Unveiling The Pareto Precept: A Deep Dive Into Pareto Charts In Six Sigma
Unveiling the Pareto Precept: A Deep Dive into Pareto Charts in Six Sigma
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Pareto Precept: A Deep Dive into Pareto Charts in Six Sigma
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Unveiling the Pareto Precept: A Deep Dive into Pareto Charts in Six Sigma. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Pareto Precept: A Deep Dive into Pareto Charts in Six Sigma
Six Sigma methodologies try for near-perfection in processes, aiming to attenuate defects and maximize effectivity. An important software in attaining this aim is the Pareto chart, a strong visible illustration that helps prioritize enchancment efforts by figuring out the "very important few" contributing elements among the many "trivial many." This text will delve into the intricacies of Pareto charts throughout the Six Sigma framework, exploring their development, functions, and limitations.
Understanding the Pareto Precept
The inspiration of the Pareto chart lies within the Pareto precept, also referred to as the 80/20 rule. This precept, noticed throughout quite a few fields, means that roughly 80% of the results come from 20% of the causes. In a producing context, this would possibly imply that 80% of product defects stem from simply 20% of the potential causes. Whereas the 80/20 ratio is a normal guideline and never a inflexible legislation, the precept highlights the disproportionate impression of a small variety of elements. Figuring out and addressing these very important few is vital to attaining important enhancements.
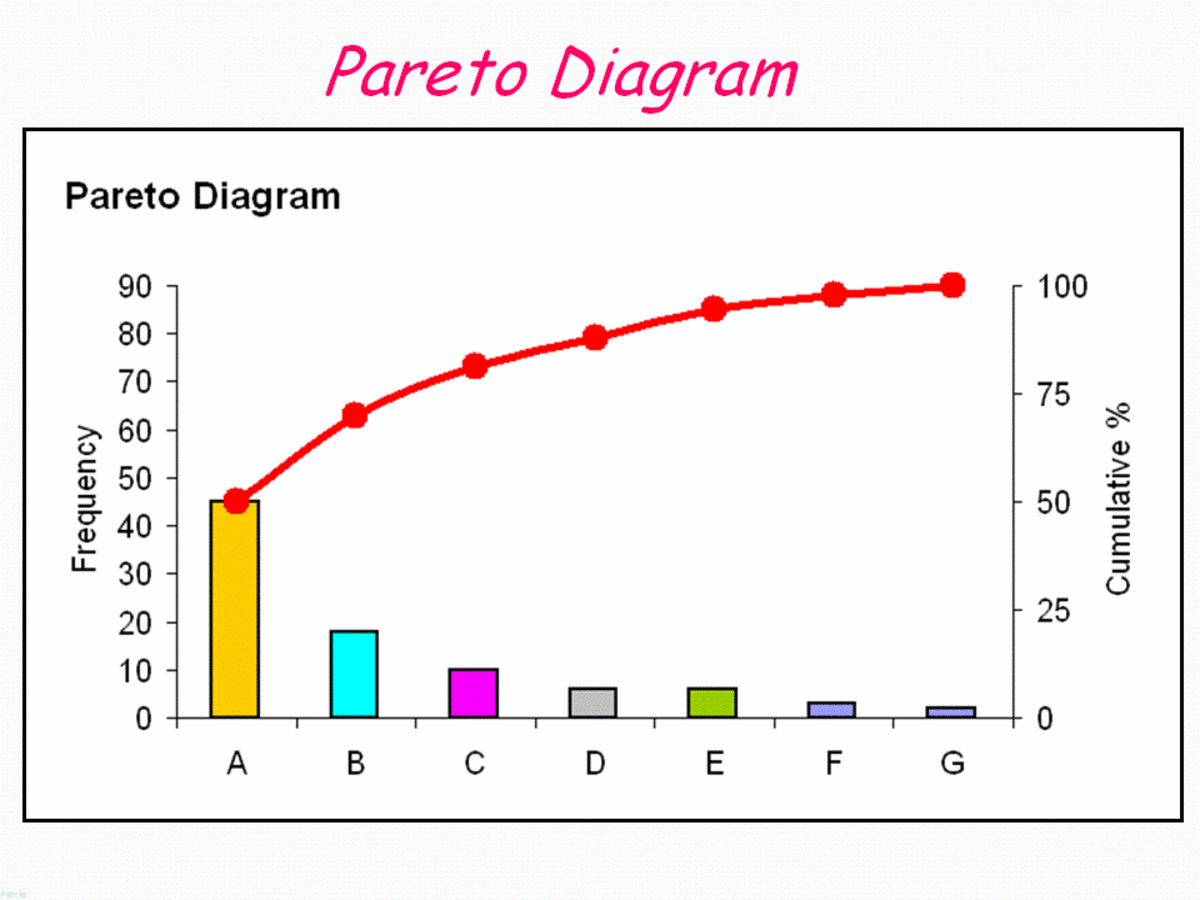
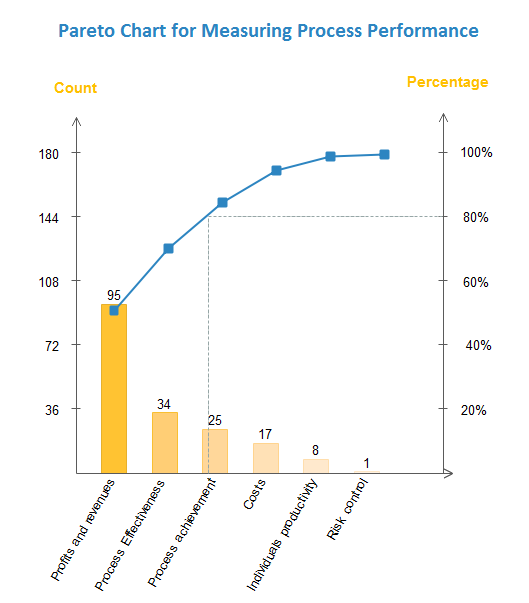
Establishing a Pareto Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Making a Pareto chart entails a scientific method:
-
Knowledge Assortment: Step one is to assemble related knowledge associated to the issue being addressed. This would possibly contain recording the variety of defects, buyer complaints, or different related metrics categorized by their root causes. Knowledge accuracy is paramount for the reliability of the chart. The info ought to be collected over a constant interval and from a consultant pattern.
-
Categorization: Manage the collected knowledge into distinct classes representing the completely different causes or elements contributing to the issue. These classes ought to be mutually unique and collectively exhaustive, making certain each knowledge level is assigned to a single class. As an example, if analyzing product defects, classes would possibly embody "materials flaws," "meeting errors," "design flaws," and "operator errors."
-
Frequency Counting: Rely the variety of occurrences for every class. This represents the frequency of every contributing issue. For instance, depend the variety of defects attributed to every class recognized in step 2.
-
Sorting and Calculation: Kind the classes in descending order based mostly on their frequency counts. Calculate the cumulative frequency for every class by including the frequency of the present class to the sum of the frequencies of all previous classes. Additionally, calculate the share of the full frequency for every class and the cumulative share.
-
Chart Creation: Assemble the chart itself. It usually consists of two elements:
-
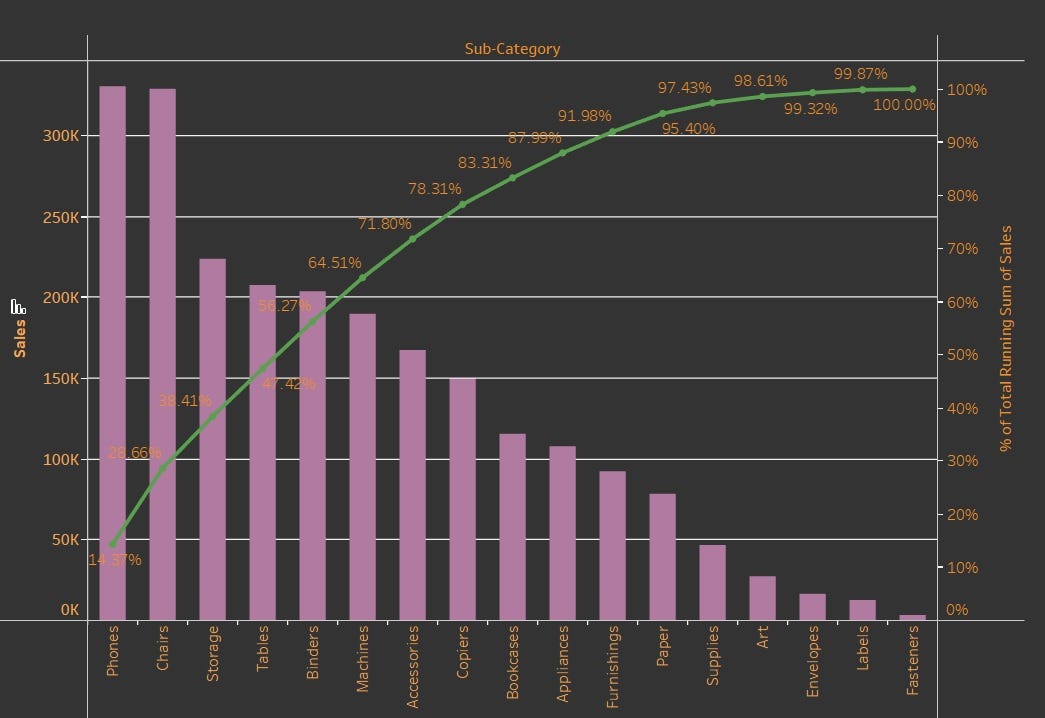
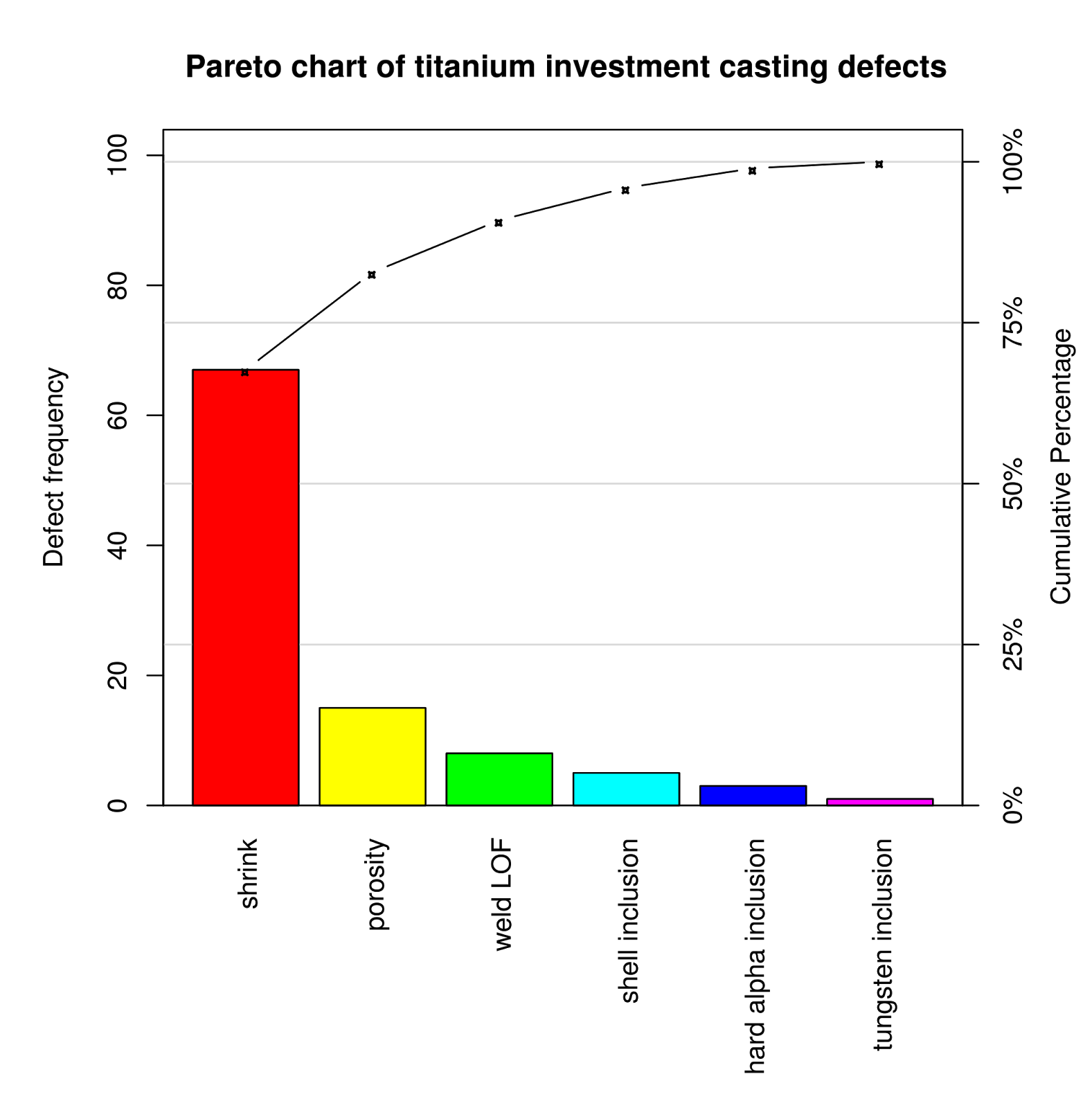
Bar Chart: A bar chart shows the frequency of every class, with the bars organized in descending order from left to proper. The peak of every bar represents the frequency of that particular class.
-
Line Graph: A line graph is superimposed on the bar chart, exhibiting the cumulative share of the full frequency. This line visually represents the Pareto precept, illustrating the cumulative impression of the contributing elements.
-
-
Labeling and Titling: Clearly label the axes, classes, and knowledge factors. Present a concise and informative title that displays the aim of the chart. For instance, a title is likely to be "Pareto Chart of Product Defects by Trigger."
Purposes of Pareto Charts in Six Sigma
Pareto charts are versatile instruments relevant throughout varied Six Sigma initiatives and industries. Some widespread functions embody:
-
Defect Evaluation: Figuring out essentially the most frequent forms of defects in a producing course of, enabling centered enchancment efforts on the important thing contributors.
-
Buyer Grievance Evaluation: Understanding the most typical buyer complaints to prioritize enhancements in product design, customer support, or different related areas.
-
Course of Enchancment: Pinpointing the most important bottlenecks or inefficiencies in a course of to optimize workflow and useful resource allocation.
-
Security Incident Evaluation: Figuring out the main causes of security incidents to implement focused preventative measures.
-
Undertaking Danger Administration: Figuring out the highest-impact dangers to focus mitigation efforts on essentially the most crucial threats.
Decoding a Pareto Chart: Figuring out the Important Few
The Pareto chart visually highlights the disproportionate impression of some key elements. The leftmost bars symbolize the "very important few," contributing considerably to the general downside. By focusing enchancment efforts on these key elements, important progress could be achieved with comparatively much less effort in comparison with addressing all elements equally. The cumulative share line helps determine the purpose at which the vast majority of the issue is addressed. As an example, if the cumulative share reaches 80% after three classes, it means that addressing these three classes will resolve 80% of the issue.
Limitations of Pareto Charts
Whereas Pareto charts are highly effective instruments, they’ve limitations:
-
Subjectivity in Categorization: The best way knowledge is categorized can affect the outcomes. Poor categorization can obscure the true underlying causes. Cautious consideration and probably skilled enter are essential for efficient categorization.
-
Oversimplification: Pareto charts could oversimplify complicated issues by focusing solely on frequency counts. They might not seize the interactions between various factors or the severity of particular person occurrences.
-
Ignoring Root Causes: Whereas figuring out essentially the most frequent elements, Pareto charts do not inherently reveal the underlying root causes. Additional investigation utilizing different Six Sigma instruments, comparable to fishbone diagrams or 5 Whys evaluation, could also be vital to grasp the foundation causes and implement efficient options.
-
Knowledge Dependency: The chart’s effectiveness depends closely on the standard and accuracy of the collected knowledge. Inaccurate or incomplete knowledge will result in deceptive conclusions.
Integrating Pareto Charts with Different Six Sigma Instruments
Pareto charts are sometimes used at the side of different Six Sigma instruments to reinforce their effectiveness. As an example, they are often mixed with:
-
Fishbone Diagrams (Ishikawa Diagrams): Used to brainstorm potential causes for the classes recognized within the Pareto chart, resulting in a deeper understanding of the foundation causes.
-
5 Whys Evaluation: Used to drill down into the foundation causes of essentially the most important classes recognized within the Pareto chart.
-
Management Charts: Used to observe the effectiveness of carried out options and make sure the enhancements are sustained over time.
Conclusion
Pareto charts are indispensable instruments within the Six Sigma arsenal, offering a transparent and concise visible illustration of the relative significance of various elements contributing to an issue. By focusing enchancment efforts on the "very important few," organizations can obtain important positive aspects in effectivity, high quality, and general efficiency. Nevertheless, it is essential to recollect the restrictions of Pareto charts and to combine them with different Six Sigma instruments for a extra complete and efficient method to problem-solving. Understanding the Pareto precept and mastering the development and interpretation of Pareto charts are important abilities for anybody in search of to leverage the facility of Six Sigma for course of enchancment.
![The Pareto Principle Explained [infographic] Free Download Nude Photo](https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/4747213/Imported_Blog_Media/Pro28TheParetoPrinciple1.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Unveiling the Pareto Precept: A Deep Dive into Pareto Charts in Six Sigma. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!