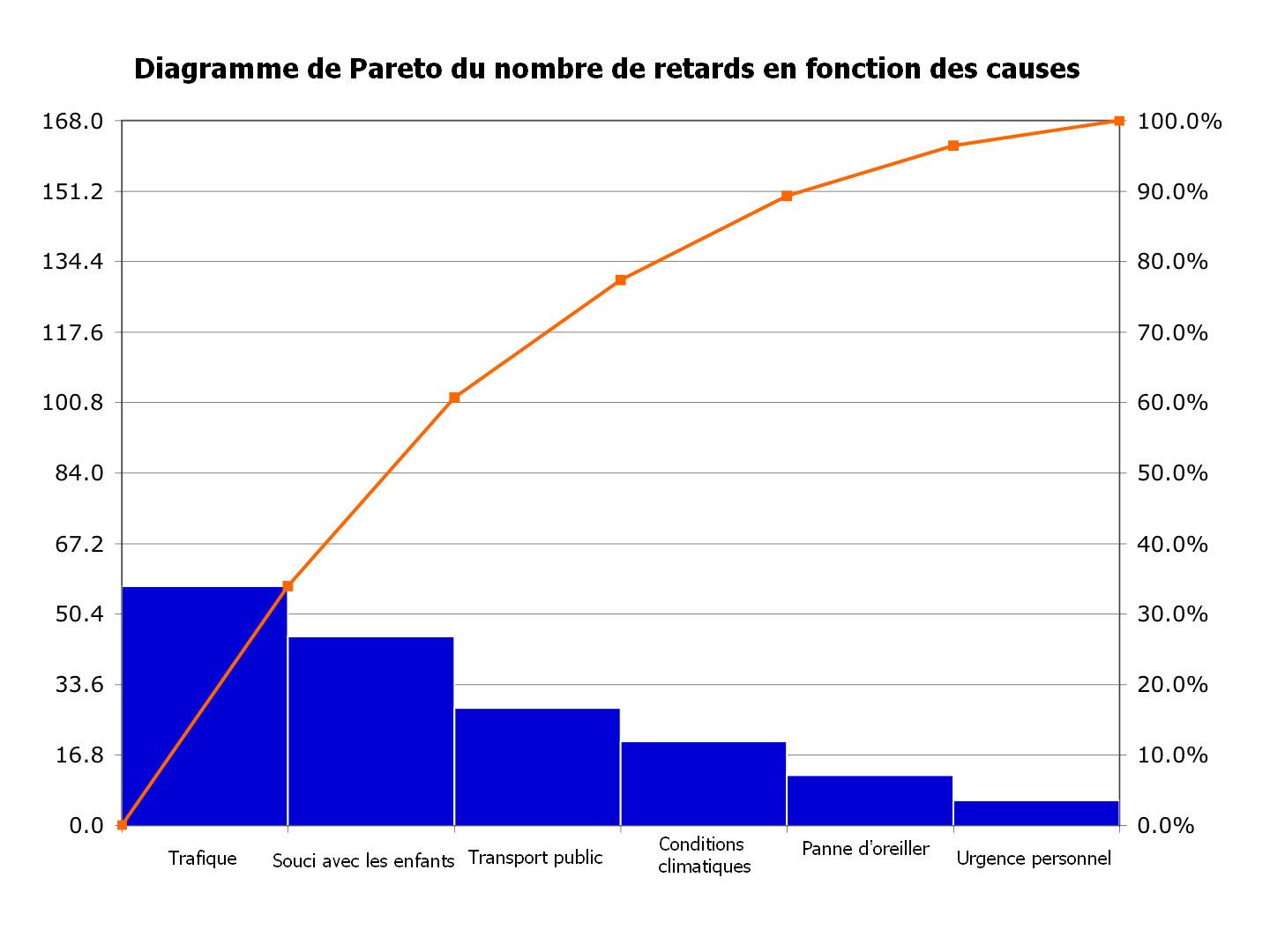
A Pareto chart, often known as a Pareto diagram, is a mixture bar and line graph that ranks causes of issues or defects in descending order of frequency. It is based mostly on the Pareto precept, typically summarized because the "80/20 rule," which means that 80% of the consequences come from 20% of the causes. Whereas the 80/20 ratio is a tenet, not a strict rule, the Pareto chart’s power lies in its skill to visually spotlight essentially the most important contributors to an issue, permitting challenge managers to focus their efforts strategically.
The chart includes two key elements:
- Bar graph: Represents the frequency of every trigger, organized in descending order from left to proper. The bars visually depict the relative contribution of every trigger to the general downside.
- Line graph: Exhibits the cumulative proportion of the whole results. This line helps determine the "important few" causes that account for almost all of the issues.
How a Pareto Chart Works:
The creation of a Pareto chart entails a number of steps:
-
Establish the Downside: Clearly outline the issue or situation you are attempting to research. This might vary from challenge delays to defects in a product, price overruns, or frequent buyer complaints.
-
Acquire Knowledge: Collect information associated to the issue. This may contain monitoring the frequency of particular causes, the length of delays, the price of defects, or the variety of buyer complaints categorized by their supply.
-
Categorize Knowledge: Group the info into significant classes. As an example, if analyzing challenge delays, classes might embody "ready for approvals," "useful resource constraints," "unexpected technical points," and many others.
-
Tally and Rank: Depend the occurrences of every class and rank them in descending order based mostly on frequency.
-
Calculate Percentages: Calculate the proportion of the whole for every class.
-
Calculate Cumulative Percentages: Calculate the cumulative proportion for every class by including the odds sequentially.
-
Create the Chart: Assemble the bar graph representing the frequency of every class, adopted by the road graph exhibiting the cumulative proportion. The chart ought to have clear labels for each axes and every class.
Instance: Challenge Delays
As an example a challenge is experiencing important delays. After accumulating information, a challenge supervisor identifies the next causes and their frequencies:
| Reason for Delay | Frequency | Proportion | Cumulative Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ready for approvals | 25 | 40% | 40% |
| Useful resource constraints | 15 | 24% | 64% |
| Unexpected technical points | 10 | 16% | 80% |
| Poor communication | 5 | 8% | 88% |
| Different | 5 | 8% | 96% |
| Complete | 60 | 100% |
A Pareto chart would visually characterize this information, clearly exhibiting that "ready for approvals" and "useful resource constraints" are essentially the most important contributors to the challenge delays (accounting for 64% of the whole delays). The challenge supervisor can then concentrate on enhancing these two areas to considerably cut back the general challenge delay.
Functions of Pareto Charts in PMP:
Pareto charts are extremely versatile in challenge administration and discover functions in varied features:
-
Threat Administration: Figuring out and prioritizing dangers based mostly on their chance and affect. The chart can visually characterize essentially the most possible and impactful dangers, permitting the challenge supervisor to focus mitigation efforts on the important few.
-
High quality Administration: Analyzing defects and figuring out the foundation causes of high quality points. This helps in implementing corrective actions to enhance services or products high quality.
-
Price Administration: Pinpointing the key price drivers in a challenge. Understanding the place nearly all of the prices are incurred permits for higher price range allocation and value management.
-
Schedule Administration: Figuring out the first causes for schedule slippage. This helps in creating methods to enhance scheduling accuracy and cut back delays.
-
Communication Administration: Analyzing the sources of communication breakdowns and specializing in enhancing essentially the most problematic areas.
-
Stakeholder Administration: Figuring out the important thing stakeholders who’ve essentially the most affect on the challenge’s success. This enables for targeted communication and engagement methods.
-
Downside Fixing: A strong instrument for root trigger evaluation, serving to pinpoint essentially the most important components contributing to an issue and guiding the event of efficient options.
Advantages of Utilizing Pareto Charts:
-
Concentrate on the Very important Few: Pareto charts assist challenge managers prioritize their efforts by specializing in essentially the most important contributors to an issue, somewhat than spreading sources thinly throughout quite a few minor points.
-
Improved Choice-Making: By offering a transparent visible illustration of the info, Pareto charts facilitate knowledgeable and data-driven decision-making.
-
Enhanced Communication: The visible nature of the chart makes it simple to speak complicated information to stakeholders, selling a shared understanding of the issue and the proposed options.
-
Efficient Downside Fixing: By figuring out the foundation causes of issues, Pareto charts contribute to simpler problem-solving and stop recurrence.
-
Elevated Effectivity: Specializing in the important few results in elevated effectivity and useful resource optimization.
Limitations of Pareto Charts:
Whereas Pareto charts are a strong instrument, they’ve some limitations:
-
Subjectivity in Categorization: The categorization of knowledge could be subjective, doubtlessly influencing the outcomes. Cautious consideration and clear definitions are essential.
-
Oversimplification: The chart could oversimplify complicated points, doubtlessly lacking refined interdependencies between completely different causes.
-
Restricted Predictive Energy: Pareto charts are descriptive somewhat than predictive. They illustrate the present scenario however do not essentially forecast future tendencies.
Conclusion:
The Pareto chart is a useful instrument within the challenge supervisor’s arsenal, providing an easy but highly effective technique to visualize and analyze information. Its skill to focus on the important few causes contributing to an issue permits for targeted effort, improved decision-making, and finally, extra profitable challenge outcomes. By understanding its strengths and limitations, PMP professionals can successfully make the most of Pareto charts to boost their challenge administration abilities and obtain higher outcomes. Integrating this straightforward but efficient instrument into your challenge administration course of can result in important enhancements in effectivity, high quality, and general challenge success. Keep in mind that the Pareto chart is handiest when mixed with different challenge administration instruments and strategies for a holistic strategy to problem-solving and decision-making.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Understanding and Using Pareto Charts in Challenge Administration (PMP). We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!